Abstract
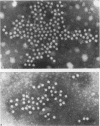
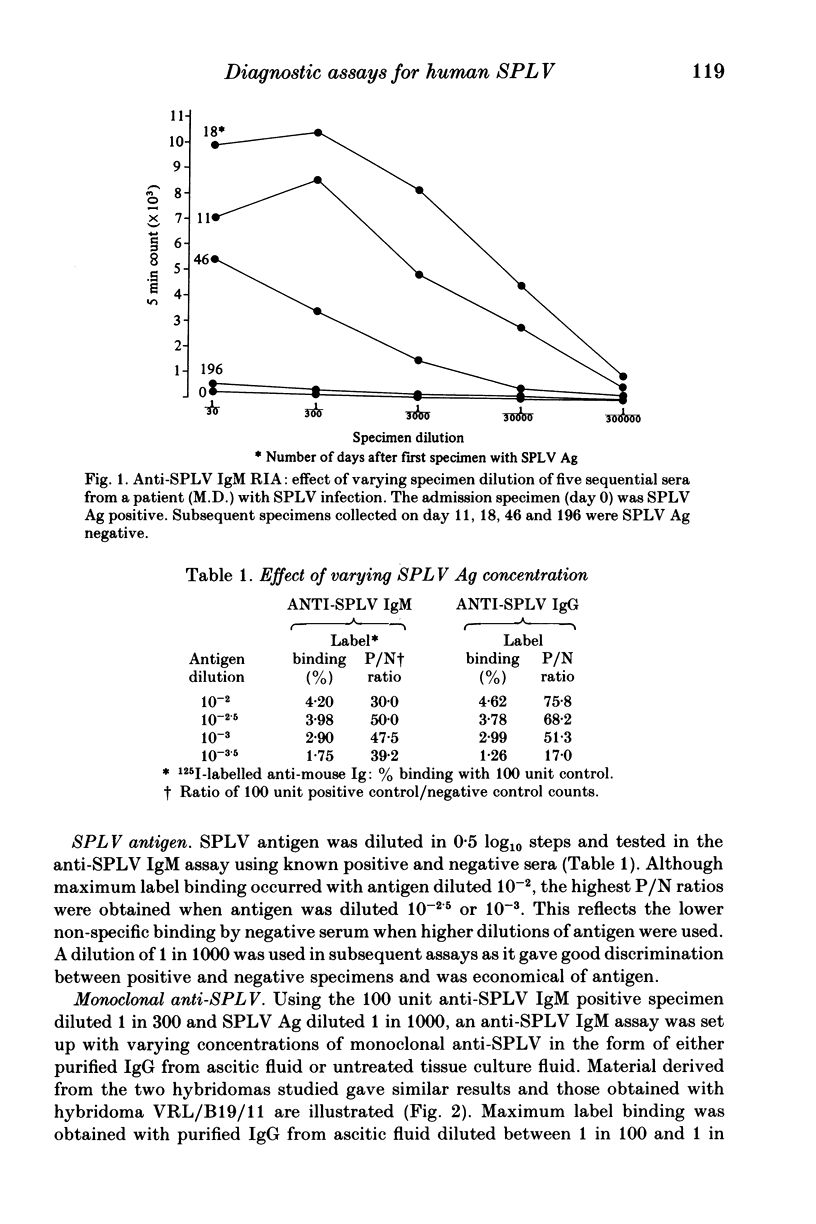
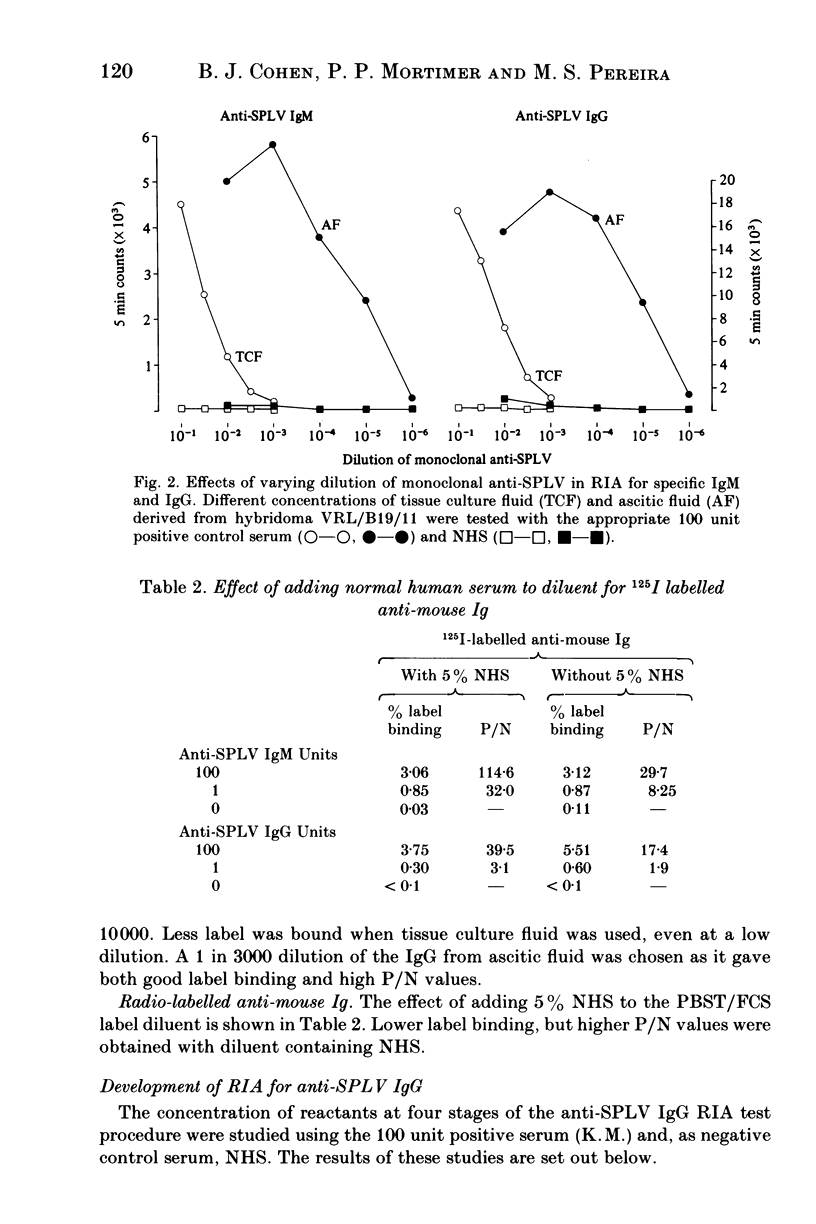
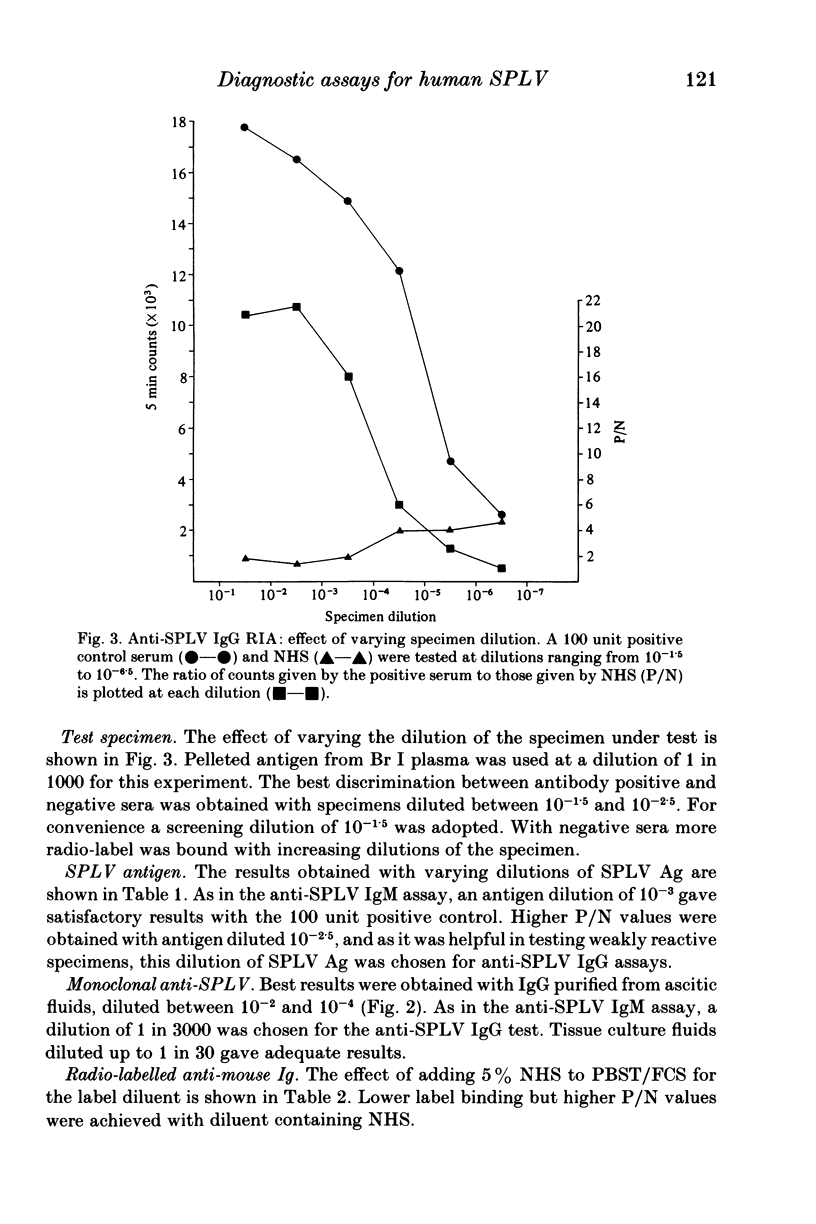
Monoclonal antibodies to the serum parvovirus-like virus (SPLV) were prepared by the hybridoma technique. They provided an antibody reagent which was used to develop solid phase antibody-capture assays for anti-SPLV IgM and IgG and for SPLV antigen. These assays were more sensitive than those based on human convalescent antibody as a reagent, and were more economical in the use of SPLV antigen. Their use enabled the serological responses to SPLV to be studied more fully and their sensitivity revealed the extent of SPLV infection. SPLV antigen was detected in four patients by both counter-immuno electrophoresis (CIE) and radioimmunoassay (RIA) and in two others by RIA alone. Parvovirus particles were seen in all six by electron microscopy. The anti-SPLV IgM response was measured in patients infected by SPLV. It was strong 5-18 days after the onset of illness, then declined and was only detectable in trace amounts after 6 months. Anti-SPLV IgG was also formed early, and persisted for at least 6 months. In a survey of 310 blood donors anti-SPLV was detected in 134 (43%) by CIE, but in 190 (61%) by IgG antibody capture RIA.
Full text
PDF










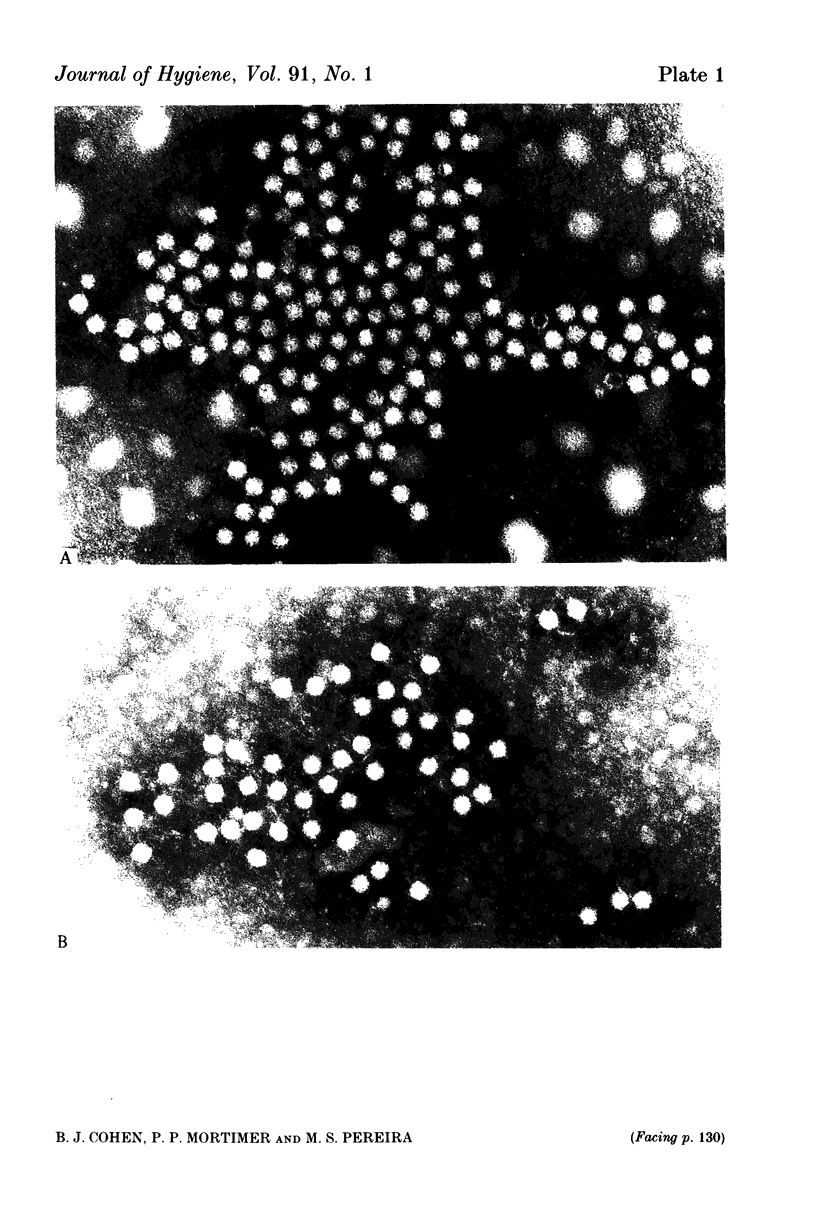
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Davis L. R., Jones S. E., Pattison J. R., Serjeant G. R. The development and use of an antibody capture radioimmunoassay for specific IgM to a human parvovirus-like agent. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):309–324. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J. The emerging story of a human parvovirus-like agent. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Aug;89(1):1–8. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Hewish R. A., Mortimer P. P. Comparison of radioimmunoassay and counter-immunoelectrophoresis for the detection of antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E., Field A. M., Cant B., Widdows D. Parvovirus-like particles in human sera. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):72–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Ranke M., Berthold H., Gerth H. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paver W. K., Clarke S. K. Comparison of human fecal and serum parvo-like viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):67–70. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.67-70.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeant G. R., Topley J. M., Mason K., Serjeant B. E., Pattison J. R., Jones S. E., Mohamed R. Outbreak of aplastic crises in sickle cell anaemia associated with parvovirus-like agent. Lancet. 1981 Sep 19;2(8247):595–597. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneerson J. M., Mortimer P. P., Vandervelde E. M. Febrile illness due to a parvovirus. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 28;280(6231):1580–1580. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6231.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Wilson-Croome R. Detection by radioimmunoassay of IgM class antibody to hepatitis B core antigen: a comparison of two methods. J Med Virol. 1980;6(3):235–247. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Yao J. L., Anderson M. J. The production of monoclonal antibodies to rubella haemagglutinin and their use in antibody-capture assays for rubella-specific IgM. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):335–350. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]