Abstract
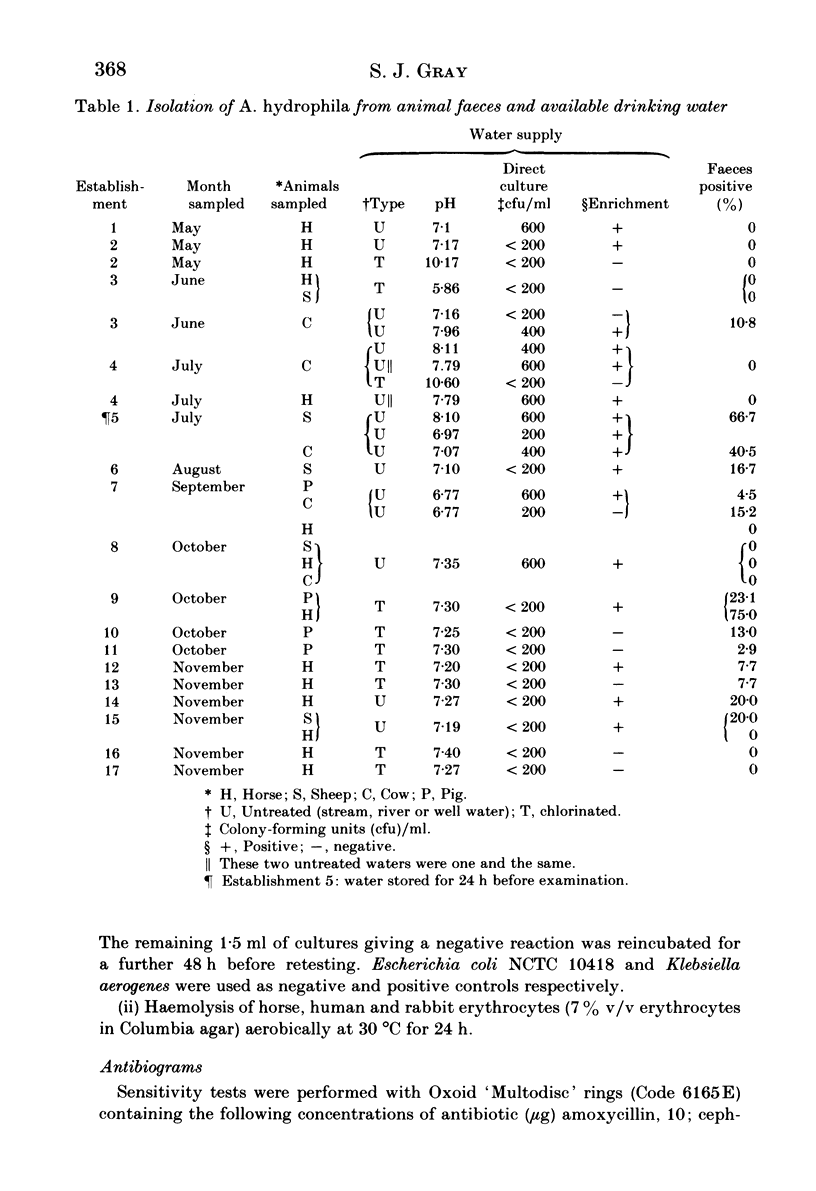
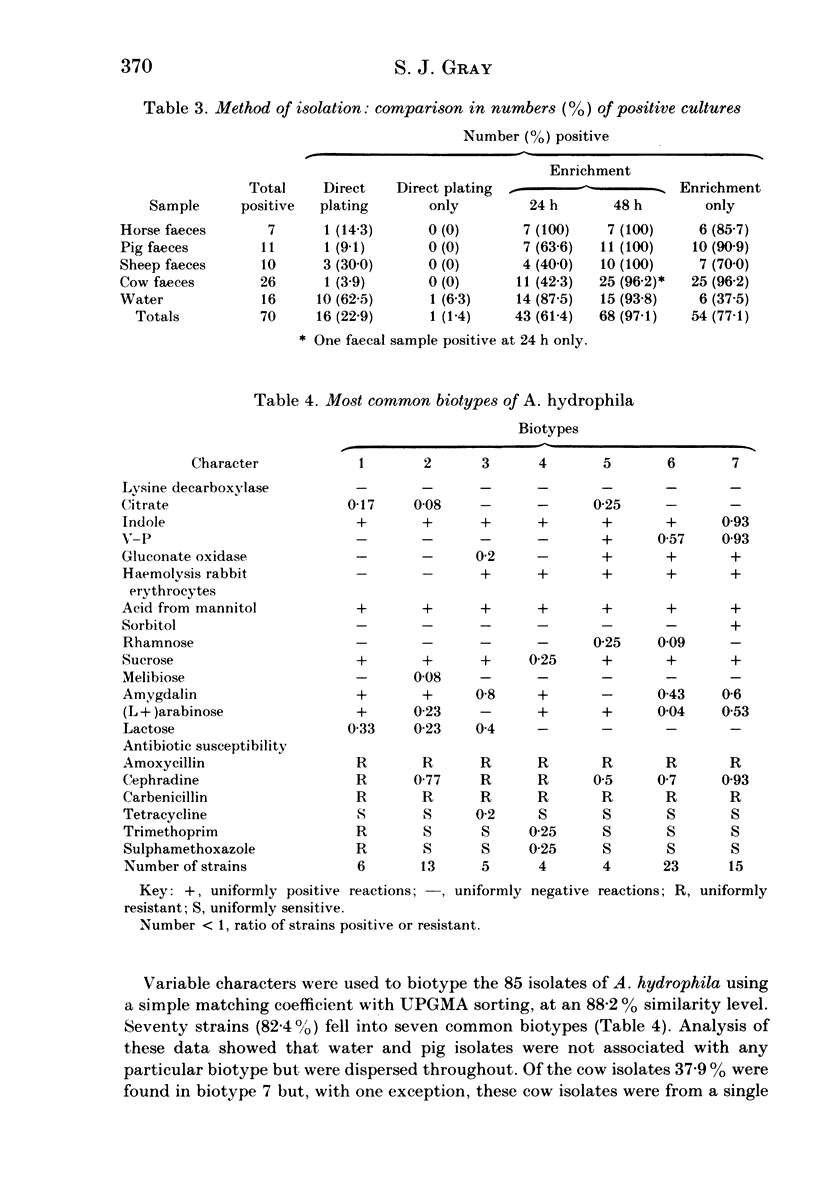
Faecal samples from 110 horses, 115 pigs, 111 sheep and 123 cows were examined for the presence of Aeromonas hydrophila, which was also sought in the available drinking water. The overall faecal rate was 11.8%, but significantly more bovine than other samples were found to be positive. There was significant association between the isolation of A. hydrophila from all animal faeces and its presence in drinking water, but this was not found when individual animal groups were analysed separately. An enrichment technique increased the total number of isolates by 77.1%. Strains of differing origins could not be differentiated by biotyping, although fermentation of sorbitol was associated with bovine isolates. There was a strong positive correlation between positive reactions for V--P, gluconate oxidase and haemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes, tests which had previously been shown to correlate with production of enterotoxin and cytotoxin. Biotypes giving positive reactions for these tests were most frequently isolated from cows, sheep and untreated water, and less frequently from pigs and horses. Most strains of A. hydrophila were resistant to amoxycillin, carbenicillin and cephradine, and sensitive to gentamicin, chloramphenicol and neomycin.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampel N., Peter G. Aeromonas bacteraemia in a burn patient. Lancet. 1981 Oct 31;2(8253):987–987. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annapurna E., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):317–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P., Shanthakumari S., Rajan D. The characterization and significance of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from an epidemic of diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Jul;62(7):1051–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Houang E. C., Lee J. V. Clustering of aeromonas hydrophila septicaemia. Lancet. 1981 Nov 28;2(8257):1232–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily O. P., Joseph S. W., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Merrell B. R., Rollins D. M., Seidler R. J., Colwell R. R., Lissner C. R. Association of Aeromonas sobria with human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.769-777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey R. S., Sanyal S. C. Characterisation and neutralisation of Aeromonas hydrophila enterotoxin in the rabbit ileal-loop model. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):347–354. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulghum D. D., Linton W. R., Taplin D. Fatal Aeromonas hydrophila infection of the skin. South Med J. 1978 Jun;71(6):739–741. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197806000-00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Rockhill R. C., Suharyono, Sunoto Aeromonas species as enteric pathogens. Lancet. 1982 Jan 23;1(8265):223–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. G., Standridge J., Jarrett F., Maki D. G. Freshwater wound infection due to Aeromonas hydrophila. JAMA. 1977 Sep 5;238(10):1053–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketover B. P., Young L. S., Armstrong D. Septicemia due to Aeromonas hydrophila: clinical and immunologic aspects. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):284–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Popoff M., Wadstrom T. Aeromonas hydrophila in acute diarrheal disease: detection of enterotoxin and biotyping of strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):96–100. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.96-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Wretlind B., Möllby R. Separation and characterization of enterotoxin and two haemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):387–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00205_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus L. C. Infectious diseases of reptiles. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Dec 1;159(11):1626–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulsdale M. T. Isolation of Aeromonas from faeces. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):351–351. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91649-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. A., Bernhardt H. E., Rosenthal S. G. Aeromonas hydrophila infections. Pediatrics. 1974 Jan;53(1):110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C., CLARKE P. H. Biochemical classification of Proteus and Providence cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):155–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Gaines J. L., Jr, Martin L., Prestwood A. K. Aeromonas-induced deaths among fish and reptiles in an eutrophic inland lake. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 15;161(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Chipman D. C. Clinical involvement of Aeromonas hydrophila. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Apr 21;120(8):942–946. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgemuth K., Pierce R. L., Kirkbride C. A. Bovine abortion associated with Aeromonas hydrophila. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Apr 1;160(7):1001–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Bucher C. Evaluation of differential and selective media for isolation of Aeromonas and Plesiomonas spp. from human feces. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.16-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Graevenitz A., Zinterhofer L. The detection of Aeromonas hydrophila in stool specimens. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Jul;7(3):124–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


