Abstract
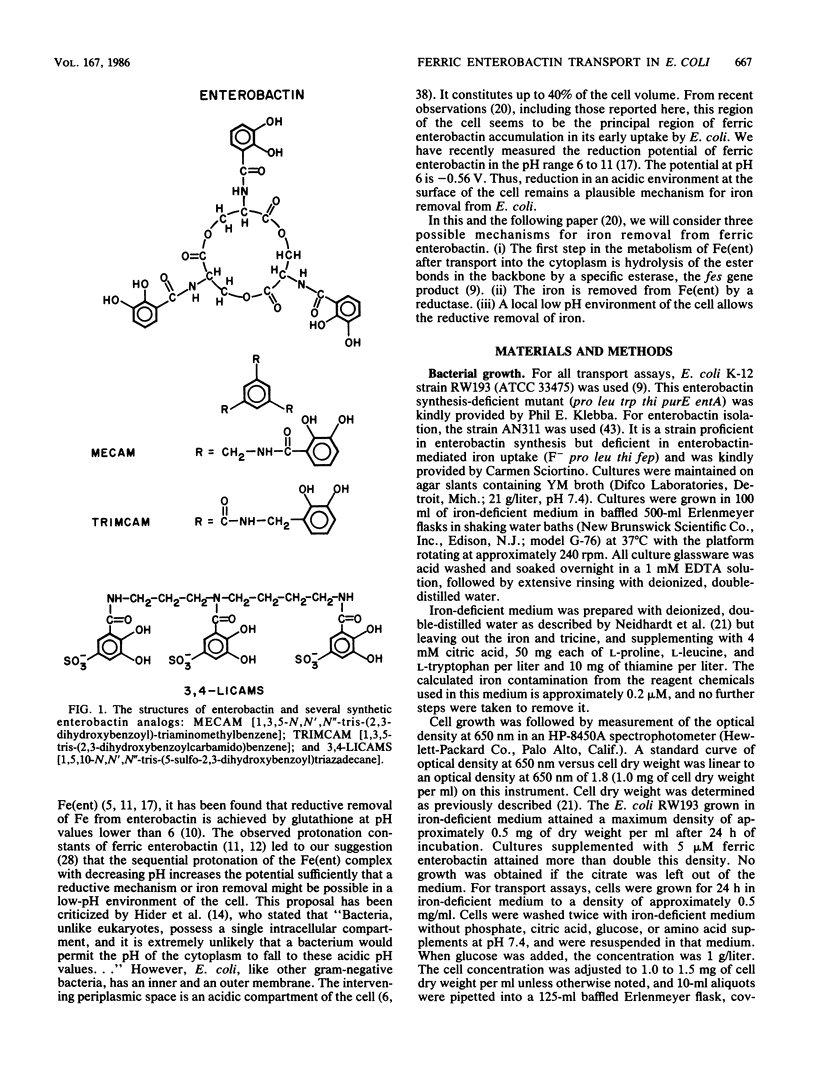
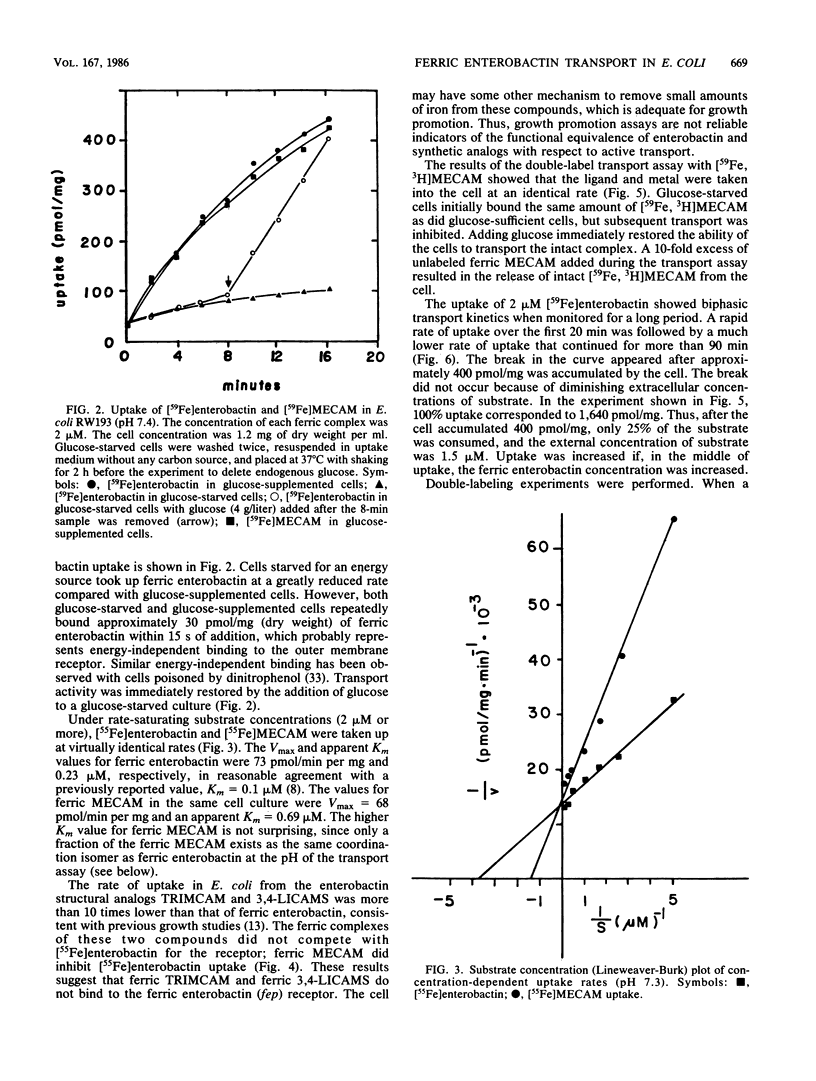
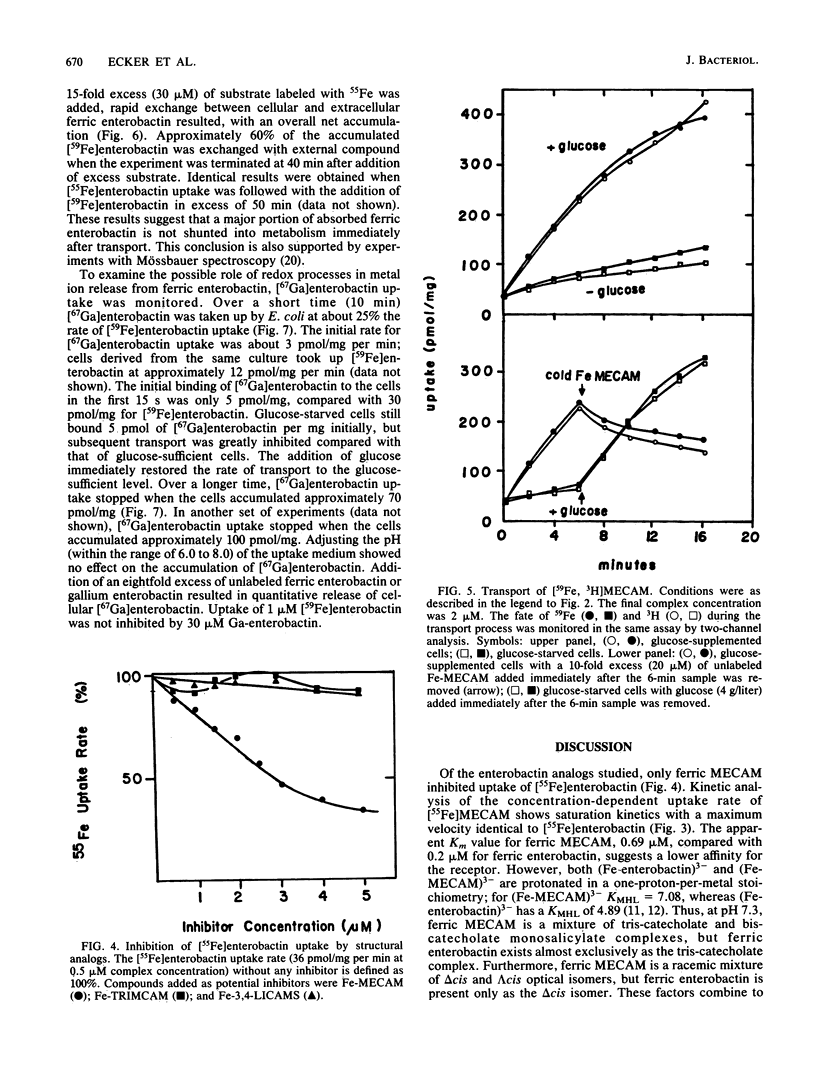
The specificity of the outer membrane protein receptor for ferric enterobactin transport in Escherichia coli and the mechanism of enterobactin-mediated transport of ferric ions across the outer membrane have been studied. Transport kinetic and inhibition studies with ferric enterobactin and synthetic structural analogs have mapped the parts of the molecule important for receptor binding. The ferric complex of the synthetic structural analog of enterobactin, 1,3,5-N,N',N''-tris-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)triaminomethylbenzene (MECAM), was transported with the same maximum velocity as was ferric enterobactin. A double-label transport assay with [59Fe, 3H]MECAM showed that the ligand and the metal are transported across the outer membrane at an identical rate. Under the growth conditions used, large fractions of the transported complexes were available for exchange across the outer membrane when a large excess of extracellular complex was added to the cell suspension; at least 60% of the internalized [59Fe]enterobactin exchanged with extracellular [55Fe]enterobactin. Internalized [59Fe, 3H]MECAM was released from the cell as the intact complex when either unlabeled Fe-MECAM or Fe-enterobactin was added extracellularly. The results suggest a mechanism of active transport of unmodified coordination complex across the outer membrane with possible accumulation in the periplasm.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryce G. F., Brot N. Studies on the enzymatic synthesis of the cyclic trimer of 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoyl-L-serine in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1708–1715. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. R., McArdle J. V., Raymond K. N. Siderophore electrochemistry: relation to intracellular iron release mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Passavant C. W., Emery T. Role of two siderophores in Ustilago sphaerogena. Regulation of biosynthesis and uptake mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 8;720(3):242–249. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood K. T., Luke R. K. Enzymatic hydrolysis of enterochelin and its iron complex in Escherichia Coli K-12. Properties of enterochelin esterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger S., Braun V., Pecoraro V. L., Raymond K. N. Iron supply to Escherichia coli by synthetic analogs of enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.109-115.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollifield W. C., Jr, Neilands J. B. Ferric enterobactin transport system in Escherichia coli K-12. Extraction, assay, and specificity of the outer membrane receptor. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1922–1928. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás M., Wilson D. M., Neilands J. B. Effect of metal binding on the conformation of enterobactin. A proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3836–3843. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. S., Gaines C. G., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Non-hydrolytic release of iron from ferrienterobactin analogs by extracts of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B., Erickson T. J., Rastetter W. H. Stereospecificity of the ferric enterobactin receptor of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3831–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Iron absorption and transport in microorganisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:27–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Enterochelin hydrolysis and iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Gibson F. The structure of enterochelin and related 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoylserine conjugates from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaha D. S., Rogers H. J. Antibacterial effect of the scandium complex of enterochelin. Studies of the mechanism of action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 18;760(2):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Neilands J. B. Enterobactin, an iron transport compound from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):989–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K., Good R. F. DNA sequence of the Escherichia coli tonB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5235–5239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Uptake of ferrienterochelin by Escherichia coli: energy dependent stage of uptake. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.26-36.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. R., Mottur G. P., Bradbeer C. Transport of vitamin B12 in Escherichia coli. Some observations on the roles of the gene products of BtuC and TonB. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4313–4319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuti M. C., Rastetter W. H., Neilands J. B. 1,3,5-Tris(N,N',N''-2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)amino-methylbenzene, a synthetic iron chelator related to enterobactin. J Med Chem. 1979 Feb;22(2):123–124. doi: 10.1021/jm00188a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitl F. L., Harris W. R., Raymond K. N. Sulfonated catecholamide analogues of enterobactin as iron sequestering agents. J Med Chem. 1979 Nov;22(11):1281–1283. doi: 10.1021/jm00197a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G., Gibson F. Isolation of enterochelin from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:394–398. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


