Abstract
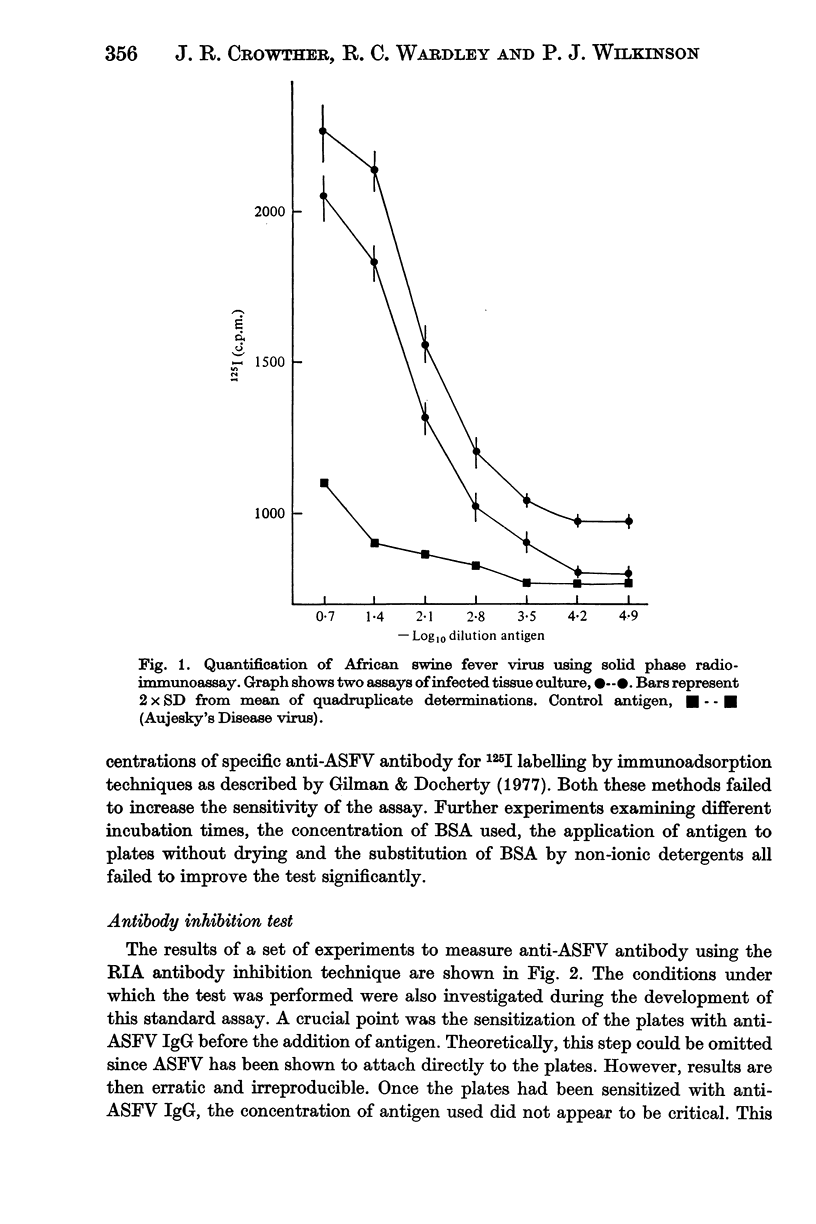
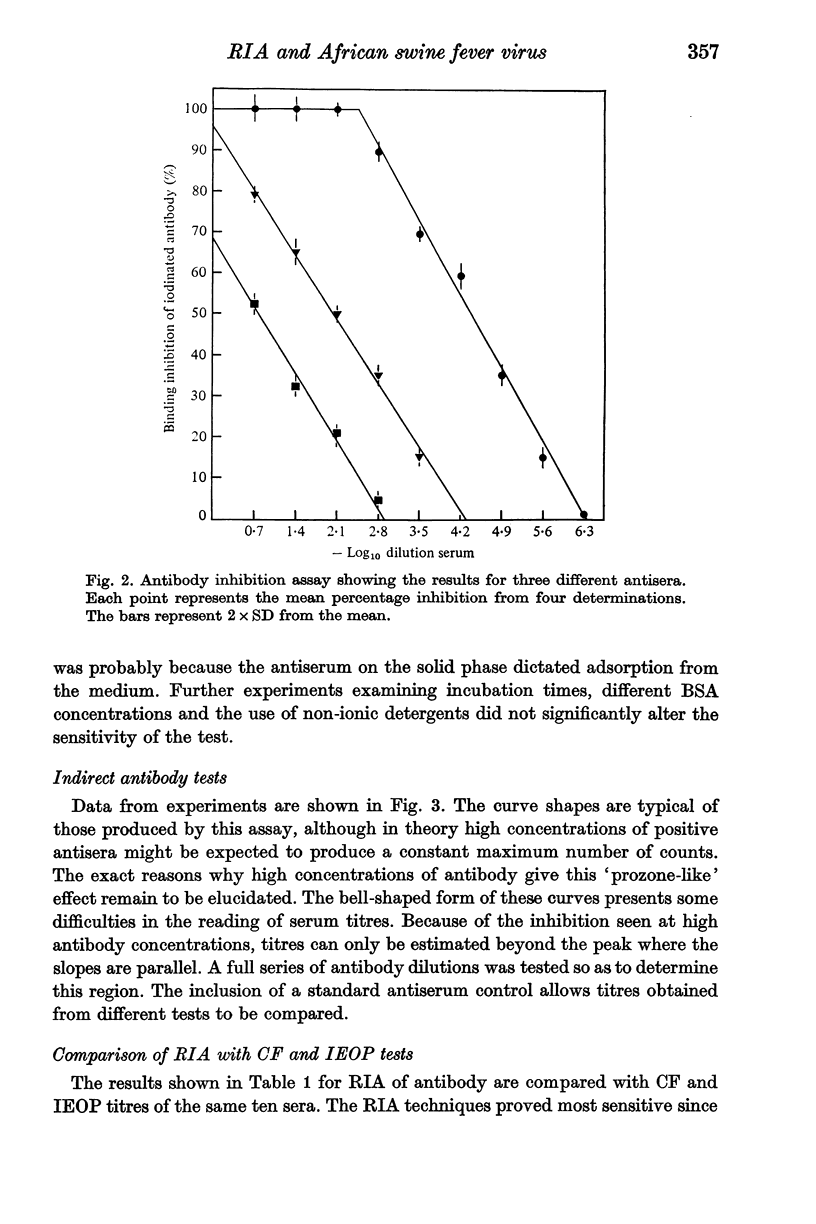
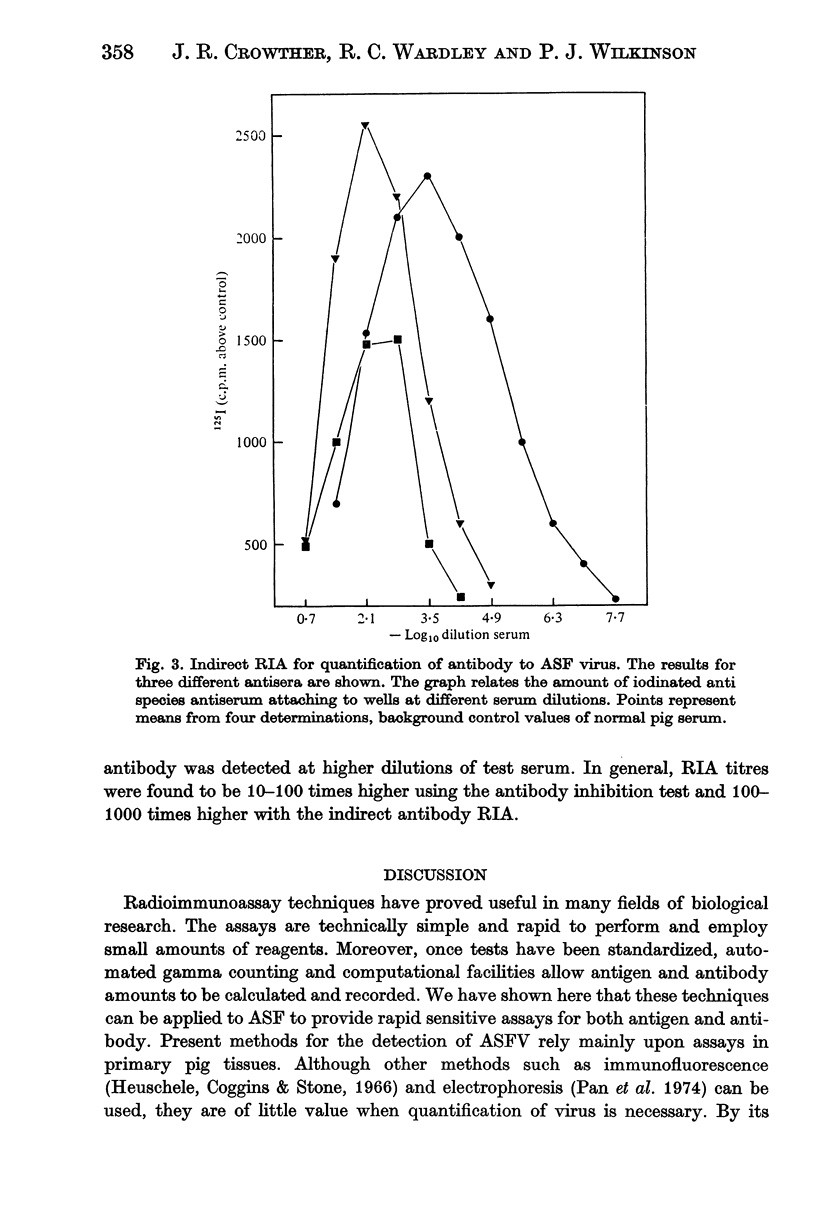
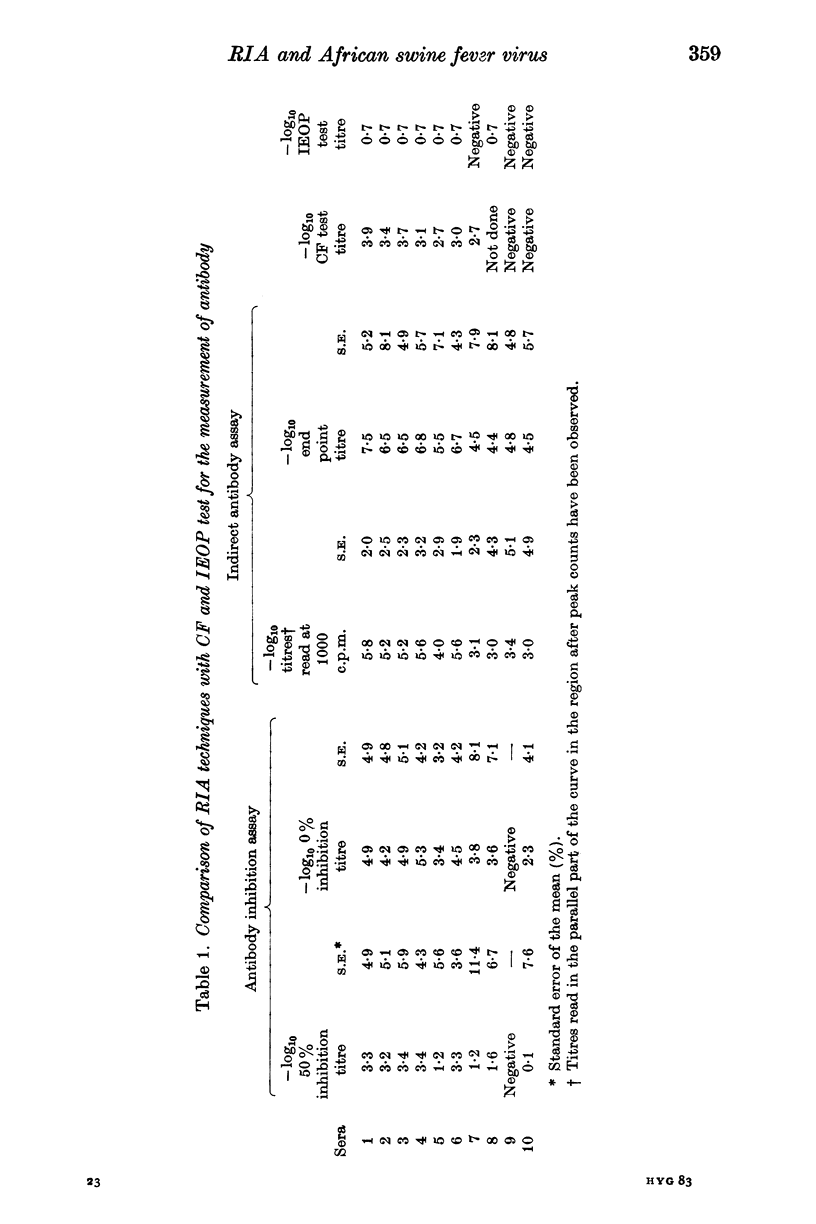
A solid phase radioimmunoassay (RIA) has been successfully developed to measure both African swine fever virus (ASFV) antigen and antibody. Studies show that the assay is reproducible and will detect limiting antigen concentrations equivalent to 50--500 HAD50/ml. Both direct and indirect antibody RIA have been developed and have proved to be approximately 100 times fore sensitive than the complement fixation test at present available and 1000 times more sensitive than the immuno-electro-osmophoresis test for the detection of ASFV antibody.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKAO Y., SANO R., SUGIURA A., SHIMOJO H. Procomplementary activity of swine serum and its elimination with periodate treatment. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1962 Aug;15:165–173. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.15.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P., Plowright W. The morphological characteristics of African swine fever virus and its resemblance to tipula iridescent virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(3):392–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01241958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer G. M., Shaddock J. H., Moore S. A., Yager P. A., Baron S. S., Levy H. B. Successful prophylaxis against rabies in mice and Rhesus monkeys: the interferon system and vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):286–291. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS W. R., COX B. F., HEUSCHELE W. P., STONE S. S. PROPAGATION AND MODIFICATION OF AFRICAN SWINE FEVER VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuschele W. P., Coggins L., Stone S. S. Fluorescent antibody studies on African swine fever virus. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Mar;27(117):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A., HAY D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan I. C., De Boer C. J., Hess W. R. African swine fever: application of immunoelectroosmophoresis for the detection of antibody. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jul;36(3):309–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan I. C., Trautman R., Hess W. R., DeBoer C. J., Tessler J., Ordas A., Botija C. S., Ovejero J., Sanchez M. C. African swine fever: comparison of four serotests on porcine serums in Spain. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jun;35(6):787–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Comparison of direct and indirect solid-phase microradioimmunoassays for the detection of viral antigens and antiviral antibody. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.567-573.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


