Abstract
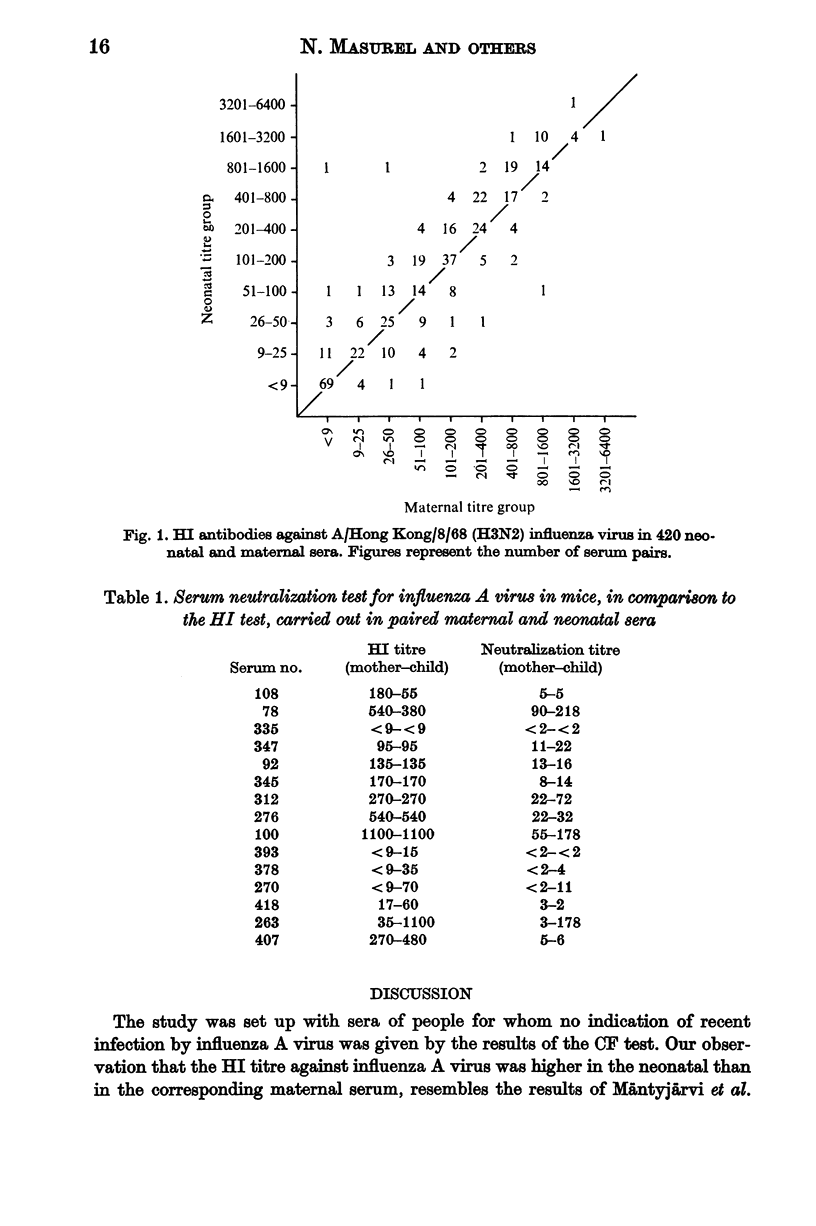
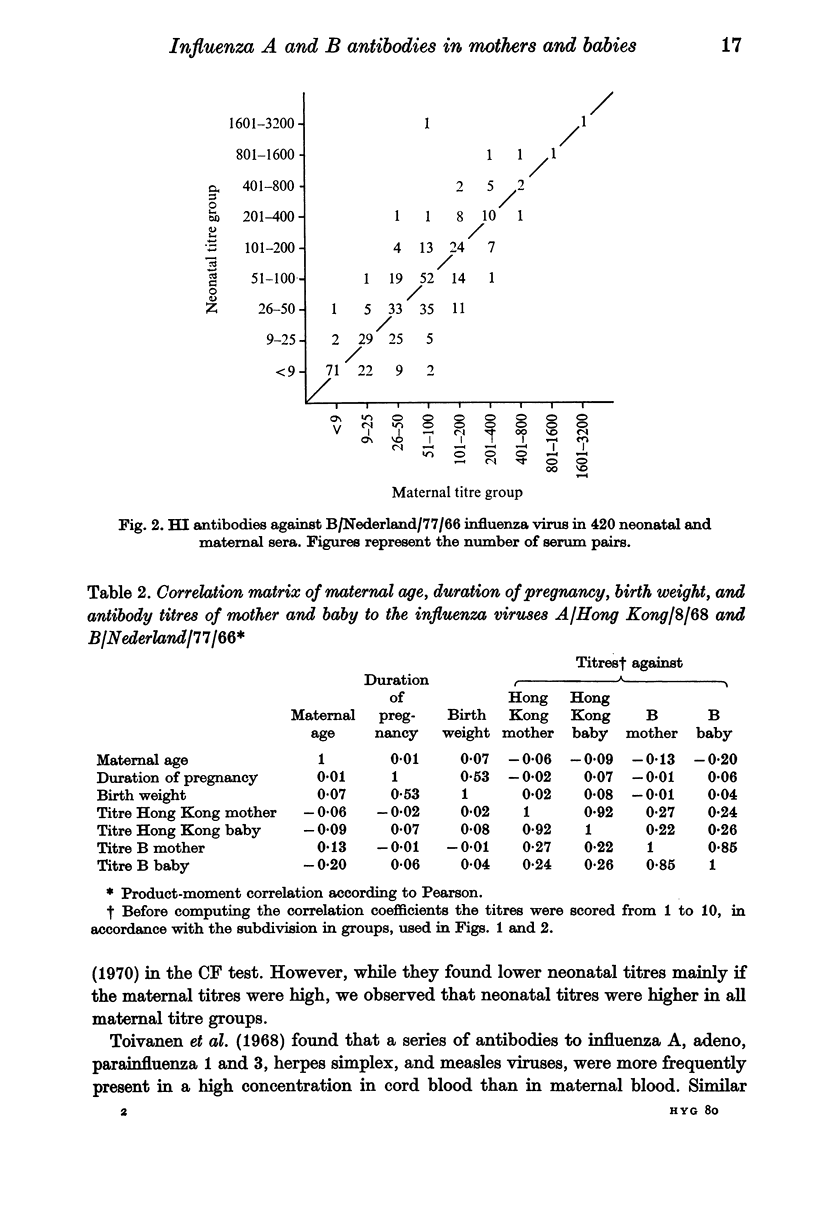
Haemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibodies against the influenza viruses A/Hong Kong/8/68 (H3N2) and B/Nederland/77/66 were determined in 420 paired sera from mothers and newborns (umbilical cord sera), sampled in 1970-1. A higher concentration of antibodies against influenza A virus was found more frequently in neonatal than in maternal sera. By contrast, low titres against influenza B virus were more frequently observed in neonatal than in maternal sera. Maternal age, duration of pregnancy, and birth-weight did not affect the results of the tests. It is suggested that the titre of the newborn against an epidemic influenza virus can be predicted from that of the mother. Furthermore, the maternal titre may be an indication of the susceptibility of the newborn infant to influenza infections.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brouwer R., de Groot I. G., Verheij F. B. Comparison of maternal and cord serum titres for measles and for rubella antibodies. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01240611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloonan M. J., Hawkes R. A., Stevens L. H. Postnatal decline of maternally acquired viral antibodies of different specificities. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Sep;69(3):435–444. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HITZIG W. H. [The blood protein picture in the healthy infant. Specific protein determinations with special reference to immunochemical methods]. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1961 Apr;16:46–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson D., Curry R. L., Beare A. S., Ward-Gardner A. The role of serum haemagglutination-inhibiting antibody in protection against challenge infection with influenza A2 and B viruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Dec;70(4):767–777. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaux J. L., Heremans J. F., Hitzig W. H. Immunoglobulin levels in cord-blood serum of negroes and Caucasians. Trop Geogr Med. 1966 Mar;18(1):10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E., Kleemola M. Human IgG subclasses in maternal and fetal serum. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntyjärvi R., Hirvonen T., Toivanen P. Maternal antibodies in human neonatal sera. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):449–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadatos C., Alexiou D., Papaevangelou G., Petropoulos H., Mendris J. Serum levels of immune globulins in postmaturity. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):222–224. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen P., Mäntyjärvi R., Hirvonen T. Maternal antibodies in human foetal sera at different stages of gestation. Immunology. 1968 Sep;15(3):395–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselius-de Casparis A., Masurel N., Kerrebijn K. F. Field trial with human and equine influenza vaccines in children: protection and antibody titres. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(2):151–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


