Abstract
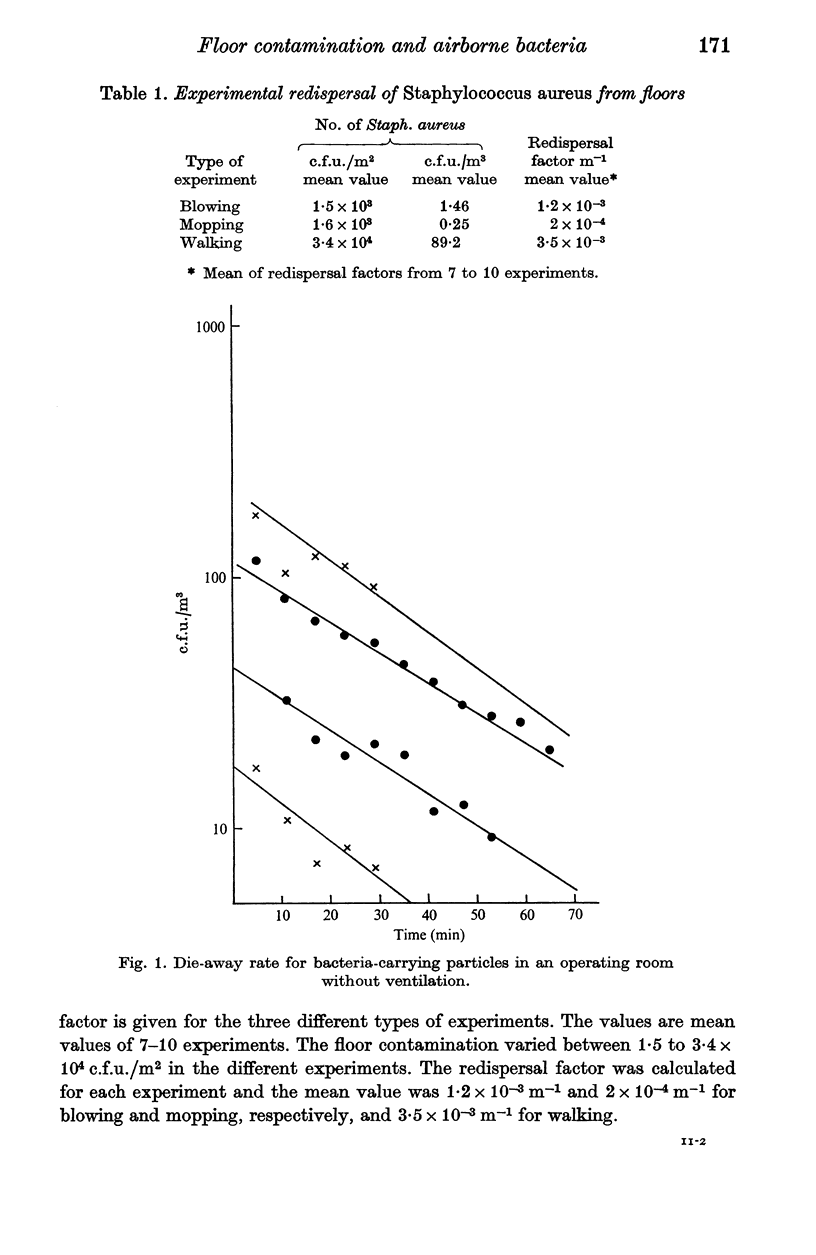
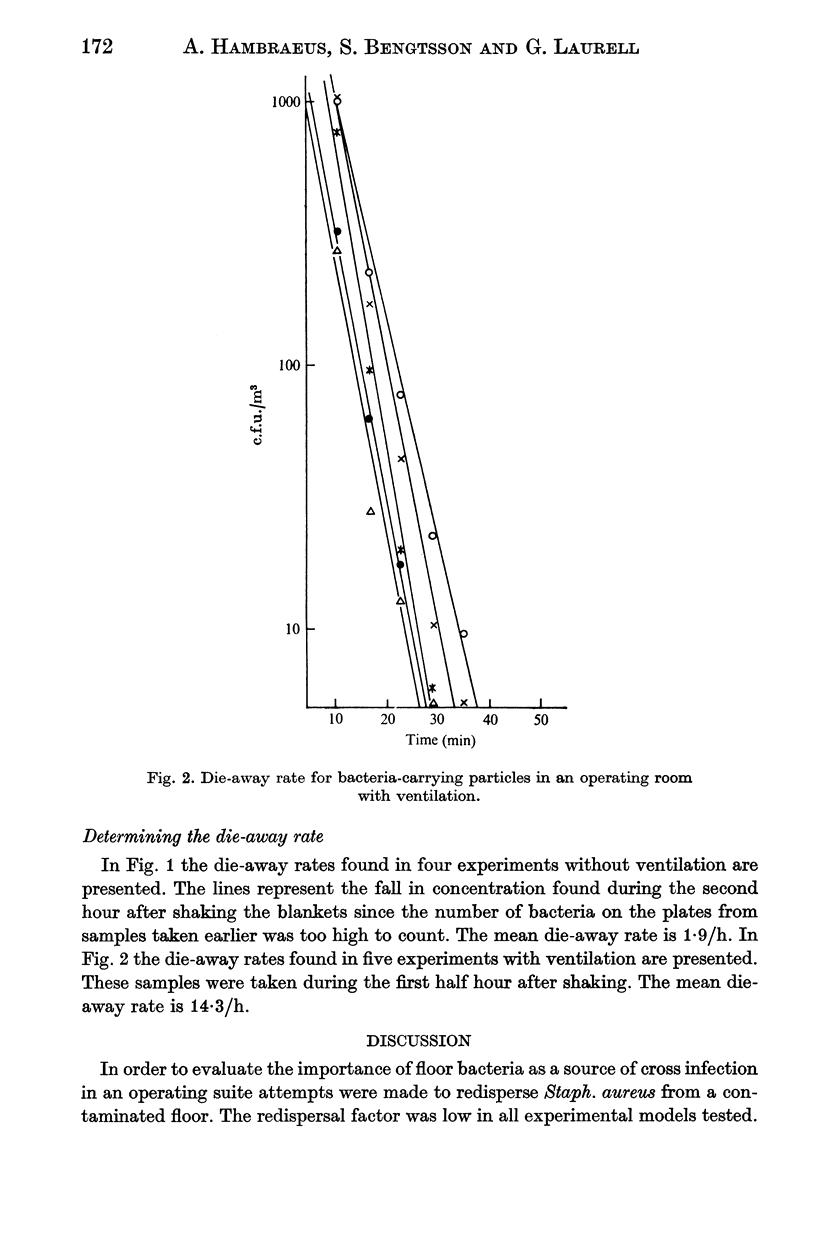
The redispersal factor for bacteria-carrying particles from a contaminated floor was determined after mopping, blowing and walking activity. Walking gave the highest redispersal factor, 3.5 X 10(-3) m-1, which was three times higher than for blowing and 17 times higher than for mopping. The mean die-away rate for the bacteria-carrying particles used was 1.9/h without ventilation and 14.3/h with ventilation. It was calculated that in the operating rooms less than 15% of the bacteria found in the air were redispersed floor bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hambraeus A., Bengtsson S., Laurell G. Bacterial contamination in a modern operating suite. 1. Effect of ventilation on airborne bacteria and transfer of airborne particles. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):121–132. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambraeus A. Dispersal and transfer of Staphylococcus aureus in an isolation ward for burned patients. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):787–797. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


