Abstract
Extraction of membranes of Mycoplasma hominis with n-butanol showed that antigenicity was associated with the non-lipid residue, which probably consisted mainly of protein, and not with the lipid itself.
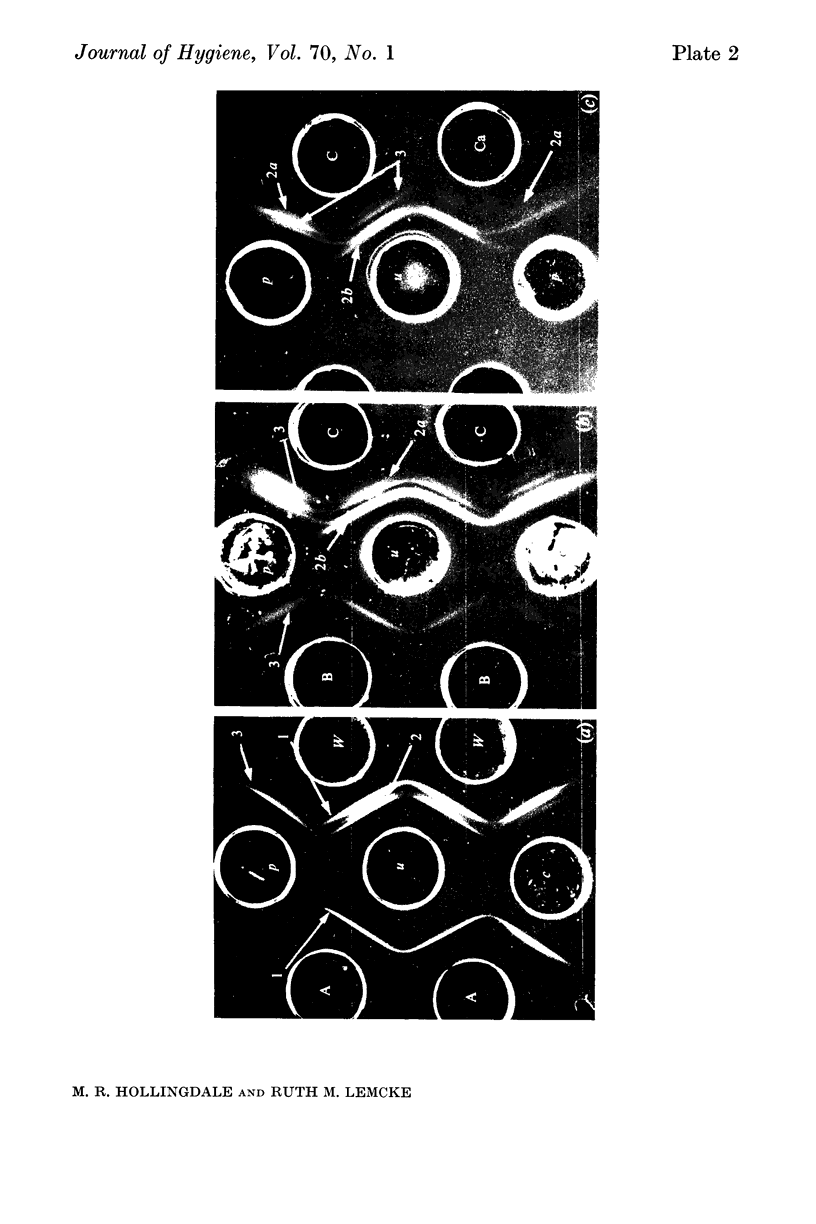
Since many membrane proteins are hydrophobic, membranes were rendered soluble in various ways. Extraction with urea or phenol was the most successful, yielding extracts which were both antigenic and serologically reactive. The urea extract could not be fractionated by polyacrylamide disk electrophoresis or by column chromatography. However, serologically active components identified by gel diffusion were separated from detergent-lysed membranes by polyacrylamide disk electrophoresis. The activities of antisera against these fractions suggested that indirect-haemagglutinating or metabolic-inhibiting antibodies can be directed against several different membrane antigens. However, the antigens identified by gel diffusion probably do not represent all the components participating in indirect haemagglutination.
Treatment of membrane suspensions with heat, alkali, periodate and various enzymes showed that the four components identified by gel diffusion could be distinguished by their differing stabilities and properties. On the basis of their lability and susceptibility to proteolytic enzymes, two were identified as proteins.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Antigenic differences within the species Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):469–477. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. The antigens of Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):585–602. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Immunological analysis of Mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.187-194.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddy A. H. The properties of the protein of the plasma membrane of ox erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr Acrylamide-gel electrophorograms by mechanical fractionation: radioactive adenovirus proteins. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae glycolipids: a novel approach to the production of antisera to membrane lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):590–597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., van Deenen L. L. The solubilization of human erythrocyte membranes by n-pentanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 1;150(2):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]