Abstract
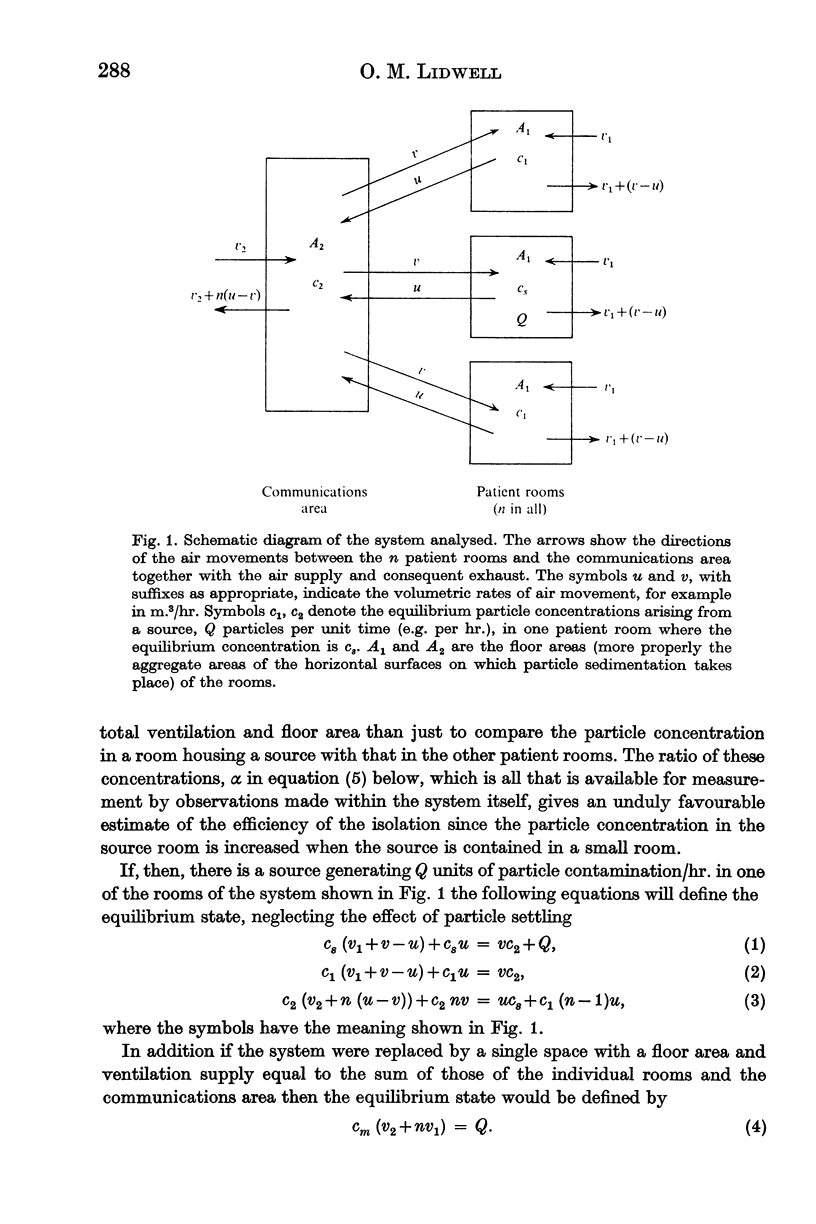
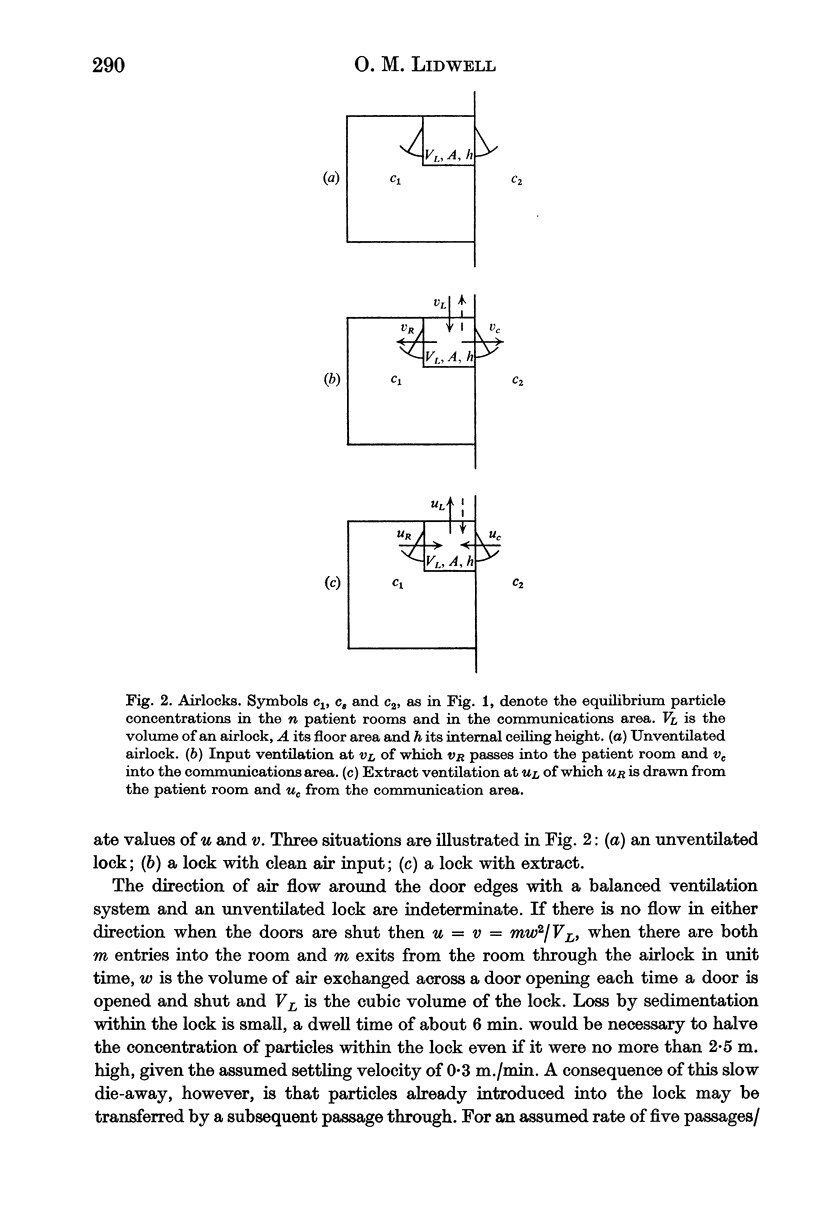
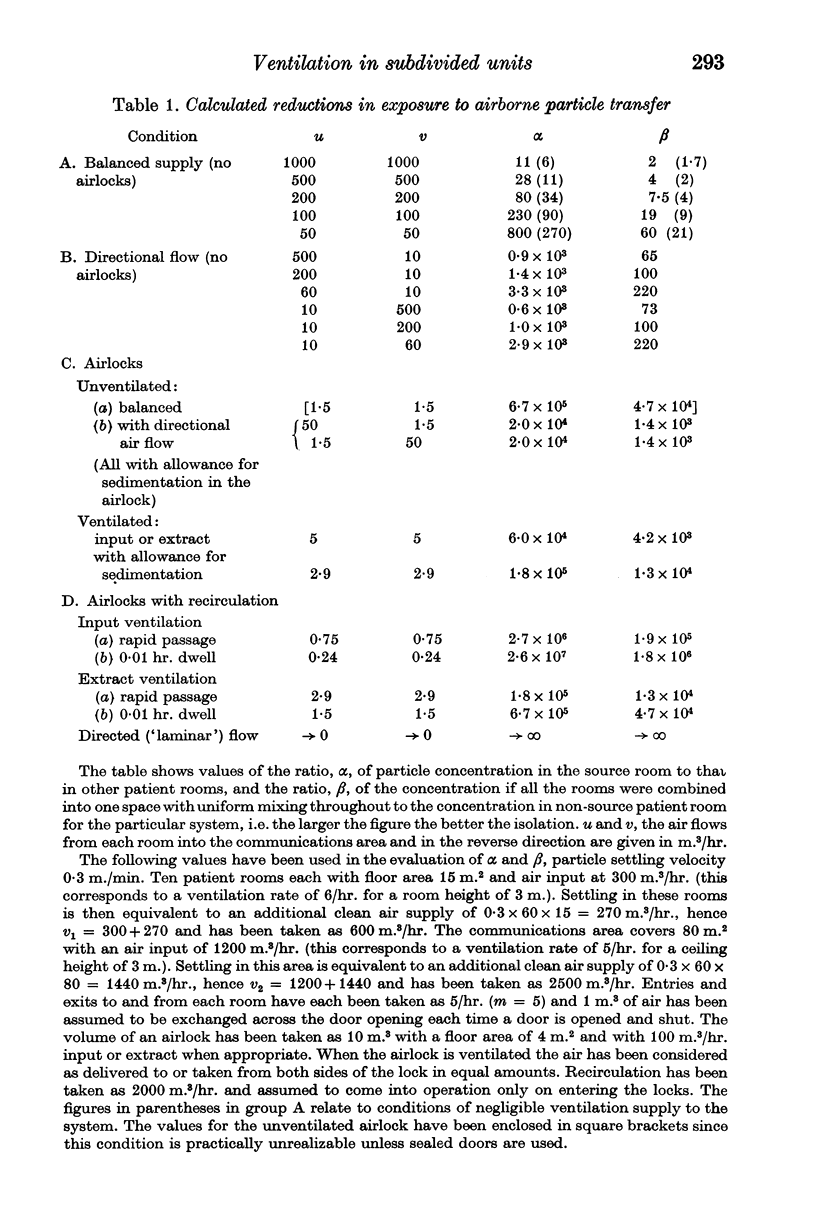
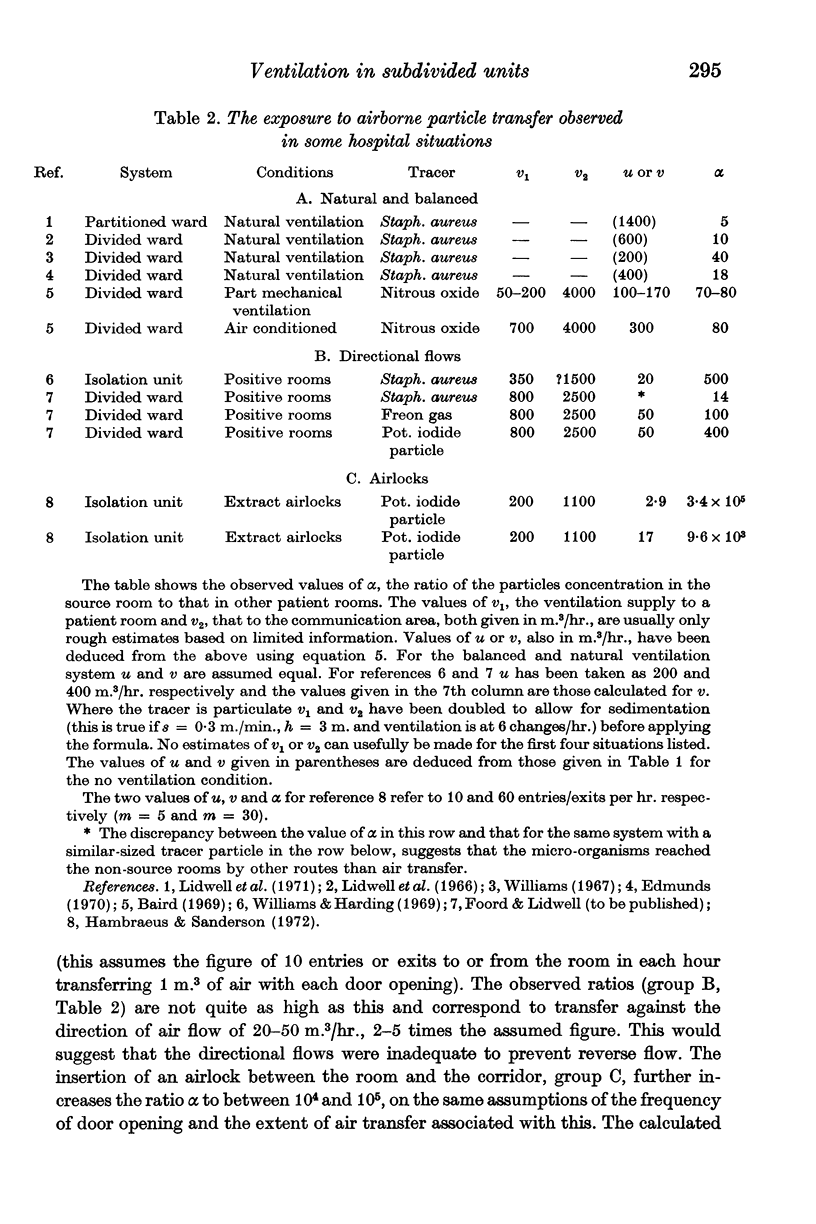
Values are deduced for the efficiency of isolation against airborne particulates, e.g. micro-organisms, of a variety of ventilation systems. The calculated values show reasonable correspondence with the limited experimental data available. Much better control and indication of the air flow is necessary if high degrees of isolation are required.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edmunds P. N. Staphylococcal infection in subdivided general surgical wards. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Dec;68(4):531–547. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambraeus A., Sanderson H. F. The control by ventilation of airborne bacterial transfer between hospital patients, and its assessment by means of a particle tracer. 3. Studies with an airborne-particle tracer in an isolation ward for burned patients. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Jun;70(2):299–312. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002235x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M., Davies J., Payne R. W., Newman P., Williams R. E. Nasal acquisition of Staphylococcus aureus in partly divided wards. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Mar;69(1):113–123. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002132x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidwell O. M., Polakoff S., Jevons M. P., Parker M. T. Staphylococcal infection in thoracic surgery: experience in a subdivided ward. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Sep;64(3):321–337. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE W. C., LIDWELL O. M., KINGSTON D. THE SIZE DISTRIBUTION OF AIRBORNE PARTICLES CARRYING MICRO-ORGANISMS. J Hyg (Lond) 1963 Dec;61:385–391. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. E., Harding L. Studies of the effectiveness of an isolation ward. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):649–658. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


