Abstract
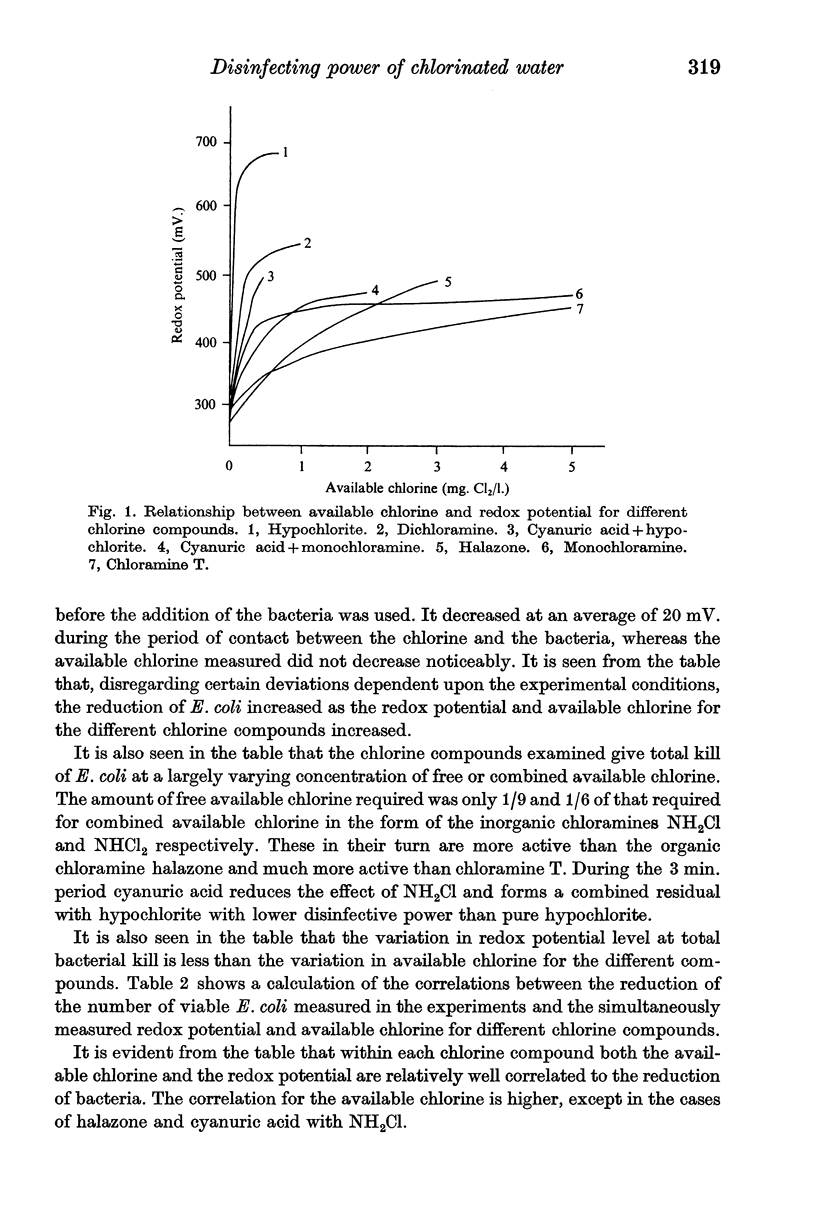
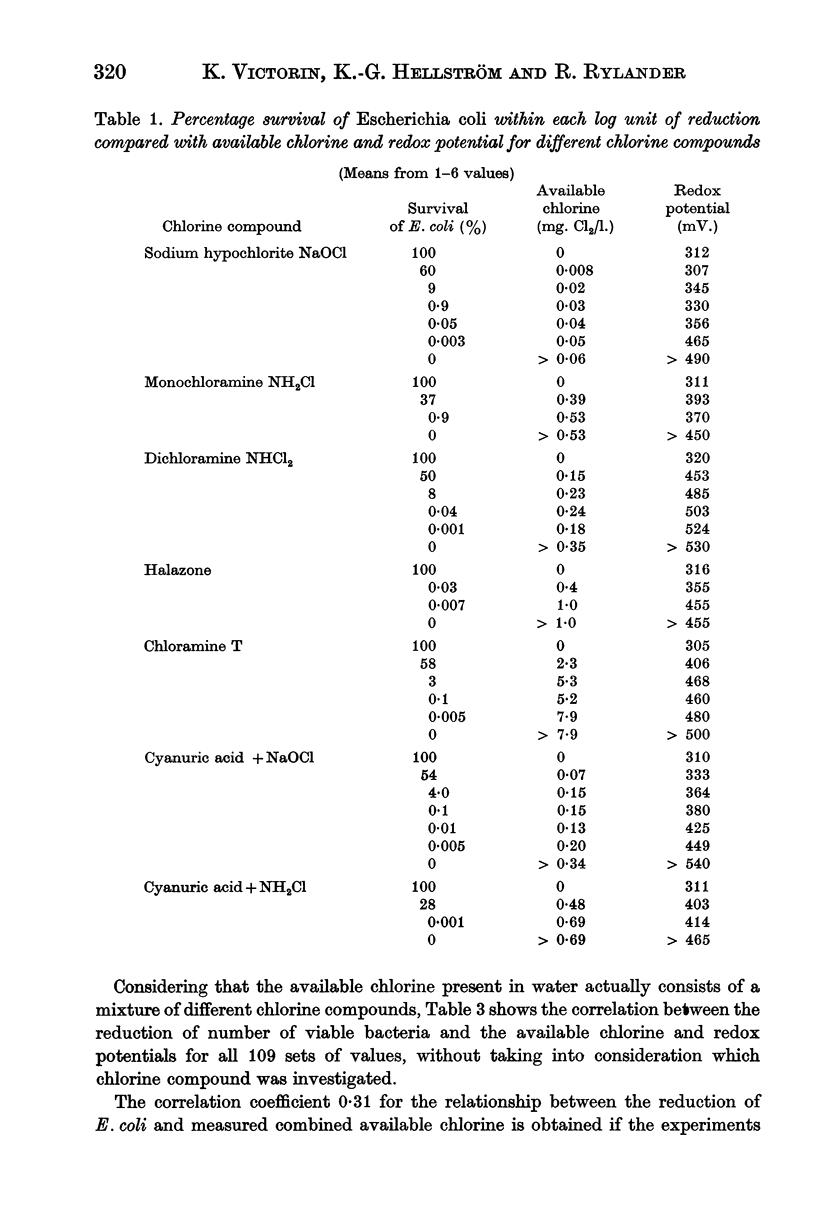
The kill of Escherichia coli within 3 min. was studied in chlorine-demand-free water using sodium hypochlorite, monochloramine, dichloramine, halazone, chloramine T, cyanuric acid + sodium hypochlorite and cyanuric acid + monochloramine. The redox potential and the available chlorine were measured. The redox potential was found to be better correlated with the disinfecting property of the water than was the amount of available chlorine. For individual pure chlorine compounds, the measuring of available chlorine showed in general a somewhat better correlation with reduction of the bacteria than the redox potential showed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black A. P., Keirn M. A., Smith J. J., Jr, Dykes G. M., Jr, Harlan W. E. The disinfection of swimming pool water. II. A field study of the disinfection of public swimming pools. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1970 Apr;60(4):740–750. doi: 10.2105/ajph.60.4.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson S., Hässelbarth U., Mecke P. Die Erfassung der desinfizierenden Wirkung gechlorter Schwimmbadwässer durch Bestimmung des Redoxpotentials. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1968 Aug;152(4):306–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNG E. THE OXIDATION POTENTIAL CONCEPT OF INACTIVATION OF POLIOVIRUS IN SEWAGE. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:141–145. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


