Abstract
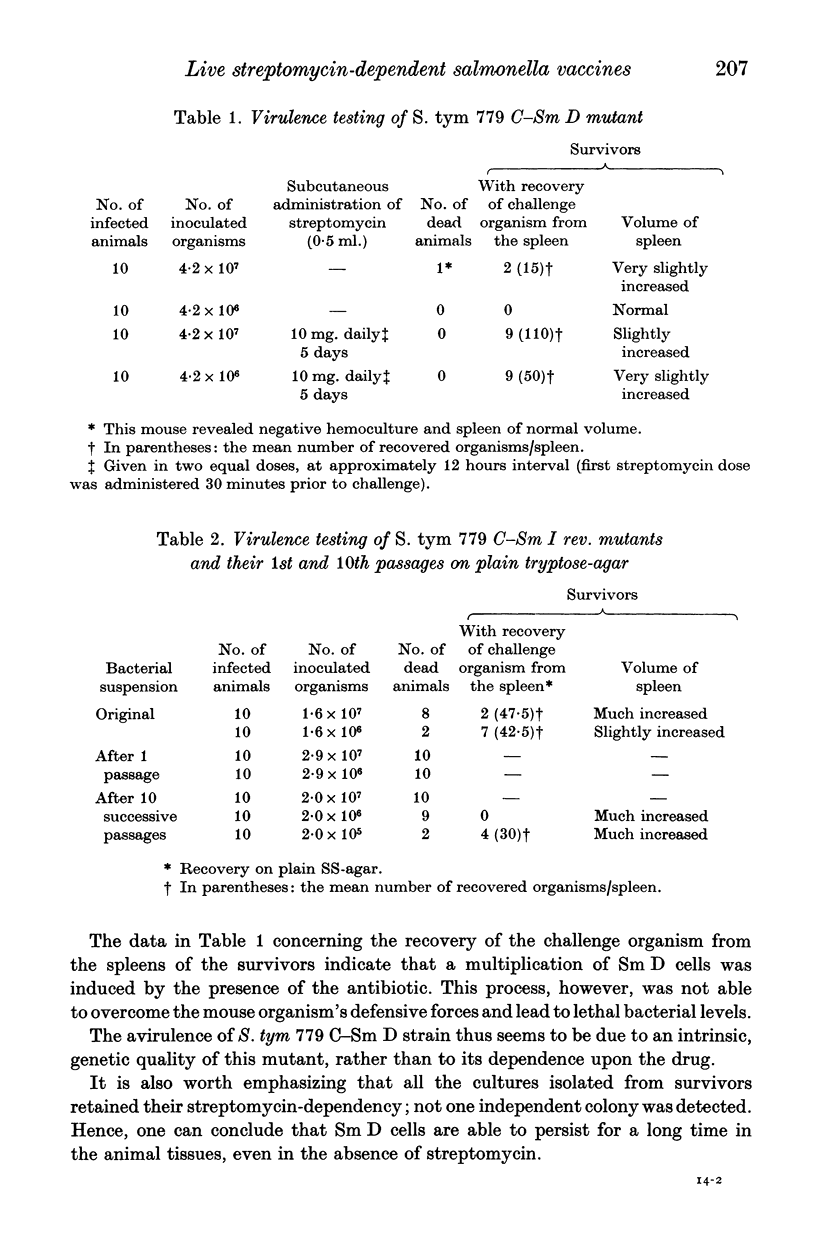
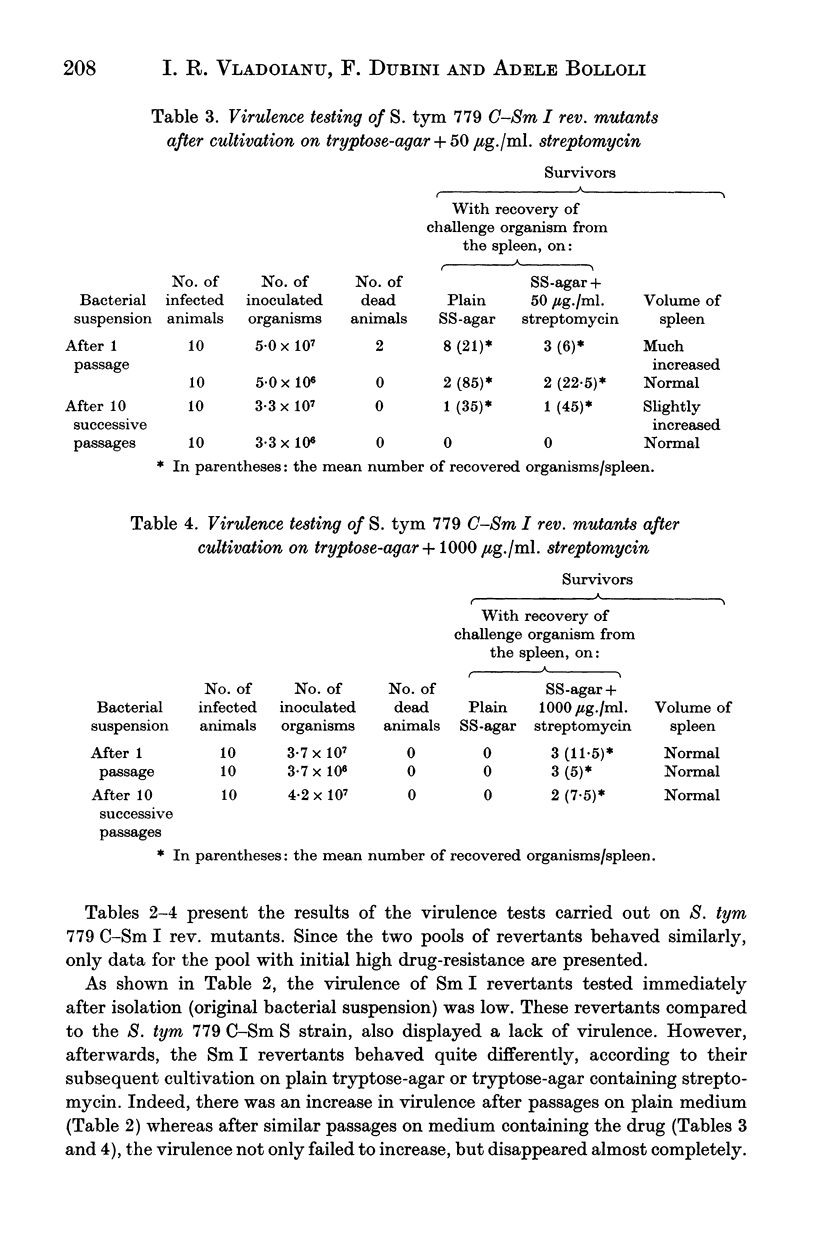
The recovery of virulence by means of reversion of a live streptomycin-dependent (Sm D) Salmonella typhimurium vaccine was studied in CD-1 Swiss mice. Initially, a one-step Sm D mutant was obtained from a virulent streptomycin-sensitive (Sm S) S. typhimurium strain. Afterwards, two pools of streptomycin-independent (Sm I) revertants were prepared from the Sm D strain. The virulence of the Sm D strain and of the Sm I revertants was tested intraperitoneally. In the virulence testing the original suspension of the Sm I revertants, as well as their 1st and 10th passages on plain medium, medium+50 mug. streptomycin/ml. and medium+1000 mug. streptomycin/ml. were used. The results show that the Sm D mutant was avirulent, its avirulence being due to an intrinsic, genetic quality. The Sm I revertants, compared to the original Sm S strain, also displayed a lack of virulence. However, afterwards, the Sm I revertants behaved quite differently, according to their subsequent passages. Indeed, there was an increase in virulence after passages on plain medium, whereas similar passages on medium containing the drug, the virulence not only failed to increase, but disappeared almost completely. Moreover, the passages on medium containing 1000 mug. streptomycin/ml. induced a return to the status of drug-dependence. The danger of recovery of virulence by means of revertants is evaluated.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. R., Rowley D. A quantitative comparison of the antigenic structure of a virulent and an avirulent strain of Salmonella typhimurium. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):551–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W., YATES M. The effects of biochemical mutation on the virulence of Bacterium typhosum; the loss of virulence of certain mutants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):85–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON L. S., FORMAL S. B. Immunization studies with living vaccine of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Aug-Sep;104:565–567. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. N., Fahey K. J. Oral Immunization in Experimental Salmonellosis III. Behavior of Virulent and Temperature-Sensitive Mutant Strains in the Intestinal Tissues of Rats. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):192–200. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.192-200.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cvjetanović B., Mel D. M., Felsenfeld O. Study of live typhoid vaccine in chimpanzees. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(4):499–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Woodward T. E. Immunity in typhoid fever: evaluation of live streptomycin-dependent vaccine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:236–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELIX A. The preparation, testing and standardization of typhoid vaccine. J Hyg (Lond) 1951 Jun-Sep;49(2-3):268–297. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURNESS G., ROWLEY D. Transduction of virulence within the species Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):140–145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral Immunization in Experimental Salmonellosis II. Characteristics of the Immune Response to Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Given by Oral and Parenteral Routes. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.183-191.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., Cooper G. N. Oral immunization against experimental salmonellosis I. Development of temperature-sensitive mutant vaccines. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):263–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.263-270.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Kent T. H., May H. C., Palmer A., Falkow S., LaBrec E. H. Protection of monkeys against experimental shigellosis with a living attenuated oral polyvalent dysentery vaccine. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):17–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.17-22.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Labrec E. H., Palmer A., Falkow S. Protection of Monkeys Against Experimental Shigellosis with Attenuated Vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.63-68.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSCHMIDT E. P., MATNEY T. S., BAUSUM H. T. Genetic analyses of mutations from streptomycin dependence to independence in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1962 Nov;47:1475–1487. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.11.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K. Streptomycin Resistance in Escherichia Coli Analyzed by Transduction. Genetics. 1960 Jan;45(1):49–62. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istrati G., Istrati M., Meitert T., Ciufeco C. Stabilité génétique du caractère non-pathogène et immunogène antiinfectieux de quelques souches de Sh. flexneri 2a. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1965 Dec;24(4):867–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Istrati G., Meitert T., Ciufeco C. Treatment of dysentery bacilli carriers with a live nonpathogenic antidysenteric vaccine. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(2):333–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISHIMOTO Y. [LIVE VACCINE IMMUNIZATION IN EXPERIMENTAL TYPHOID WITH A STREPTOMYCIN DEPENDENT STRAIN OF SALMONELLA ENTERITIDIS]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1965 Apr;20:195–202. doi: 10.3412/jsb.20.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Early antibody response in mice to either infection or immunization with Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.773-778.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Arsić B. L., Nikolić B. D., Radovanić M. L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 4. Oral immunization with live monotypic and combined vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):375–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Papo R. G., Terzin A. L., Vuksić L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 2. Safety tests and reactogenicity studies on a live dysentery vaccine intended for use in field trials. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):637–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Terzin A. L., Vuksić L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 1. Immunization of mice against experimental Shigella infection. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):633–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Terzin A. L., Vuksić L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 3. Effective oral immunization against Shigella flexneri 2a in a field trial. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):647–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D., Gangarosa E. J., Radovanovic M. L., Arsic B. L., Litvinjenko S. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 6. Protection of children by oral immunization with streptomycin-dependent Shigella strains. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(4):457–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine T. F., Jr, Finland M. Observations on Bacteria Sensitive to, Resistant to, and Dependent upon Streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1948 Aug;56(2):207–218. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.2.207-218.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M. Infectivity and antigenicity of streptomycin-dependent Salmonella typhosa. J Infect Dis. 1967 Feb;117(1):101–107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEWE E. Effects of modified host metabolism and altered defense mechanisms on survival time and pathogen counts in tissues and total body of mice infected intravenously with Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1958 May-Jun;102(3):275–293. doi: 10.1093/infdis/102.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VLADOIANU I. R., DIMACHE G., ANTOHI S., VLADOIANU C., ZARMA O. LABORATORY TESTS ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL VACCINATION OF YOUNG CHILDREN AGAINST TYPHOID AND PARATYPHOID A AND B. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:37–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VLADOIANU I. R., DIMACHE G. CONTRIBU TII ROM INE STI LA STUDIUL VACCIN ARII ANTITIFOIDICE PE CALE ORAL A. Microbiol Parazitol Epidemiol (Bucur) 1965 Mar-Apr;10:97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlădoianu I. R., Dimache G. Comportement des souris DBA et H envers l'infection expérimentale avec S. typhimurium. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1964 Mar;23(1):59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


