Abstract
A survey was carried out on the occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus on fish and shellfish, as sold in The Netherlands.
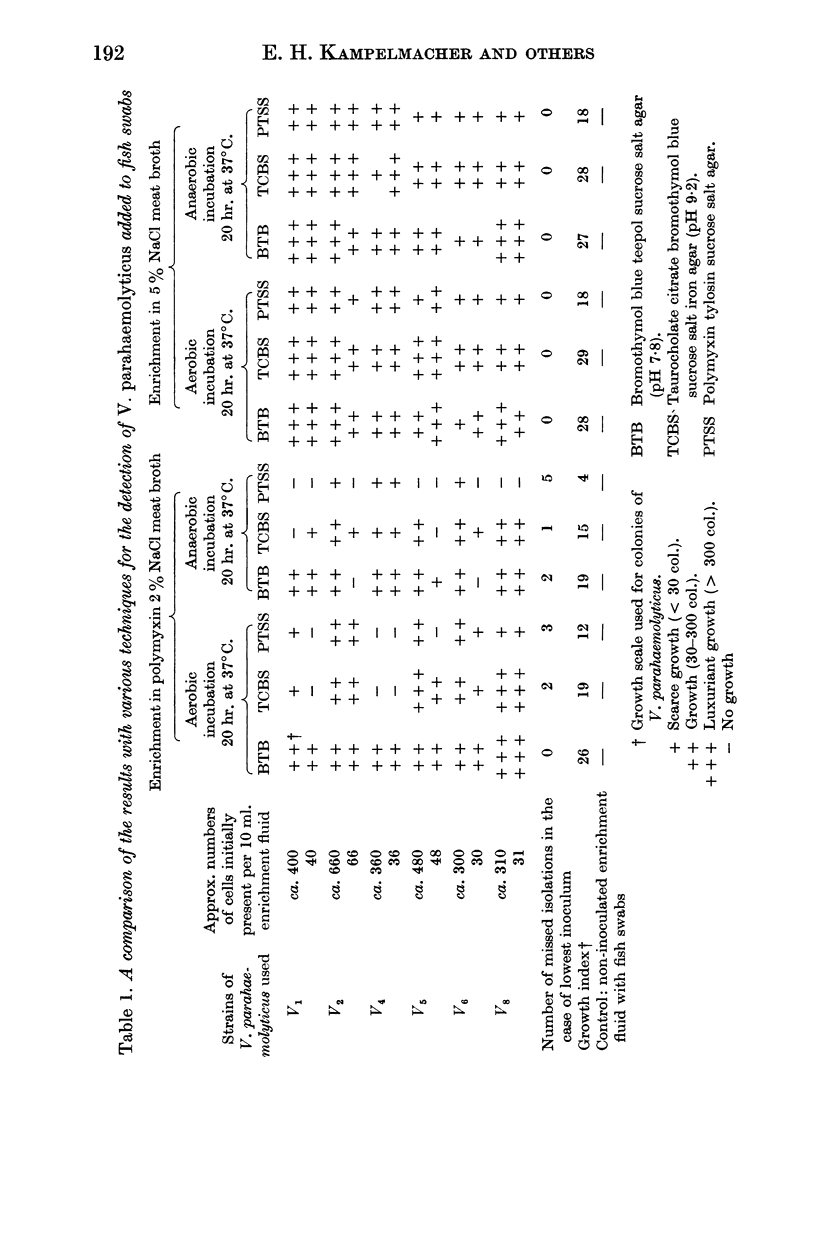
The optimal mode of detection of this bacterium appeared to be: (i) enrichment of swabs taken from the surface and the gills in freshly prepared meat broth with 5% NaCl; (ii) streaking onto Teepol bromothymol blue agar (BTB) and taurocholate bromothymol blue sucrose agar (TCBS); (iii) confirmation of suspect colonies by testing for mode of growth in butts/slants of a Kligler type glucose sucrose iron thiosulphate agar, formation of indole in 2% NaCl 2% trypticase water, anaerobic utilization of starch in the presence of 5% NaCl and oxidase reaction according to Kovacs (1956).
A total of 407 samples, stemming from 17 types of fish and shellfish, taken at three fish shops, was examined by this technique. Only one specimen, i.e. a haddock, was found to contain V. parahaemolyticus. This contamination rate of approximately 0·3% correlates well with data found earlier for fish landed in Northern Germany.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baross J., Liston J. Isolation of vibrio parahaemolyticus from the Northwest Pacific. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1263–1264. doi: 10.1038/2171263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOBAYASHI T., ENOMOTO S., SAKAZAKI R., KUWAHARA S. [A NEW SELECTIVE ISOLATION MEDIUM FOR THE VIBRIO GROUP; ON A MODIFIED NAKANISHI'S MEDIUM (TCBS AGAR MEDIUM)]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1963 Nov;18:387–392. doi: 10.3412/jsb.18.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz G. E., Colwell R. R., Lovelace E. Vibrio parahaemolyticus from the blue crab Callinectes sapidus in Chesapeake Bay. Science. 1969 Jun 13;164(3885):1286–1287. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3885.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossel D. A., Kampelmacher E. H., van Noorle Jansen L. M. The optimal mode of transport for swabs obtained from surfaces examined for organisms causing food-borne disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Mar;66(1):59–66. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAZAKI R., IWANAMI S., FUKUMI H. STUDIES ON THE ENTEROPATHOGENIC, FACULTATIVELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA, VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND ITS TAXONOMICAL POSITION. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1963 Aug;16:161–188. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.16.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Kato T., Obara Y., Yamai S. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. 3. Enteropathogenicity. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):325–331. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert R. H. Das Vorkommen der Aeromonaden in oberirdischen Gewässern. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1967 Mar;150(7):688–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temmyo R. Studies on the prevention of outbreaks of food poisoning caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Bull Tokyo Med Dent Univ. 1966 Dec;13(4):489–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. Q. Isolations of organisms related to Vibrio parahemolyticus from American estuarine sediments. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Mar;16(3):543–546. doi: 10.1128/am.16.3.543-546.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen-Yoji H., Sakai S., Terayama T., Kudo Y., Ito T., Benoki M., Nagasaki M. Epidemiology, enteropathogenicity, and classification of Vi.rio parahaemolyticus. J Infect Dis. 1965 Dec;115(5):436–444. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.5.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


