Abstract
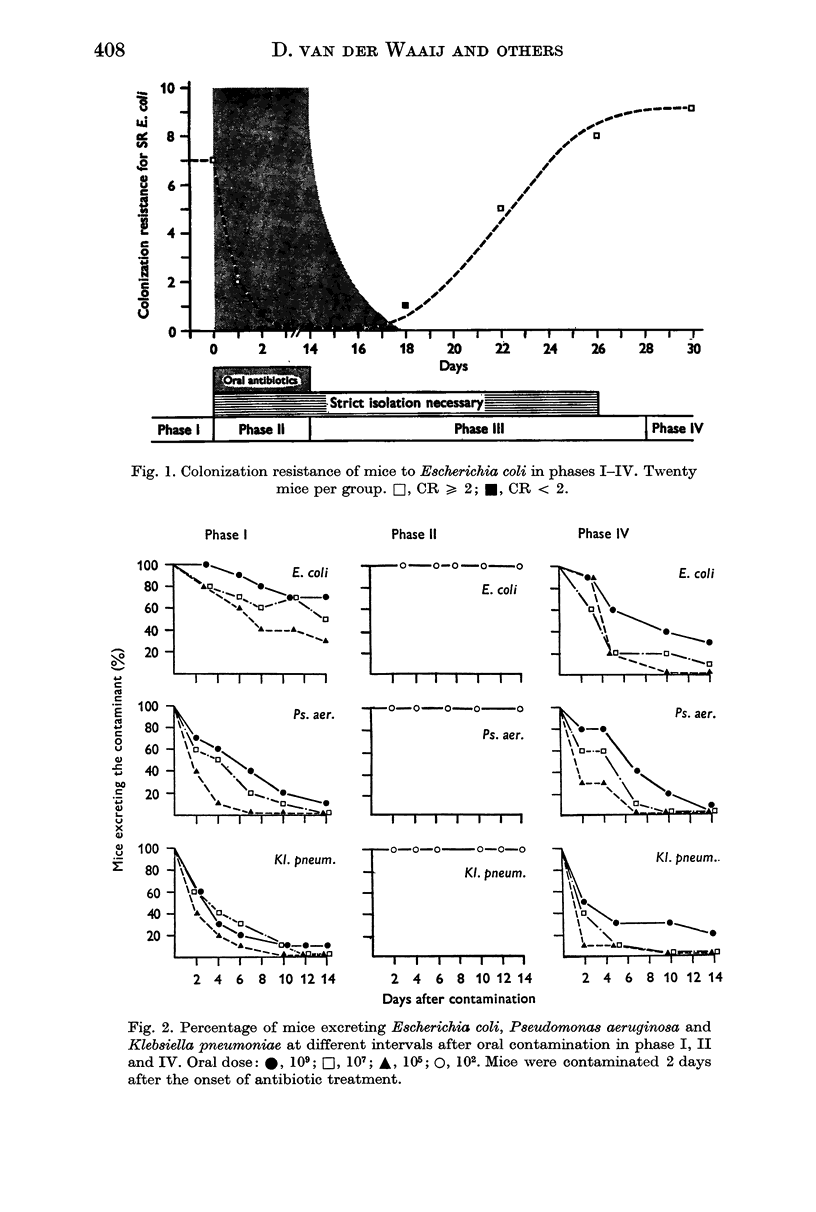
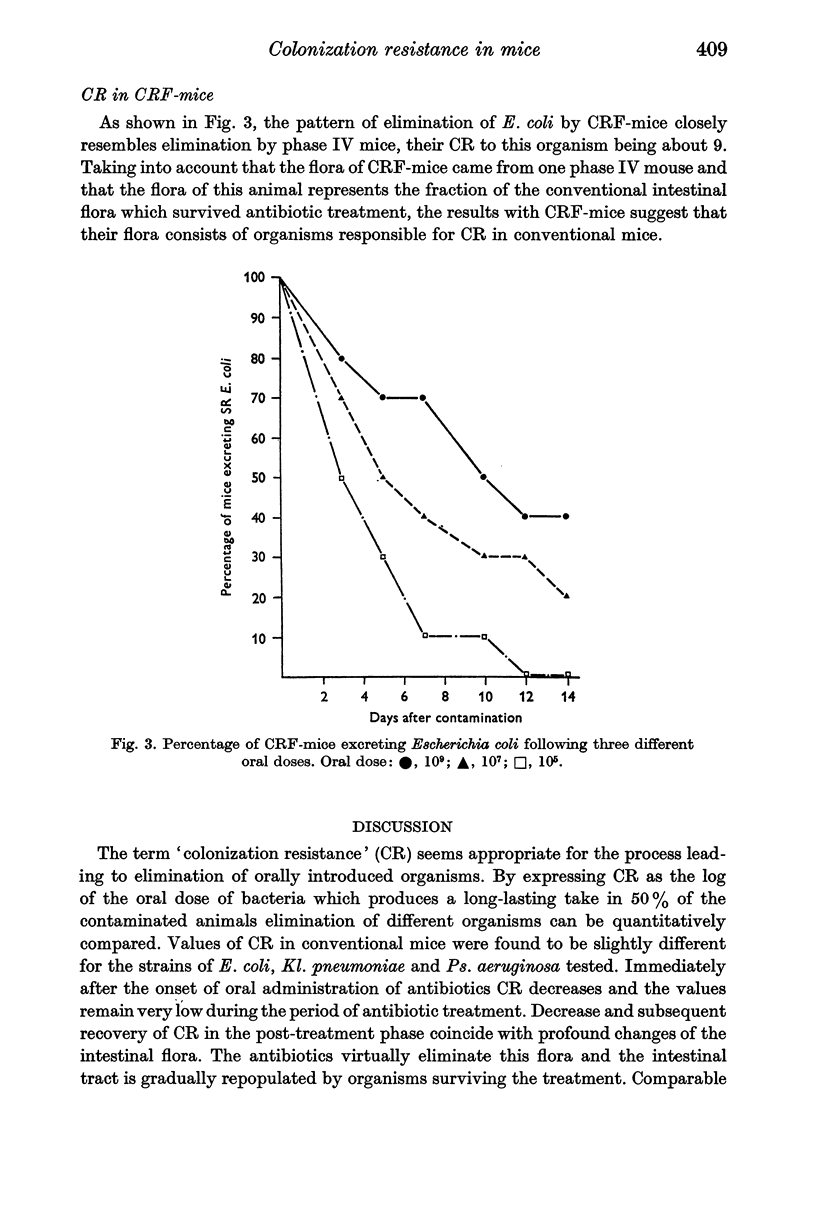
The effect of oral administration of antibiotics on the intestinal flora of conventional mice and their resistance to colonization by orally introduced Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa was studied. Colonization resistance (CR) was expressed as the log of the oral bacterial dose followed by a persistent take in 50% of the contaminated animals. The intestinal flora was virtually eliminated by the antibiotics and this elimination was accompanied by a precipitous fall of CR. CR gradually returned to normal values during the period of repopulation of the intestinal tract by the organisms surviving the treatment. Antibiotic treatment resulted in the disappearance of Enterobacteriaceae, enterococci, staphylococci and yeasts and, under appropriate housing conditions, the animals remained free of these organisms indefinitely. Germ-free mice contaminated with the intestinal flora of an antibiotic-treated animal and their offspring housed in a germ-free isolator showed high values of CR. Their intestinal flora consisted of anaerobic bacteria only. Apparently, these anaerobes are responsible for CR in these and in conventional mice.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on gastrointestinal motility. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):301–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on the resistance of the small intestine to infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1604-1608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P. Enhanced susceptibility to Salmonella infection in streptomycin-treated mice. J Infect Dis. 1962 Sep-Oct;111:117–127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. II. FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR ITS LOSS FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:817–828. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING V. M., COSGROVE G. E. Intestinal helminths in various strains of laboratory mice. Lab Anim Care. 1963 Feb;13:46–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBS R., COSTELLO R. ASSOCIATION OF GERMFREE MICE WITH BACTERIA ISOLATED FROM NORMAL MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:77–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. Cultural and biochemical characteristics of the genus Chromobacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):70–98. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R. Alterations in the mouse cecum and its flora produced by antibacterial drugs. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):97–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Ruseler-van Embden J. G. The intestinal flora of colonization-resistant mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Sep;69(3):413–421. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D., Andreas A. H. Prevention of airborne contamination and cross-contamination in germ-free mice by laminar flow. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Mar;69(1):83–89. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D., Sturm C. A. Antibiotic decontimination of the digestive tract of mice. Technical procedures. Lab Anim Care. 1968 Feb;18(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D. The persistent absence of Enterobacteriaceae from the intestinal flora of mice following antibiotic treatment. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):32–38. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]