Abstract
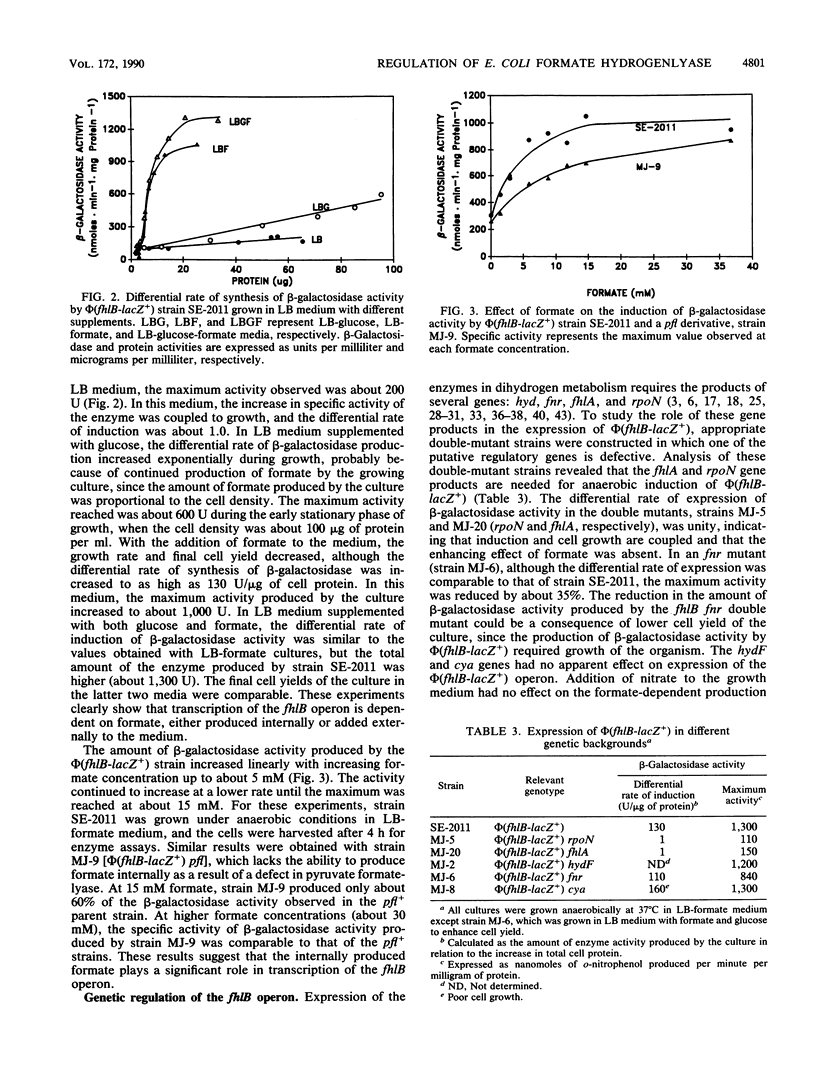
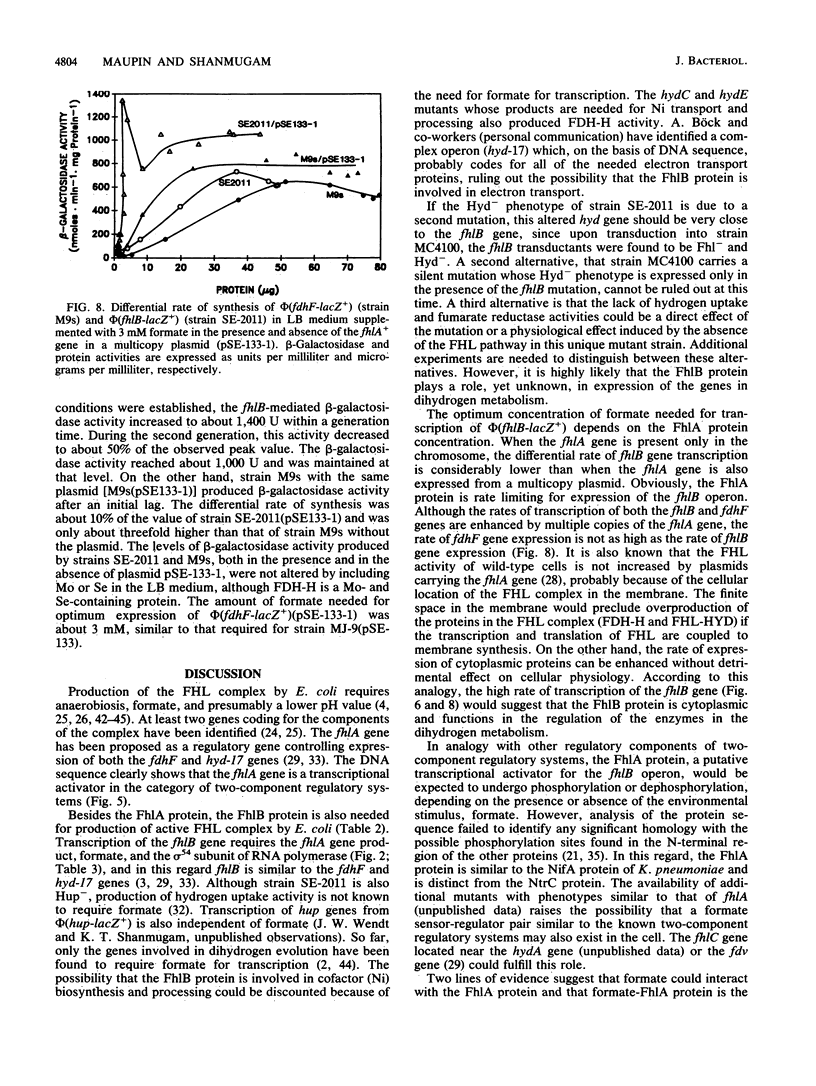
A new gene whose product is required for the production of formate hydrogenlyase (FHL) has been identified in Escherichia coli. This gene, termed fhlB, maps between the frdA (94.4 min) and argI (96.6 min) genes on the E. coli chromosome and is transcribed in a clockwise direction toward argI. Biochemical analysis of an FhlB- mutant, strain SE-2011 [phi(fhlB-lacZ+)], revealed that the mutant lacks formate dehydrogenase activity associated with FHL (FDH-H) and hydrogenase activity. As a result of these defects, fermentative hydrogen production and hydrogen uptake reactions were undetectable in strain SE-2011. Fumarate reductase activity of this mutant was also reduced to about 15% of the levels of the parent (strain MC4100), and strain SE-2011 did not produce succinate as a fermentation end product. Regulation of expression of the fhlB gene, studied as production of beta-galactosidase activity by strain SE-2011, revealed that the operon is expressed at low levels under aerobic conditions. Under anaerobic growth conditions, this activity increased by two- to threefold. Addition of formate enhanced the differential rate of synthesis of the fhlB gene product to as high as 130 U of beta-galactosidase specific activity per microgram of cell protein, but only under anaerobic conditions. Formate-dependent expression of phi(fhlB-lacZ+) required the sigma 54 subunit of RNA polymerase and the fhlA gene product. The concentration of formate required for maximum expression of the fhlB gene was about 15 mM; this value decreased to about 3 mM in the presence of plasmid pSE-133, which carries the fhlA gene in a multicopy plasmid. DNA sequence analysis of the fhlA gene showed that the FhlA protein is 686 amino acids long and has an anhydrous molecular weight of 78,086. On the basis of sequence homology with other transcriptional activators such as NtrC, HydG, and Klebsiella pneumoniae NifA proteins, the FhlA protein was deduced to be a transcriptional activator controlling the production of FHL. It is proposed that formate interacts with the FhlA protein and that this active complex initiates transcription of the fhlB gene. The FhlA and FhlB proteins act as a cascade in regulating the production of FDH-H and the FHL-linked hydrogenase and ultimately the production of FHL and fermentative hydrogen.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Böck A. Characterization of a cis regulatory DNA element necessary for formate induction of the formate dehydrogenase gene (fdhF) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Sawers R. G., Böck A. Involvement of the ntrA gene product in the anaerobic metabolism of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):535–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00327209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Zinoni F., Sawers G., Böck A. Factors affecting transcriptional regulation of the formate-hydrogen-lyase pathway of Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Jun;148(1):44–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00429646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer E., Silhavy T. J., Weisemann J. M., Weinstock G. M. Lambda placMu: a transposable derivative of bacteriophage lambda for creating lacZ protein fusions in a single step. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1084–1093. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1084-1093.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri A., Krasna A. I. Isolation of genes required for hydrogenase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3289–3298. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. P. The fermentation pathways of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;5(3):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Edwards E. S., DeMoss J. A. Resolution of distinct selenium-containing formate dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1317–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1317-1324.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY C. T., GEST H. BIOLOGICAL FORMATION OF MOLECULAR HYDROGEN. Science. 1965 Apr 9;148(3667):186–192. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3667.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Patel P., Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Isolation and characterization of mutant strains of Escherichia coli altered in H2 metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.344-352.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Ríos J., Sánchez-Pescador R., Urdea M., Covarrubias A. A. The complete nucleotide sequence of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2757–2770. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecher A., Zinoni F., Böck A. The seleno-polypeptide of formic dehydrogenase (formate hydrogen-lyase linked) from Escherichia coli: genetic analysis. Arch Microbiol. 1985 May;141(4):359–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00428850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecher A., Zinoni F., Jatisatienr C., Wirth R., Hennecke H., Böck A. On the redox control of synthesis of anaerobically induced enzymes in enterobacteriaceae. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Nov;136(2):131–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00404787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Lee J. H., Shanmugam K. T. Cloning of hydrogenase genes and fine structure analysis of an operon essential for H2 metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.353-360.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Lee J. H., Shanmugam K. T. Gene-product relationships of fhlA and fdv genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5440–5445. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5440-5445.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Biochemical and genetic analysis of hydrogen metabolism in Escherichia coli: the hydB gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5433–5439. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5433-5439.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Hydrogen metabolism in Escherichia coli: biochemical and genetic evidence for a hydF gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5446–5451. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5446-5451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Differential expression of hydrogenase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli K-12: evidence for a third isoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1324–1331. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1324-1331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlensog V., Birkmann A., Böck A. Mutations in trans which affect the anaerobic expression of a formate dehydrogenase (fdhF) structural gene. Arch Microbiol. 1989;152(1):83–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00447016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V. Nitrate respiration in relation to facultative metabolism in enterobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):190–232. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.190-232.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Randomly induced Escherichia coli K-12 Tn5 insertion mutants defective in hydrogenase activity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.831-836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Reijnders W. N., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Initial cloning and sequencing of hydHG, an operon homologous to ntrBC and regulating the labile hydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4448–4456. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4448-4456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R., Boxer D. H. Pleiotropic hydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli K12: growth in the presence of nickel can restore hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A. Genetic and physiological characterization of new Escherichia coli mutants impaired in hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):167–179. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A. Regulation of the fdhF gene encoding the selenopolypeptide for benzyl viologen-linked formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00329847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yerkes J. H., Casson L. P., Honkanen A. K., Walker G. C. Anaerobiosis induces expression of ant, a new Escherichia coli locus with a role in anaerobic electron transport. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):180–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.180-186.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Beier A., Pecher A., Wirth R., Böck A. Regulation of the synthesis of hydrogenase (formate hydrogen-lyase linked) of E. coli. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Nov;139(4):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00408370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Stadtman T. C., Böck A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the selenocysteine-containing polypeptide of formate dehydrogenase (formate-hydrogen-lyase-linked) from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



