Abstract
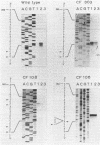
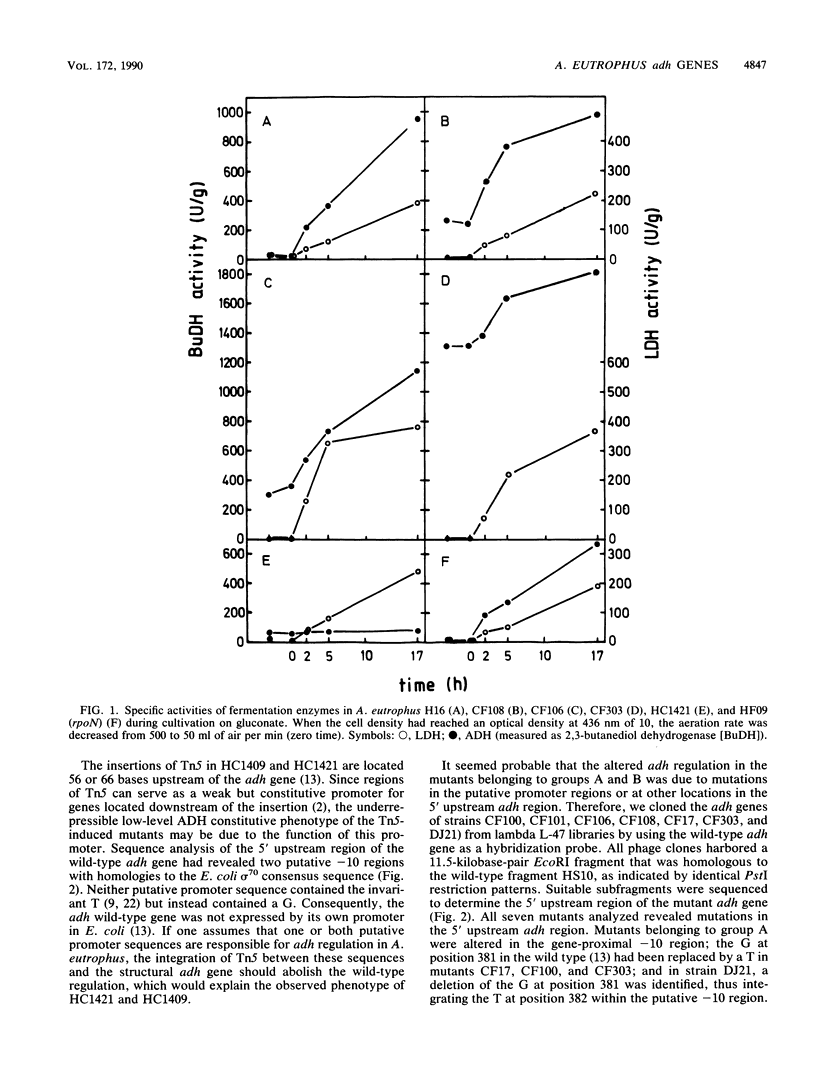
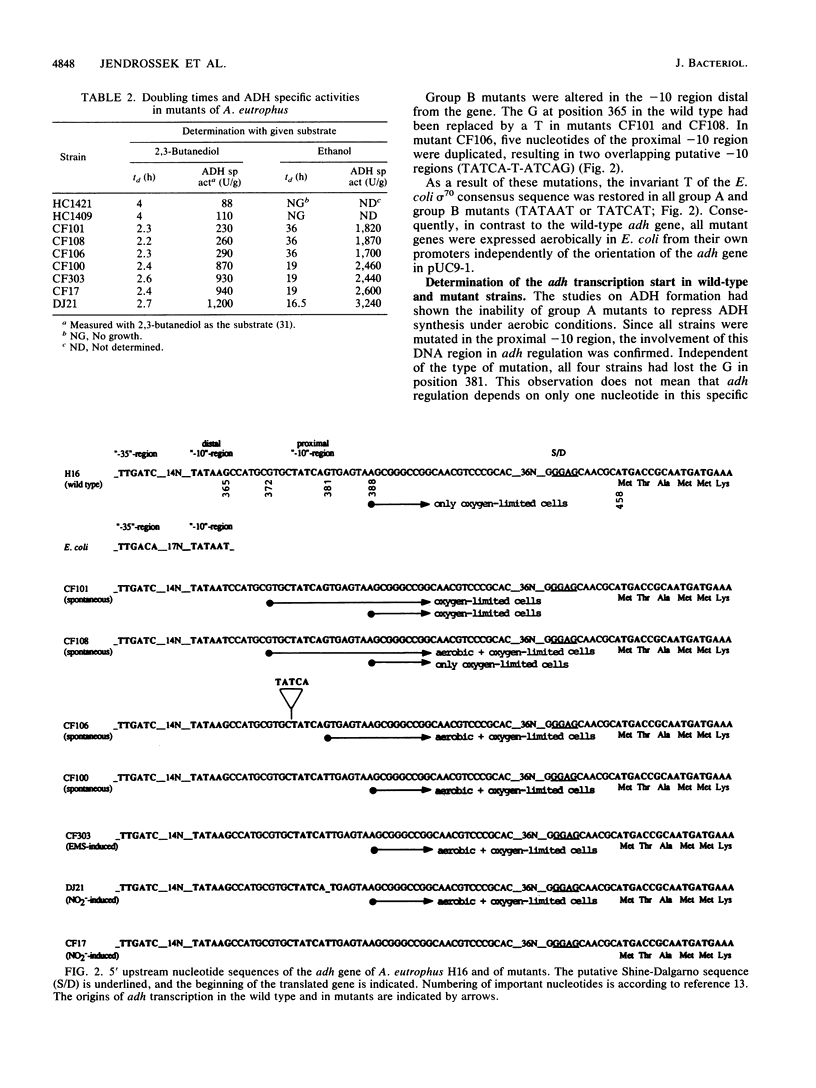
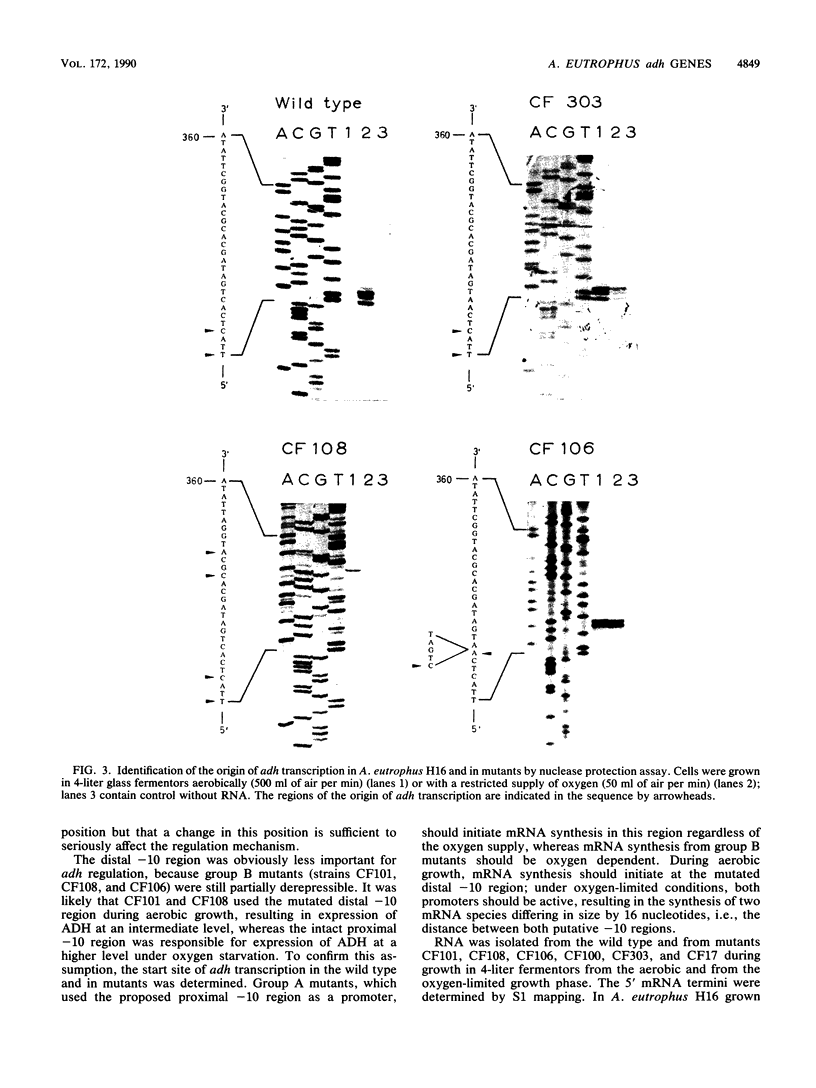
The nucleotide sequence of the gene that encodes the fermentative, derepressible alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 and of adjacent regions was recently determined. Two potential -10 regions resembling the Escherichia coli sigma 70 consensus sequence were identified 77 and 93 nucleotides upstream of the structural gene. By determination of the 5' mRNA terminus of the wild-type adh gene, the proximal -10 region was identified as responsible for adh expression under derepressive conditions. Transcription started seven nucleotides downstream of this region, at position 388. Sequence analysis of seven mutants expressing the adh gene under aerobic conditions revealed mutations in one or the other potential -10 region. In all seven strains, the mutations restored the invariant T of the E. coli promoter consensus sequence. Mutants altered in the proximal -10 region transcribed the adh gene under aerobic conditions with the same 5' mRNA terminus as in the wild type; gene expression was impaired very little under aerobic conditions. Mutants altered in the distal -10 region also transcribed the adh gene aerobically but were still partially derepressible. The 5' mRNA terminus was seven nucleotides downstream of the distal -10 region, at position 372. When these mutants were cultivated under conditions of restricted oxygen supply, the adh gene was transcribed from both -10 regions, resulting in the synthesis of two mRNA species with different 5' termini.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg D. E., Weiss A., Crossland L. Polarity of Tn5 insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.439-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Sawers R. G., Böck A. Involvement of the ntrA gene product in the anaerobic metabolism of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):535–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00327209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Barr G. C., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and the anaerobic and growth phase regulation of tonB gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2816–2826. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2816-2826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fründ C., Priefert H., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Biochemical and genetic analyses of acetoin catabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6539–6548. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6539-6548.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Fregeau C., Préfontaine G., Brousseau R. Construction of a family of universal expression plasmid vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogrefe C., Römermann D., Friedrich B. Alcaligenes eutrophus hydrogenase genes (Hox). J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.43-48.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek D., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Alcohol dehydrogenase gene from Alcaligenes eutrophus: subcloning, heterologous expression in Escherichia coli, sequencing, and location of Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5248–5256. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5248-5256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrossek D., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Three different proteins exhibiting NAD-dependent acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activity from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):541–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Jendrossek D., Fründ C., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus alcohol dehydrogenase gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):685–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.685-692.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. Hydrogen evolution by strictly aerobic hydrogen bacteria under anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):633–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.633-639.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaux P. G., Herendeen S. L., Bloch P. L., Neidhardt F. C. Transient rates of synthesis of individual polypeptides in E. coli following temperature shifts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römermann D., Warrelmann J., Bender R. A., Friedrich B. An rpoN-like gene of Alcaligenes eutrophus and Pseudomonas facilis controls expression of diverse metabolic pathways, including hydrogen oxidation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1093-1099.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarimo S. S., Pine M. J. Taxonomic comparison of the amino termini of microbial cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):368–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.368-374.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Schlegel H. G. Mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus defective in autotrophic metabolism. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):123–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00402299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S., Urban M., Friedrich B. Mutagenesis of Alcaligenes eutrophus by insertion of the drug-resistance transposon Tn5. Arch Microbiol. 1982 May;131(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00405879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbüchel A., Schlegel H. G. A multifunctional fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase from the strict aerobe Alcaligenes eutrophus: purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):555–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDE E. [Studies on growth and synthesis of stored substance by Hydrogenomonas]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:109–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER J. P. THE NH2-TERMINAL RESIDUES OF THE PROTEINS FROM CELL-FREE EXTRACTS OF E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Nov;7:483–496. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Yura T. Transient regulation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli upon shift-up of growth temperature. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1133-1140.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Droffner M. L. Mechanisms determining aerobic or anaerobic growth in the facultative anaerobe Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaborosch C., Schneider K., Schlegel H. G., Kratzin H. Comparison of the NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of the four non-identical subunits of the NAD-linked hydrogenases from Nocardia opaca 1b and Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. S., Hearst J. E. Transcription of oxygen-regulated photosynthetic genes requires DNA gyrase in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]