Abstract
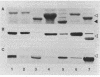
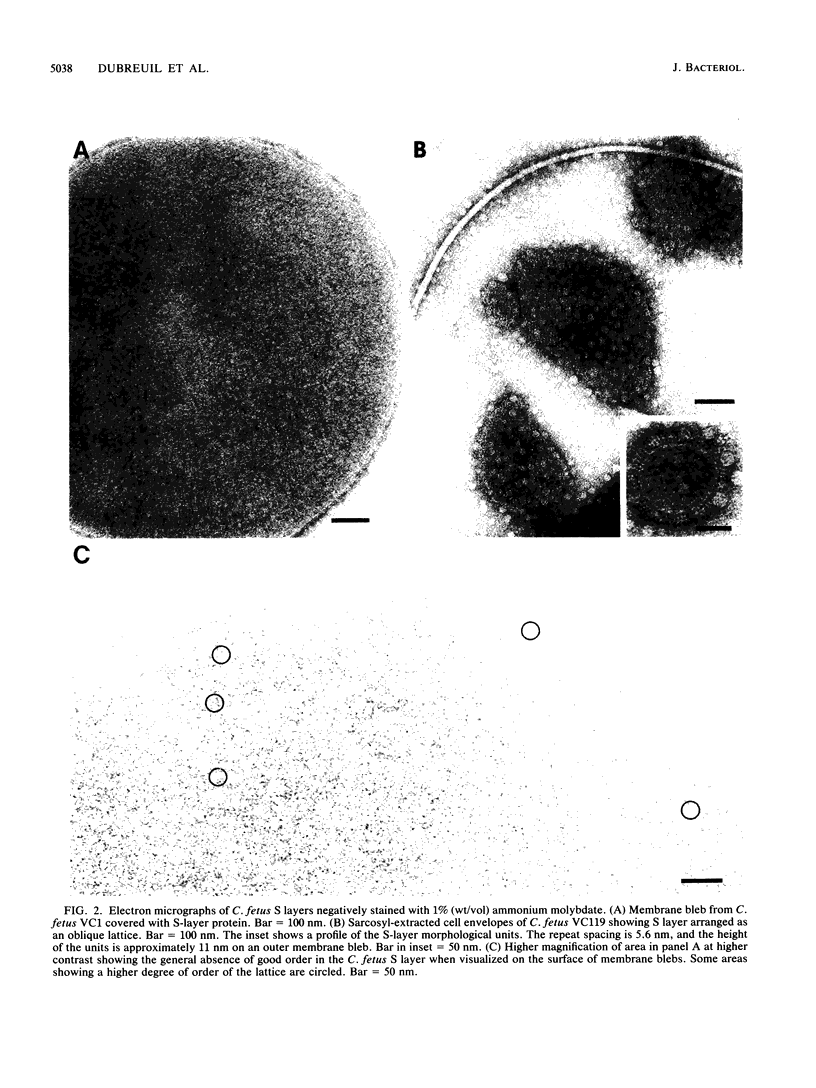
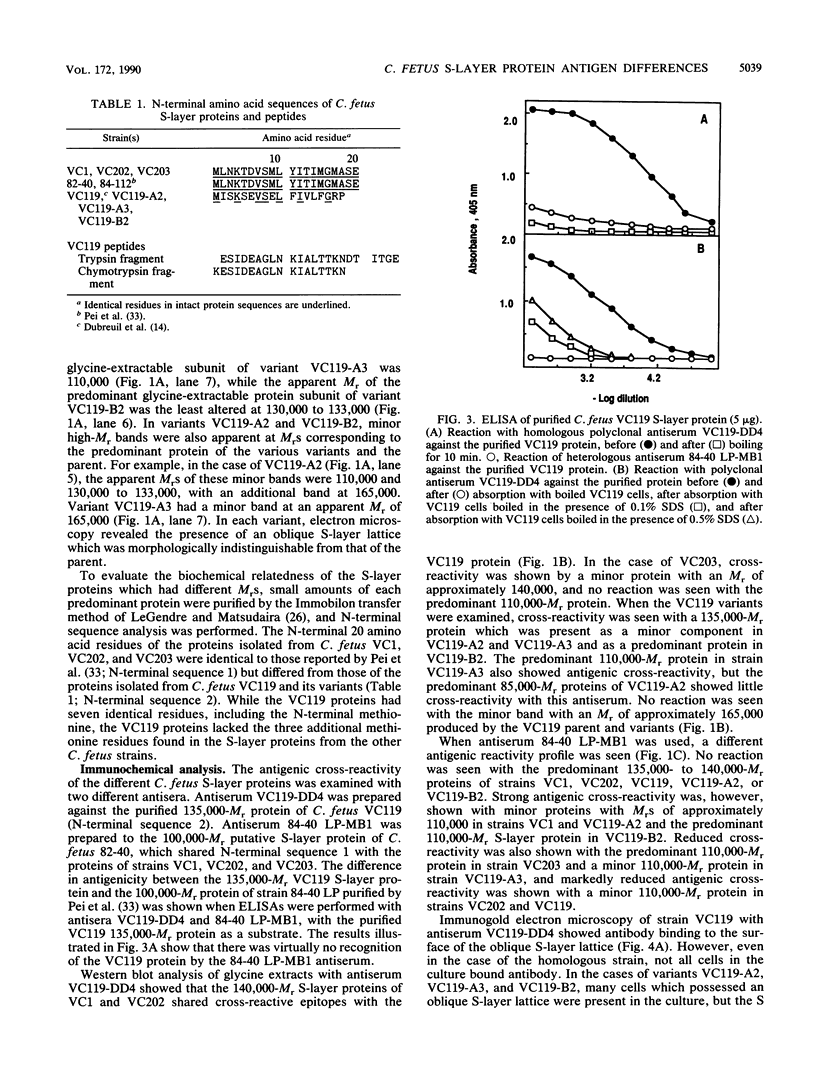
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of S-layer proteins extracted from Campylobacter fetus strains by using acid glycine buffer showed that the predominant S-layer proteins of different strains had subunit molecular weights in the range of 90,000 to 140,000. Electron microscopy revealed oblique S-layer lattices with a spacing of approximately 5.6 nm (gamma = 75 degrees) on wild-type strains VC1, VC119, VC202, and VC203. Three variants of C. fetus VC119 producing a predominant S-layer subunit protein of different molecular weight (Mr) from that of the parent were also examined. Each variant produced an oblique lattice morphologically indistinguishable from that of the parent. Amino-terminal sequence analysis showed that the S-layer proteins of the VC119 parent and variants were identical up to residue 18 and that this sequence differed from but was related to the first 16 N-terminal residues shared by the S-layer proteins of the three other wild-type C. fetus isolates. Western immunoblot analysis with an antiserum prepared to the VC119 protein and an antiserum prepared to C. fetus 84-40 LP (Z. Pei, R. T. Ellison, R. V. Lewis, and M. J. Blaser, J. Biol. Chem. 263:6416-6420, 1988) showed that strains of C. fetus were capable of producing S-layer proteins with at least four different antigenic specificities. Immunoelectron microscopy with antiserum to the VC119 S-layer protein showed that C. fetus cultures contained cells with immunoreactive oblique S-layer lattices as well as cells with oblique S-layer lattices which did not bind antibody. This suggests that C. fetus S-layer proteins undergo antigenic variation. Thermal denaturation experiments indicated that the antigenicity conferred by the surface-exposed C. fetus S-layer epitopes was unusually resistant to heat, and the thermal stability appeared to be due to the highly organized lattice structure of the S. layer. Protease digestion of purified VC119 S-layer protein revealed a trypsin-, chymotrypsin-, and endoproteinase Glu-C-resistant domain with an apparent Mr of 110,000, which carried the majority of the epitopes of the S-layer protein, and a small enzyme-sensitive domain. The trypsin- and chymotrypsin-resistant polypeptides shared an overlapping sequence which differed from the N-terminal sequence of the intact S-layer protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Cloning of the gene for the surface array protein of Aeromonas salmonicida and evidence linking loss of expression with genetic deletion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4086–4091. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4086-4091.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence relatedness between thermophilic members of the genus Campylobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Nov;128(11):2515–2522. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-11-2515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Reassembly in vitro of the superficial cell wall components of Spirillum putridiconcyhylium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Apr;55(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Superficial macromolecular arrays on the cell wall of Spirillum putridiconchylium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1019–1038. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1019-1038.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Hopkins J. A., Heinzer I., Bryner J. H., Wang W. L. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections: serum resistance associated with high-molecular-weight surface proteins. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):696–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Repine J. E., Joiner K. A. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections. Failure of encapsulated Campylobacter fetus to bind C3b explains serum and phagocytosis resistance. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1434–1444. doi: 10.1172/JCI113474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Greaves D. R. Programmed gene rearrangements altering gene expression. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):658–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3544215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Bier P. J., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: antigenic variation of the bacterium during infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatherage J. F., Taylor K. A., Amos L. A. Three-dimensional arrangement of the cell wall protein of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):823–848. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Lallier R., Trust T. J. Surface antigens of virulent strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jun;12(1-4):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Logan S. M., Cubbage S., Eidhin D. N., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Beveridge T. J., Ferris F. G., Trust T. J. Structural and biochemical analyses of a surface array protein of Campylobacter fetus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4165–4173. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4165-4173.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. A., Smit J., Agabian N. Transcriptional analysis of the major surface array gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4706–4713. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4706-4713.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francioli P., Herzstein J., Grob J. P., Vallotton J. J., Mombelli G., Glauser M. P. Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Feb;145(2):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Umeda A., Takade A., Murata K., Amako K. Hexagonal surface layer of Campylobacter fetus isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2563–2565. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2563-2565.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. A., Logan S. M., Guerry P., Trust T. J. Antigenic variation of Campylobacter flagella. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5066–5071. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5066-5071.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Murray R. G. The isolation of surface array proteins from bacteria. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;62(11):1181–1189. doi: 10.1139/o84-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N., Matsudaira P. Direct protein microsequencing from Immobilon-P Transfer Membrane. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Sumper M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9724–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Guerry P., Rollins D. M., Burr D. H., Trust T. J. In vivo antigenic variation of Campylobacter flagellin. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2583–2585. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2583-2585.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Wiltberger H. A., Winter J. Major outer membrane protein of Campylobacter fetus: physical and immunological characterization. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1258-1265.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner P., Pum D., Sleytr U. B. Characterization of the ultrastructure and the self-assembly of the surface layer of Bacillus stearothermophilus strain NRS 2004/3a. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1986 Oct-Dec;97(1-3):73–88. doi: 10.1016/s0889-1605(86)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Vibrio fetus Immunogen. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):562–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.562-566.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z., Ellison R. T., 3rd, Lewis R. V., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of a family of high molecular weight surface-array proteins from Campylobacter fetus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6416–6420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Baumeister W. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of the gene for the surface (HPI)-layer protein of Deinococcus radiodurans in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1048-1054.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Trust T. J., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W. Purification and characterization of the cell surface virulent A protein from Aeromonas salmonicida. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2934–2939. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pum D., Sára M., Sleytr U. B. Structure, surface charge, and self-assembly of the S-layer lattice from Bacillus coagulans E38-66. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5296–5303. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5296-5303.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Zoltowska B., Trust T. J., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Campylobacter pylori, the spiral bacterium associated with human gastritis, is not a true Campylobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2137–2141. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2137-2141.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Johnson J. L., Krieg N. R. Differential characteristics of catalase-positive campylobacters correlated with DNA homology groups. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m84-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Reversible staining and peptide mapping of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose after separation by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. D., Hall C. E., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Persistent genital tract infection with Vibrio fetus intestinalis associated with serotypic alteration of the infecting strain. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Nov;34(11):1399–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Elimination of genital vibriosis in female cattle by systemic immunization with killed cells or cell-free extracts of Campylobacter fetus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):463–472. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Hall C. E., Corbell L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: cure of genital infection in females by systemic immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.245-251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Agabian N. Cloning of the major protein of the Caulobacter crescentus periodic surface layer: detection and characterization of the cloned peptide by protein expression assays. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1137–1145. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1137-1145.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Uchihi R., Tabata R., Takahashi Y., Hashiba H., Sasaki T., Yamagata H., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S. Characterization of the genes coding for two major cell wall proteins from protein-producing Bacillus brevis 47: complete nucleotide sequence of the outer wall protein gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):365–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.365-373.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi N., Tabata R., Takemura T., Yamagata H., Udaka S. Molecular cloning of a major cell wall protein gene from protein-producing Bacillus brevis 47 and its expression in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1054-1060.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]