Abstract
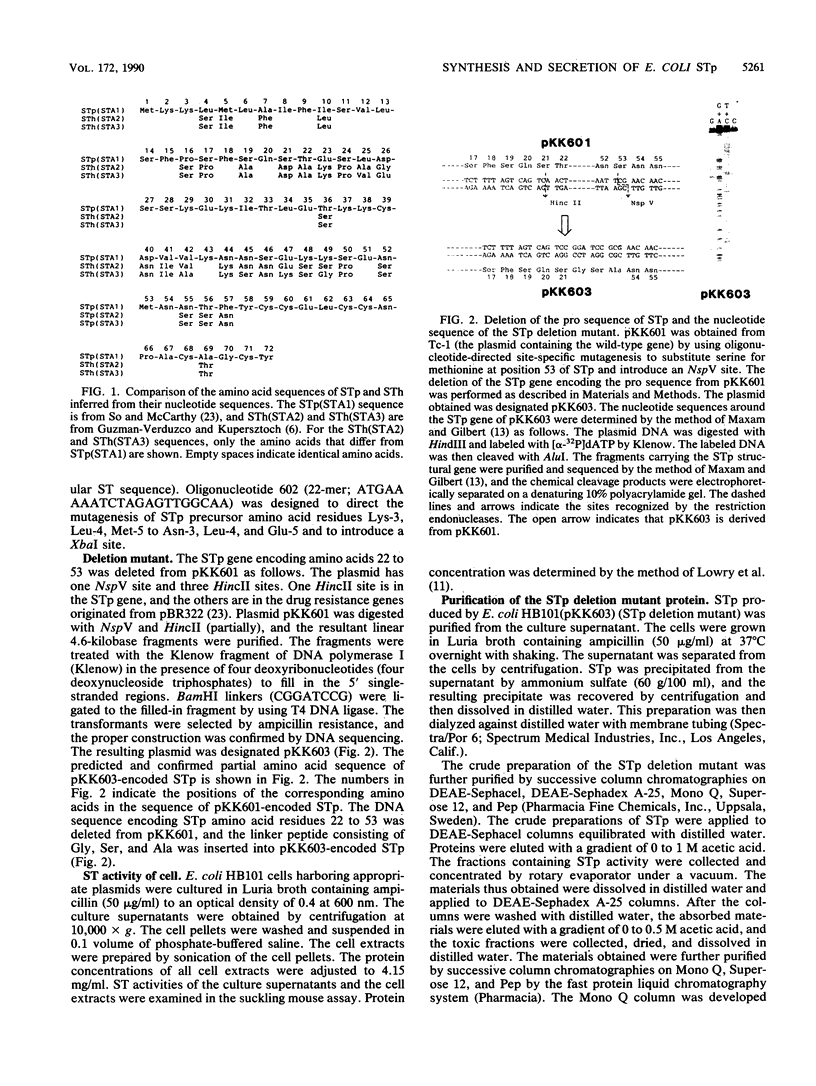
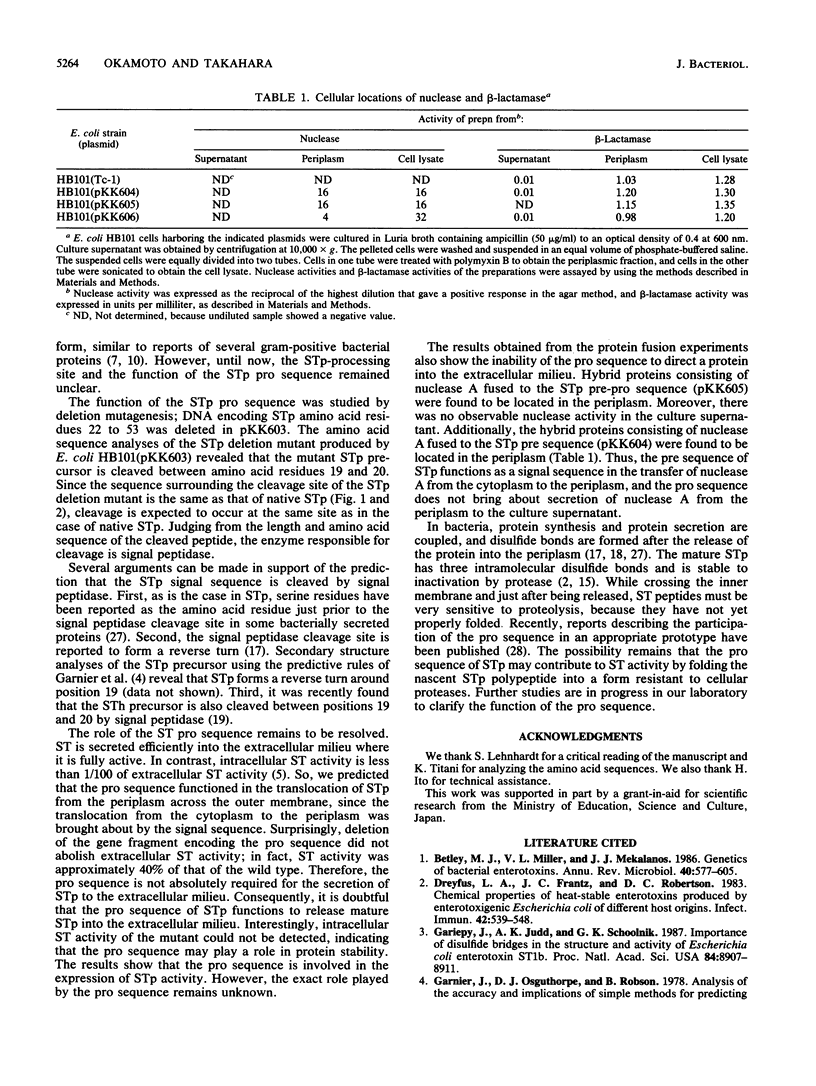
Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STp is presumed from its DNA sequence to be synthesized in vivo as a 72-amino-acid residue precursor that is cleaved to generate mature STp consisting of the 18 carboxy-terminal amino acid residues. There are two methionine residues in the inferred STp sequence in addition to the methionine residue at position 1. In order to confirm production of the STp 72-amino-acid residue precursor, we substituted the additional methionine residues by oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis. Since these substitutions did not cause a significant change in STp production, it can be concluded that STp is normally synthesized as the 72-amino-acid residue precursor. The length of the STp precursor indicated the existence of a pro sequence between the signal peptide and the mature protein. In order to identify the pro sequence and determine its role in protein secretion, deletion and fusion proteins were made. A deletion mutant in which the gene fragment encoding amino acid residues 22 to 53 of STp was removed was made. STp activity was found in the culture supernatant of cells. Amino acid sequence analysis of the purified STp deletion mutant revealed that the pro sequence encompasses amino acid residues 20 to 54. A hybrid protein consisting of STp amino acids 1 to 53 fused in frame from residue 53 to nuclease A was not secreted into the culture supernatant. These results indicate that the pro sequence does not function to guide periplasmic protein into the extracellular milieu.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betley M. J., Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Genetics of bacterial enterotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:577–605. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariépy J., Judd A. K., Schoolnik G. K. Importance of disulfide bridges in the structure and activity of Escherichia coli enterotoxin ST1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8907–8911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Rectification of two Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin allele sequences and lack of biological effect of changing the carboxy-terminal tyrosine to histidine. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.645-648.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán-Verduzco L. M., Fonseca R., Kupersztoch-Portnoy Y. M. Thermoactivation of a periplasmic heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):146–151. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.146-151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Takagi H., Inouye M. Requirement of pro-sequence for the production of active subtilisin E in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7859–7864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnhardt S., Pollitt S., Inouye M. The differential effect on two hybrid proteins of deletion mutations within the hydrophobic region of the Escherichia coli OmpA signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1716–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Yukitake J., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A. Substitutions of cysteine residues of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2121–2125. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2121-2125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Yukitake J., Miyama A. Reduction of enterotoxic activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by substitution for an asparagine residue. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2144–2148. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2144-2148.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Zalkin H. Role of primary structure and disulfide bond formation in beta-lactamase secretion. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Guzmán-Verduzco L. M., Kupersztoch Y. M. Two precursors of the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: evidence of extracellular processing. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):265–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Takahashi I., Yamagishi S. Iodometric assay method for beta-lactamase with various beta-lactam antibiotics as substrates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):910–913. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonishi Y., Hidaka Y., Koizumi M., Hane M., Aimoto S., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Mode of disulfide bond formation of a heat-stable enterotoxin (STh) produced by a human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. A genetic system for analysis of staphylococcal nuclease. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieglitz H., Cervantes L., Robledo R., Fonseca R., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F., Kupersztoch Y. M. Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Ficoll-generated minicells of an Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin gene. Plasmid. 1988 Jul;20(1):42–53. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara M., Hibler D. W., Barr P. J., Gerlt J. A., Inouye M. The ompA signal peptide directed secretion of Staphylococcal nuclease A by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2670–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Hitouji T., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin isolated from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 18D. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Ohta Y., Jordan F., Inouye M. Pro-sequence of subtilisin can guide the refolding of denatured subtilisin in an intermolecular process. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):483–484. doi: 10.1038/339483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]