Abstract
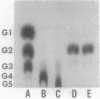
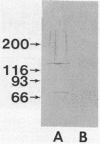
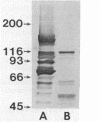
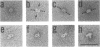
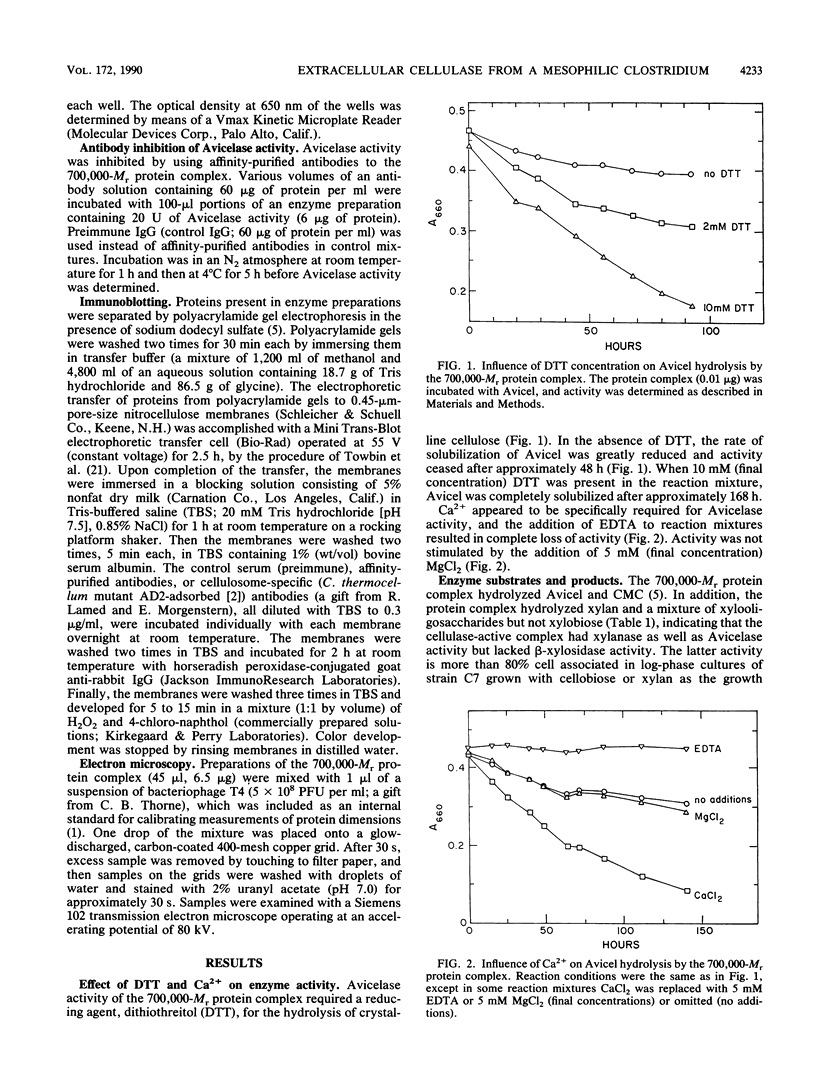
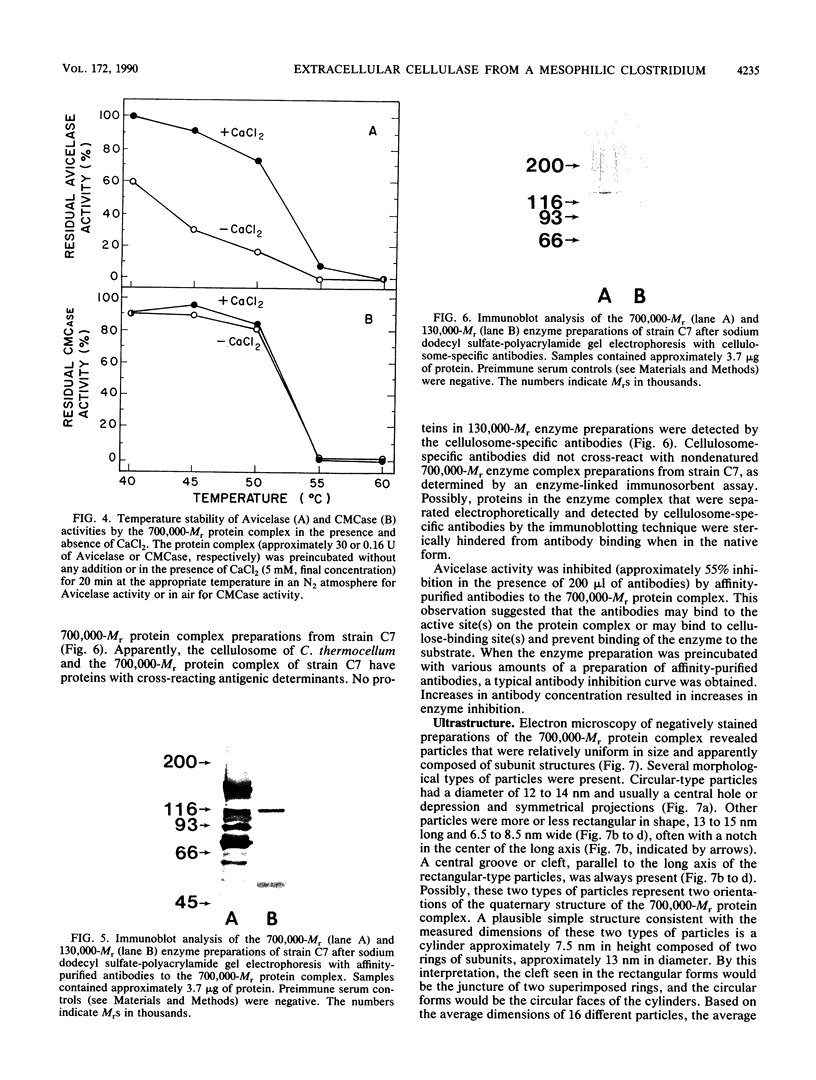
An extracellular, 700,000-Mr multiprotein complex that catalyzed the hydrolysis of crystalline cellulose (Avicel) was isolated from cultures of Clostridium sp. strain C7, a mesophile from freshwater sediment. In addition to cellulose (Avicel, ball-milled filter paper), the multiprotein complex hydrolyzed carboxymethylcellulose, cellodextrins, xylan, and xylooligosaccharides. Hydrolysis of cellulose or cellotetraose by the complex yielded cellobiose as the main product. Cellopentaose or cellohexaose was hydrolyzed by the complex to cellotriose or cellotetraose, respectively, in addition to cellobiose. Xylobiose was the main product of xylan hydrolysis, and xylobiose and xylotriose were the major products of xylooligosaccharide hydrolysis. Activity (Avicelase) resulting in hydrolysis of crystalline cellulose required Ca2+ and a reducing agent. The multiprotein complex had temperature optima for Avicelase, carboxymethylcellulase, and xylanase activities at 45, 55, and 55 degrees C, respectively, and pH optima at 5.6 to 5.8, 5.5, and 6.55, respectively. Electron microscopy of the 700,000-Mr enzyme complex revealed particles relatively uniform in size (12 to 15 nm wide) and apparently composed of subunit structures. Elution of strain C7 concentrated culture fluid from Sephacryl S-300 columns yielded an A280 peak in the 130,000-Mr region. Pooled fractions from the 130,000-Mr peak had carboxymethylcellulase activity but lacked Avicelase activity. Except for the inability to hydrolyze cellulose, the 130,000-Mr preparation had a substrate specificity identical to that of the 700,000-Mr protein complex. A comparison by immunoblotting techniques of proteins in the 130,000- and 700,000-Mr preparations, indicated that the two enzyme preparations had cross-reacting antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann H. W. La classification des phages caudés des entérobactéries. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1976 May;24(5):359–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Kenig R., Lamed R. Adherence of Clostridium thermocellum to cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):818–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.818-827.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bounias M. N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride as a new reagent for nanomole quantification of sugars on thin-layer plates by a mathematical calibration process. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavedon K., Leschine S. B., Canale-Parola E. Cellulase system of a free-living, mesophilic clostridium (strain C7). J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4222–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4222-4230.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan M. P., Hon-Nami K., Hon-Nami H., Ljungdahl L. G., Paulin J. J., Rigsby W. E. The cellulolytic enzyme complex of Clostridium thermocellum is very large. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):904–909. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grépinet O., Chebrou M. C., Béguin P. Purification of Clostridium thermocellum xylanase Z expressed in Escherichia coli and identification of the corresponding product in the culture medium of C. thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4576–4581. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4576-4581.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamed R., Setter E., Bayer E. A. Characterization of a cellulose-binding, cellulase-containing complex in Clostridium thermocellum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.828-836.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Forsberg C. W., Rattray J. B. Purification and Characterization of Two Endoxylanases from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):644–650. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.644-650.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leschine S. B., Canale-Parola E. Mesophilic cellulolytic clostridia from freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):728–737. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.728-737.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie C. R., Bilous D., Patel G. B. Studies on Cellulose Hydrolysis by Acetivibrio cellulolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):243–248. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.243-248.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer F., Coughlan M. P., Mori Y., Ljungdahl L. G. Macromolecular Organization of the Cellulolytic Enzyme Complex of Clostridium thermocellum as Revealed by Electron Microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2785–2792. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2785-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno J. D., Bayer R. The limits of the ledger in public health promotion. Hastings Cent Rep. 1985 Dec;15(6):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. E., Bauchop T., Gregg K. The isolation and comparison of cellulase genes from two strains of Ruminococcus albus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):921–930. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]