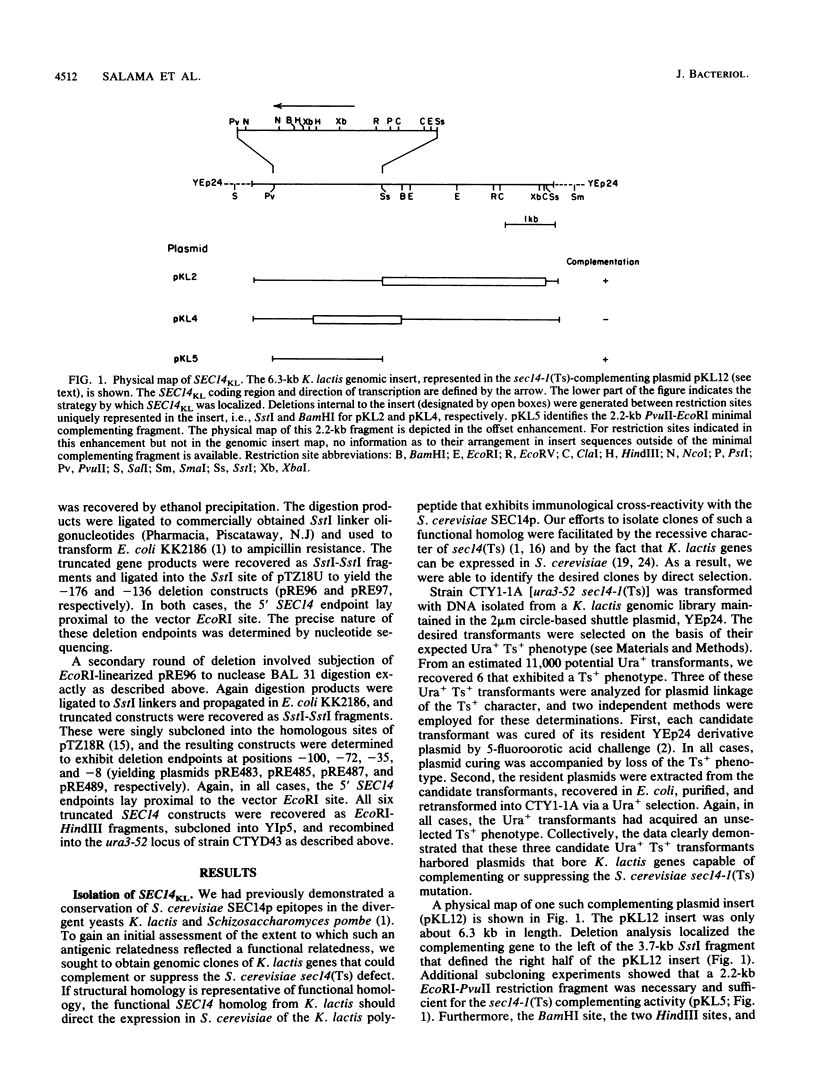
Abstract
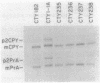
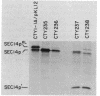
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC14 gene encodes a cytosolic factor that is required for secretory protein movement from the Golgi complex. That some conservation of SEC14p function may exist was initially suggested by experiments that revealed immunoreactive polypeptides in cell extracts of the divergent yeasts Kluyveromyces lactis and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. We have cloned and characterized the K. lactis SEC14 gene (SEC14KL). Immunoprecipitation experiments indicated that SEC14KL encoded the K. lactis structural homolog of SEC14p. In agreement with those results, nucleotide sequence analysis of SEC14KL revealed a gene product of 301 residues (Mr, 34,615) and 77% identity to SEC14p. Moreover, a single ectopic copy of SEC14KL was sufficient to render S. cerevisiae sec14-1(Ts) mutants, or otherwise inviable sec14-129::HIS3 mutant strains, completely proficient for secretory pathway function by the criteria of growth, invertase secretion, and kinetics of vacuolar protein localization. This efficient complementation of sec14-129::HIS3 was observed to occur when the rates of SEC14pKL and SEC14p synthesis were reduced by a factor of 7 to 10 with respect to the wild-type rate of SEC14p synthesis. Taken together, these data provide evidence that the high level of structural conservation between SEC14p and SEC14pKL reflects a functional identity between these polypeptides as well. On the basis of the SEC14p and SEC14pKL primary sequence homology to the human retinaldehyde-binding protein, we suggest that the general function of these SEC14p species may be to regulate the delivery of a hydrophobic ligand to Golgi membranes so that biosynthetic secretory traffic can be supported.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankaitis V. A., Malehorn D. E., Emr S. D., Greene R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC14 gene encodes a cytosolic factor that is required for transport of secretory proteins from the yeast Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1271–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover W. H., Ryan J. P., Bassford P. J., Jr, Walsh K. A., Bollinger J., Randall L. L. Suppression of a signal sequence mutation by an amino acid substitution in the mature portion of the maltose-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1794–1800. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1794-1800.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Goldflam S., Harris S. E., Saari J. C. Cloning of the cDNAs encoding the cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein from bovine and human retina and comparison of the protein structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18688–18692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshler J. O., Larson G. P., Rossi J. J. Kluyveromyces lactis maintains Saccharomyces cerevisiae intron-encoded splicing signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2208–2213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Riley M. I. The lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis. Biotechnology. 1989;13:19–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Pfeffer S. R., Clary D. O., Wattenberg B. W., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Yeast and mammals utilize similar cytosolic components to drive protein transport through the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Vassarotti A., Garrett J., Geller B. L., Takeda M., Douglas M. G. The amino terminus of the yeast F1-ATPase beta-subunit precursor functions as a mitochondrial import signal. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):523–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a look at yeasts divided. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):781–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmeron J. M., Jr, Johnston S. A. Analysis of the Kluyveromyces lactis positive regulatory gene LAC9 reveals functional homology to, but sequence divergence from, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7767–7781. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer I., Emr S., Gross C., Schekman R. Invertase signal and mature sequence substitutions that delay intercompartmental transport of active enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1664–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreekrishna K., Dickson R. C. Construction of strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that grow on lactose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7909–7913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford C. A., Daniels L. B., Park F. J., Jones E. W., Van Arsdell J. N., Innis M. A. The PEP4 gene encodes an aspartyl protease implicated in the posttranslational regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2500–2510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]