Abstract
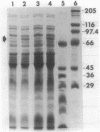
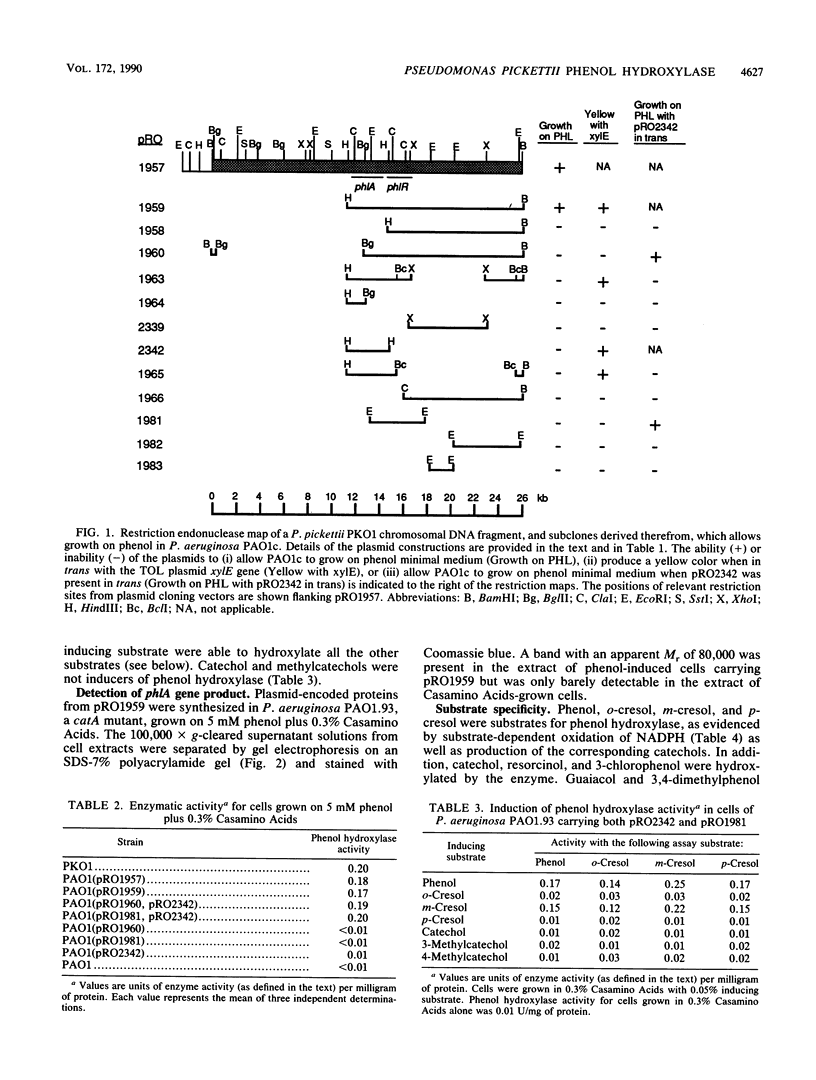
A 26-kilobase BamHI restriction endonuclease DNA fragment was cloned from Pseudomonas pickettii PKO1, a strain isolated from a soil microcosm that had been amended with benzene, toluene, and xylene. This DNA fragment, cloned into vector plasmid pRO1727 and designated pRO1957, allowed Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1c to grow on phenol as the sole source of carbon. Physical and functional restriction endonuclease maps have been derived for the cloned DNA fragment. Two DNA fragments carried in trans and derived from subclones of pRO1957 show phenol hydroxylase activity in cell extracts of P. aeruginosa. Deletion and subcloning analyses of these fragments indicated that the gene encoding phenol hydroxylase is positively regulated. Phenol and m-cresol were shown to be inducers of the enzyme. o-Cresol and p-cresol did not induce enzymatic activity but could be metabolized by cells that had been previously exposed to phenol or m-cresol; moreover, the enzyme exhibited a rather broad substrate specificity and was sensitive to thiol-inhibiting reagents. A novel polypeptide with an estimated molecular mass of 80,000 daltons was detected in extracts of phenol-induced cells of P. aeruginosa carrying plasmid pRO1959.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Wigmore G. J. Metabolism of phenol and cresols by mutants of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1112–1120. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1112-1120.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beadle C. A., Smith A. R. The purification and properties of 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase from a strain of Acinetobacter species. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuskey S. M., Peccoraro V., Olsen R. H. Initial catabolism of aromatic biogenic amines by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO: pathway description, mapping of mutations, and cloning of essential genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2398–2404. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2398-2404.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuskey S. M., Wolff J. A., Phibbs P. V., Jr, Olsen R. H. Cloning of genes specifying carbohydrate catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):865–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.865-871.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist C. F., Hegeman G. D. Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.869-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal A., Neujahr H. Y. Induction of phenol-metabolizing enzymes in Trichosporon cutaneum. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Sep;130(1):54–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00527072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal A., Neujahr H. Y. Metabolism of phenol and resorcinol in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.13-21.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groseclose E. E., Ribbons D. W., Hughes H. 3-Hydroxybenzoate 6-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurujeyalakshmi G., Oriel P. Isolation of phenol-degrading Bacillus stearothermophilus and partial characterization of the phenol hydroxylase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):500–502. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.500-502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa K., Stanier R. Y. Crystallization and properties of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase from Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2453–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. J., Bayly R. C. Control of catechol meta-cleavage pathway in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1363–1370. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1363-1370.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Molecular cloning of TOL genes xylB and xylE in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1137–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1137-1143.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaar M. A., Habicht J. K., Heinaru A. L. Degradation of phenol and m-toluate in Pseudomonas sp. strain EST1001 and its Pseudomonas putida transconjugants is determined by a multiplasmid system. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5111–5116. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5111-5116.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukor J. J., Olsen R. H., Ballou D. P. Cloning and expression of the catA and catBC gene clusters from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4458–4465. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4458-4465.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukor J. J., Olsen R. H., Siak J. S. Recruitment of a chromosomally encoded maleylacetate reductase for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3385–3390. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3385-3390.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T., Chapman P. J. Purification and properties of a plasmid-encoded 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalover J. L., Ribbons D. W., Hughes H. 3-Hydroxybenzoate 4-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):888–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neujahr H. Y., Gaal A. Phenol hydroxylase from yeast. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Trichosporon cutaneum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):386–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neujahr H. Y., Lindsjö S., Varga J. M. Oxidation of phenols by cells and cell-free enzymes from Candida tropicalis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(2):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00394378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., DeBusscher G., McCombie W. R. Development of broad-host-range vectors and gene banks: self-cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.60-69.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Hansen J. Evolution and utility of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa drug resistance factor. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):837–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.837-844.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Franklin F. C., Tsuda M., Holroyd D., Bagdasarian M. Molecular analysis of a plasmid-encoded phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas CF600. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White-Stevens R. H., Kamin H. Studies of a flavoprotein, salicylate hydroxylase. I. Preparation, properties, and the uncoupling of oxygen reduction from hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2358–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., Olsen R. H., Ballou D. P. Cloning, expression, and regulation of the Pseudomonas cepacia protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5907–5914. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5907-5914.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]