Abstract
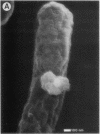
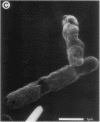
Biochemical and genetic studies have suggested that a transmembrane tunnel structure penetrating the inner and outer membranes is formed during the lytic action of bacteriophage phi X174 protein E. In this study we directly visualized the lysis tunnel by using high-magnification scanning and transmission electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF
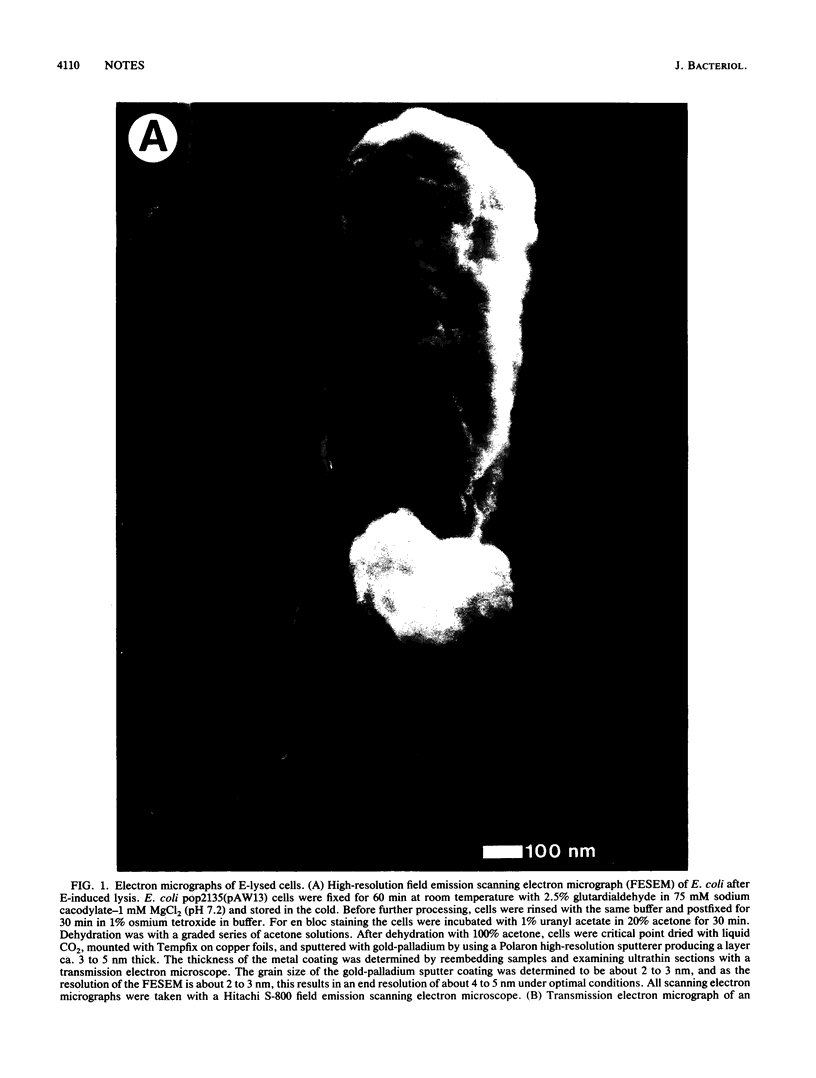




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman E., Young K., Garrett J., Altman R., Young R. Subcellular localization of lethal lysis proteins of bacteriophages lambda and phiX174. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1008-1011.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrell B. G., Air G. M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Overlapping genes in bacteriophage phiX174. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):34–41. doi: 10.1038/264034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., DeBlois R. W. Diffusion constant and dimension of bacteriophage phi X174 as determined by self-beat laser light spectroscopy and electron microscopy. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):975–980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.975-980.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Henrich B., Lubitz W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by cloned phi X174 gene E depends on its expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Linke R. P., Lubitz W. Evidence for membrane-bound oligomerization of bacteriophage phi X174 lysis protein-E. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4552–4558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Lubitz W. Influence of C-terminal modifications of phi X174 lysis gene E on its lysis-inducing properties. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1209–1213. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. J., Hayashi M. Lytic activity localized to membrane-spanning region of phi X174 E protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):120–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00330198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON C. A., SINSHEIMER R. L. KINETICS OF BACTERIOPHAGE RELEASE BY SINGLE CELLS OF PHI X174-INFECTED E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:206–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Lubitz W., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli by induction of cloned phi X174 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00334146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubitz W., Harkness R. E., Ishiguro E. E. Requirement for a functional host cell autolytic enzyme system for lysis of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage phi X174. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):385–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.385-387.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKERT A., ZILLIG W. STUDIES ON THE LYSIS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI C BY BACTERIOPHAGE PHI-X174. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:88–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratea D., Young K., Young R. Deletion and fusion analysis of the phage phi X174 lysis gene E. Gene. 1985;40(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Lubitz W., Bakker E. P. Proton-motive-force-dependent step in the pathway to lysis of Escherichia coli induced by bacteriophage phi X174 gene E product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1750–1752. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1750-1752.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Lubitz W. Biochemical characterization of phi X174-protein-E-mediated lysis of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Anderson R. J., Hafner R. J. Lysis of Escherichia coli by the bacteriophage phi X174 E protein: inhibition of lysis by heat shock proteins. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4334–4341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4334-4341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]