Abstract
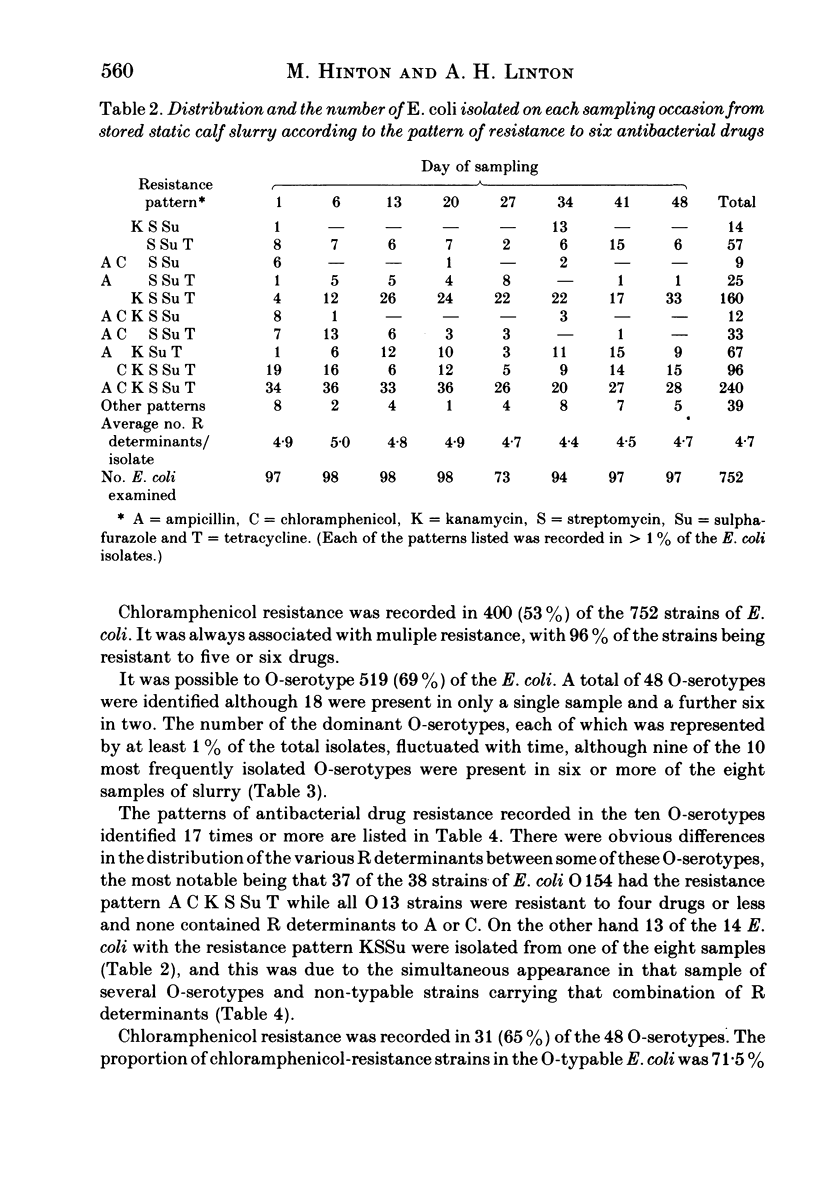
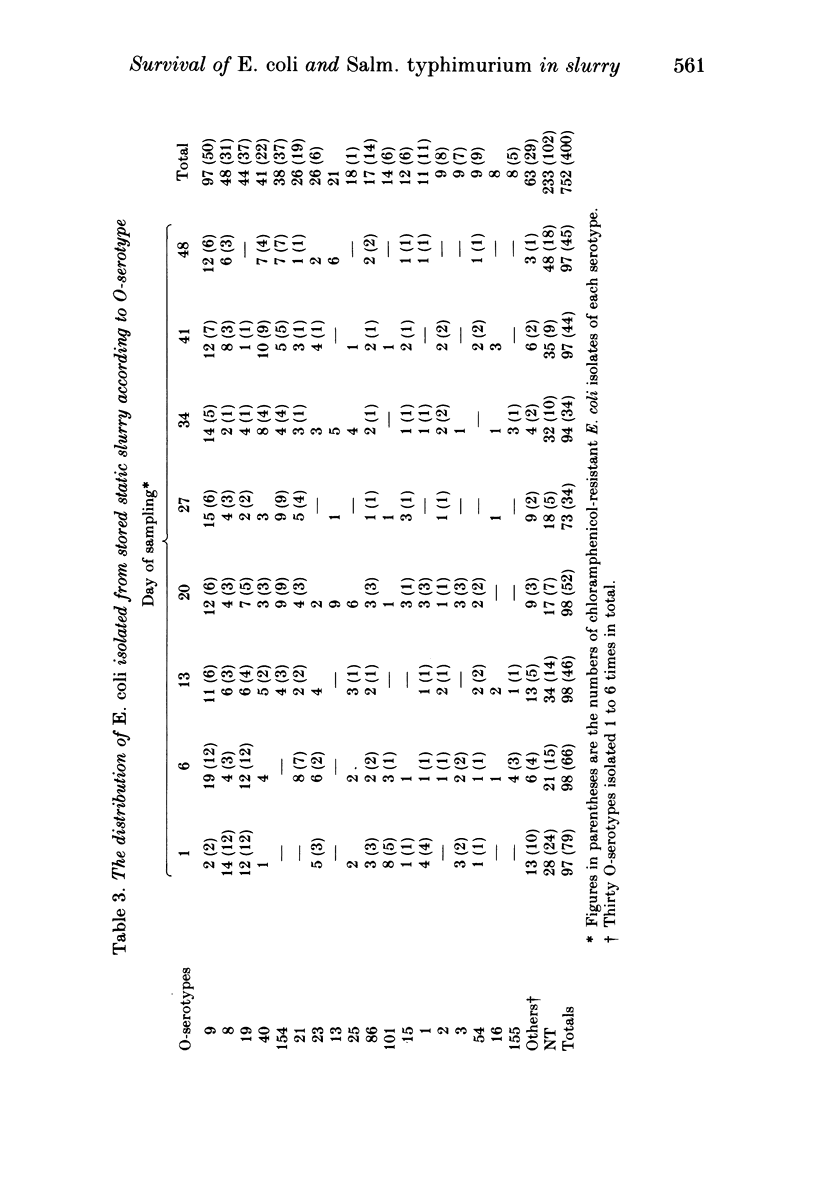
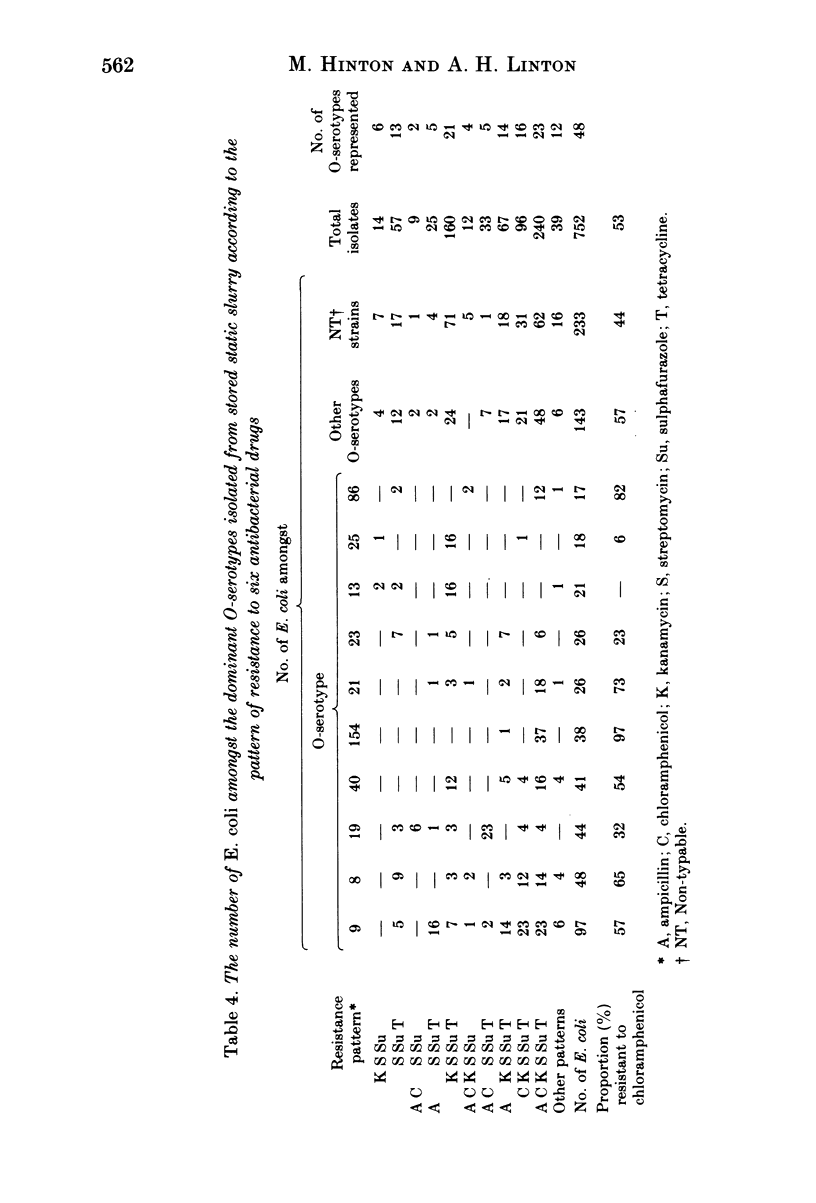
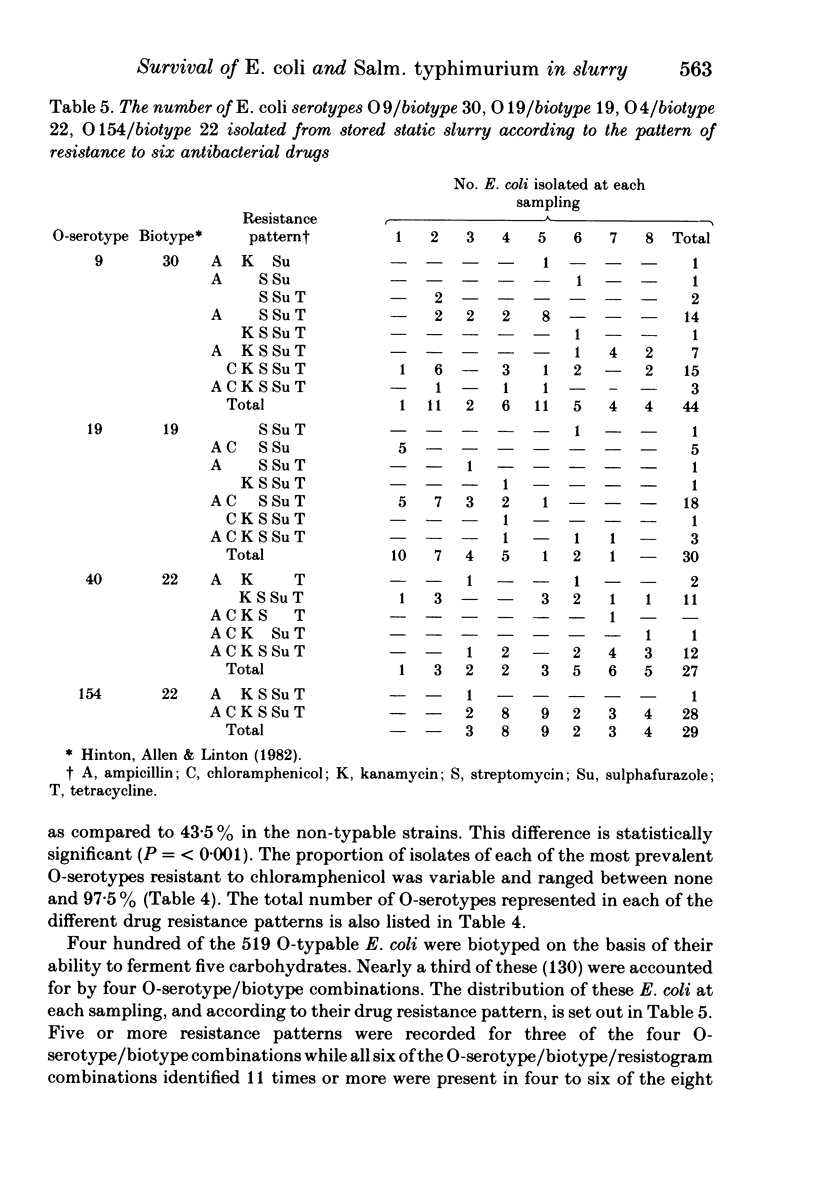
Salmonella typhimurium phage type DT 193 survived in small numbers, in stored static slurry derived from veal calves, for the 7-week period of observation. The viable coliform count fell by 1 1/2 logs during the first 2 weeks of storage, thereafter there were only relatively small fluctuations in the coliform population. In all 735 of 752 Escherichia coli isolates examined from eight samples of slurry were resistant to 3-6 antibacterial drugs. There was no dramatic change in the overall level of drug resistance amongst the E. coli with time. Chloramphenicol resistance was recorded in 400 (55%) of the E. coli. It was always associated with multiple resistance, with 96% of the strains being resistant to 5 or 6 drugs, although the proportion of isolates of each of the ten most prevalent O-serotypes resistant to chloramphenicol was variable and ranged between none and 97.5%. The use of biotyping together with O-serotyping indicated that the E. coli population was extremely complex, although certain components of the population remained relatively stable within the dominant flora with time since several of the more common O-serotype/biotype combinations were isolated from more than half of the eight slurry samples examined.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edel W., Kampelmacher E. H. Salmonella isolation in nine European laboratories using a standardized technique. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley C. L., Howe K., Linton A. H., Linton K. B., Richmond M. H. Distribution of R plasmids among the O-antigen types of Escherichia coli isolated from human and animal sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):122–131. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M., Allen V., Linton A. H. The biotyping of Escherichia coli isolated from healthy farm animals. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Jun;88(3):543–555. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K., Linton A. H. The distribution of O-antigen types of Escherichia coli in normal calves, compared with man, and their R plasmid carriage. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;40(3):317–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. W. Animal health today--problems of large livestock units. Disease hazards associated with slurry disposal. Br Vet J. 1980 Nov-Dec;136(6):529–542. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)32131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Osborne A. D. The effects of feeding tetracycline, nitrovin and quindoxin on the drug-resistance of coli-aerogenes bacteria from calves and pigs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;38(3):255–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Jennett N. E., Heard T. W. Multiplication of Salmonella in liquid feed and its influence on the duration of excretion in pigs. Res Vet Sci. 1970 Sep;11(5):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Timoney J. F., Hinton M. The ecology of chloramphenicol-resistance in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli in calves with endemic salmonella infection. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;50(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. J., Burrows M. R. The survival of Escherichia coli and Salmonella dublin in slurry on pasture and the infectivity of S. dublin for grazing calves. Br Vet J. 1971 Nov;127(11):536–543. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


