Abstract
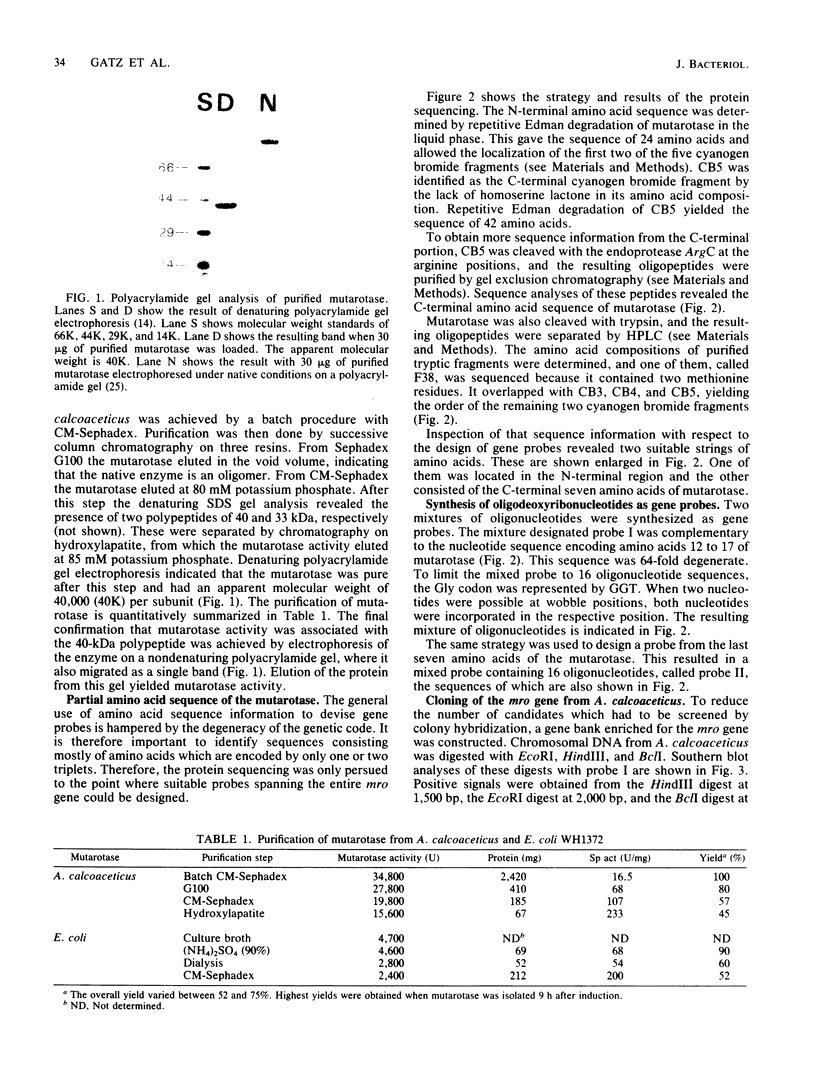
This article describes the cloning of the mutarotase gene from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and its expression in Escherichia coli. Purification of mutarotase (EC 5.1.3.3) led to a single polypeptide of 40 kilodaltons. The sequences of 27 N-terminal and 76 C-terminal amino acids were determined. From six amino acids of the N-terminal and seven amino acids of the C-terminal portion of the protein, the sequences of two oligonucleotides were deduced. These were synthesized and used as gene probes. Completely restricted chromosomal DNA from A. calcoaceticus was size fractioned, and only fractions hybridizing with the gene probes were used to construct gene banks enriched for the mutarotase determinant. With the N-terminal gene probe, a bank of 6- to 7-kilobase-pair BclI fragments in pBR327 was obtained. A total of 1,200 candidates were screened by colony hybridization followed by dot-blot analysis of purified plasmids from positive candidates and subsequent Southern blot analysis of the respective restricted plasmids, and 500 base pairs (bp) from the 5' end of the mutarotase gene were isolated by this procedure. The 3' portion of the gene was isolated from a gene bank containing 1,500-bp-long HindIII fragments inserted in M13mp11. This bank was screened by dot-blot analysis of single-stranded phage DNA with the C-terminal gene probe. The isolated gene fragments were fused at a common restriction site in their overlapping region to yield the complete mutarotase gene. High-level expression of mutarotase in E. coli was achieved when the gene was placed under transcriptional control of the phage lambda promoter pL. More than 90% of mutarotase activity was found in the culture medium. The E. coli-derived mutarotase was purified and shown to be identical to the A. calcoaceticus-derived product with respect to the molecular weight and N-terminal amino acid sequence. The expression of mutarotase in E. coli was increased 200-fold in comparison to that the wild-type A. calcoaceticus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAILEY J. M., PENTCHEV P. G., WOO J. DISTRIBUTION OF A "MUTAROTASE" ACTIVITY IN RAT TISSUES AND POSSIBLE FUNCTION IN ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SUGARS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 25;94:124–129. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banauch D., Brümmer W., Ebeling W., Metz H., Rindfrey H., Lang H., Leybold K., Rick W., Staudinger H. J. Eine Glucose-Dehydrogenase für die Glucose-Bestimmung in Körperflüssigkeiten. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1975 Mar;13(3):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Remaut E., Hershfield M. V., Das H. K., Helinski D. R., Yanofsky C., Franklin N. Construction of plasmid cloning vehicles that promote gene expression from the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1979 Jan;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillen W., Klock G., Kaffenberger I., Wray L. V., Reznikoff W. S. Purification of the TET repressor and TET operator from the transposon Tn10 and characterization of their interaction. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6605–6613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEILIN D., HARTREE E. F. Biological catalysis of mutarotation of glucose. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):341–348. doi: 10.1042/bj0500341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Keighren M. A., Kinsey J. A., Eaton M., Fincham J. R. Cloning of the am (glutamate dehydrogenase) gene of Neurospora crassa through the use of a synthetic DNA probe. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Immunoenzymatic detection of expressed gene fragments cloned in the lac Z gene of E. coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):509–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa I. Rapid polarographic mutarotase assay with -D-glucose oxidase. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa I., Toyoda Y., Okuda J. Purification and properties of hog kidney mutarotase. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1981 Jun;29(6):1702–1707. doi: 10.1248/cpb.29.1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulhern S. A., Fishman P. H., Kusiak J. W., Bailey J. M. Physical characteristics and chemi-osmotic transformations of mutarotases from various species. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4163–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda J., Miwa I., Maeda K., Tokui K. Rapid and sensitive, colorimetric determination of the anomers of D-glucose with D-glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and mutarotase. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Oct;58(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda J., Miwa I. Mutarotase effect on micro determinations of D-glucose and its anomers with -D-glucose oxidase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Sep;43(1):312–315. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda J., Miwa I., Toyoda Y. Multiple forms of rat kidney mutarotase. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1976 Nov;24(11):2893–2895. doi: 10.1248/cpb.24.2893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salnikow J., Lehmann A., Wittmann-Liebold B. Improved automated solid-phase microsequencing of peptides using DABITC. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90803-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammler P., Ehwald R., Göring H. Mutarotase in galactose-induced baker's yeast. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1974;19(6):479–488. doi: 10.1007/BF02872913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W., Goebel W. Synthesis and secretion of hemolysin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):53–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.53-59.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G., Buse G. Studien an Cytochrom-c-Oxidase, I. Reinigung und Charakterisierung des Enzyms aus Rinderherzen und Identifizierung der im Komplex enthaltenen Peptidketten. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Aug;357(8):1125–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda Y., Miwa I., Okuda J. Affinity purification, crystallization, and amino acid analysis of hog kidney mutarotase type II. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982 Aug;30(8):2880–2884. doi: 10.1248/cpb.30.2880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda Y., Miwa I., Okuda J. Multiple forms of mutarotases from the kidney, liver, and small intestine of rats: purification, properties, subcellular localization and developmental changes. J Biochem. 1983 Aug;94(2):421–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]