Abstract
One hundred and nineteen volunteers were divided into five groups, and each volunteer inoculated subcutaneously with an aqueous subunit B/Hong Kong/73 vaccine containing 40, 20, 10, or 5 micrograms of HA or saline alone in a 0.5 ml volume. The incidence of reactions was recorded 24 h after inoculation. One month following immunization the serum HI antibody to B/Hong Kong/73 virus was measured; each volunteer was inoculated intranasally with live, attenuated influenza B (RB77) virus; and the incidence of infection by the challenge virus was determined by HI antibody response. The results showed that the incidence of reactions to all doses of vaccine were relatively low, the severity mild, and the duration short. However, the incidence of reactions was highest for those given 40 micrograms HA and least for those given 5 micrograms HA. The serum HI antibody responses to vaccine showed a dose-response relationship. For volunteers given 40 micrograms HA, 22 (96%) showed a fourfold rise in antibody titre and all volunteers had antibody titres of greater than 40 following immunization: for volunteers given 5 micrograms HA the g.m.t. increased from 16.6 to 86.1; and for those given 10 and 20 micrograms HA the response was intermediate. Following challenge, the lowest incidence of infection was seen in volunteers given the highest dose of vaccine. However, all doses of vaccine induced some protection against challenge virus infection, and the incidence of infection was directly related to the serum antibody titre at the time of challenge. The 50% protection titre of serum HI antibody was estimated as 15 to 20.
Full text
PDF

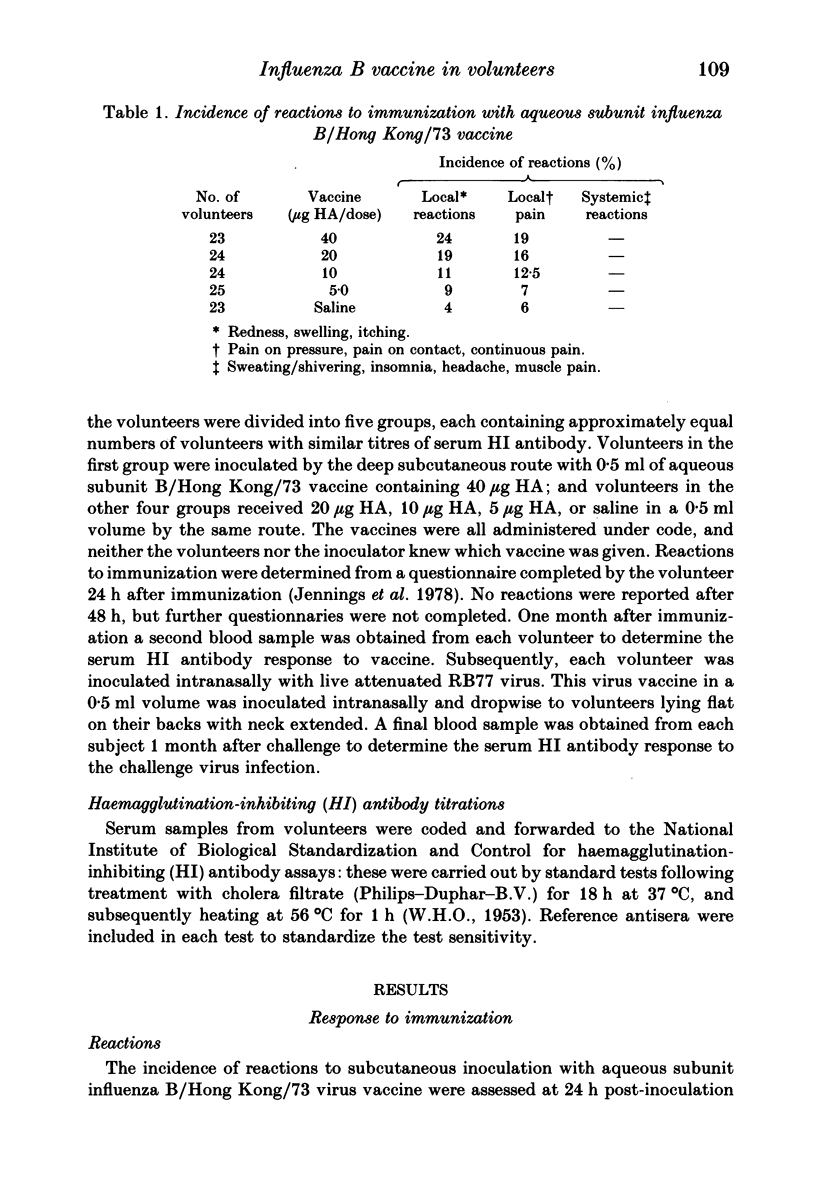
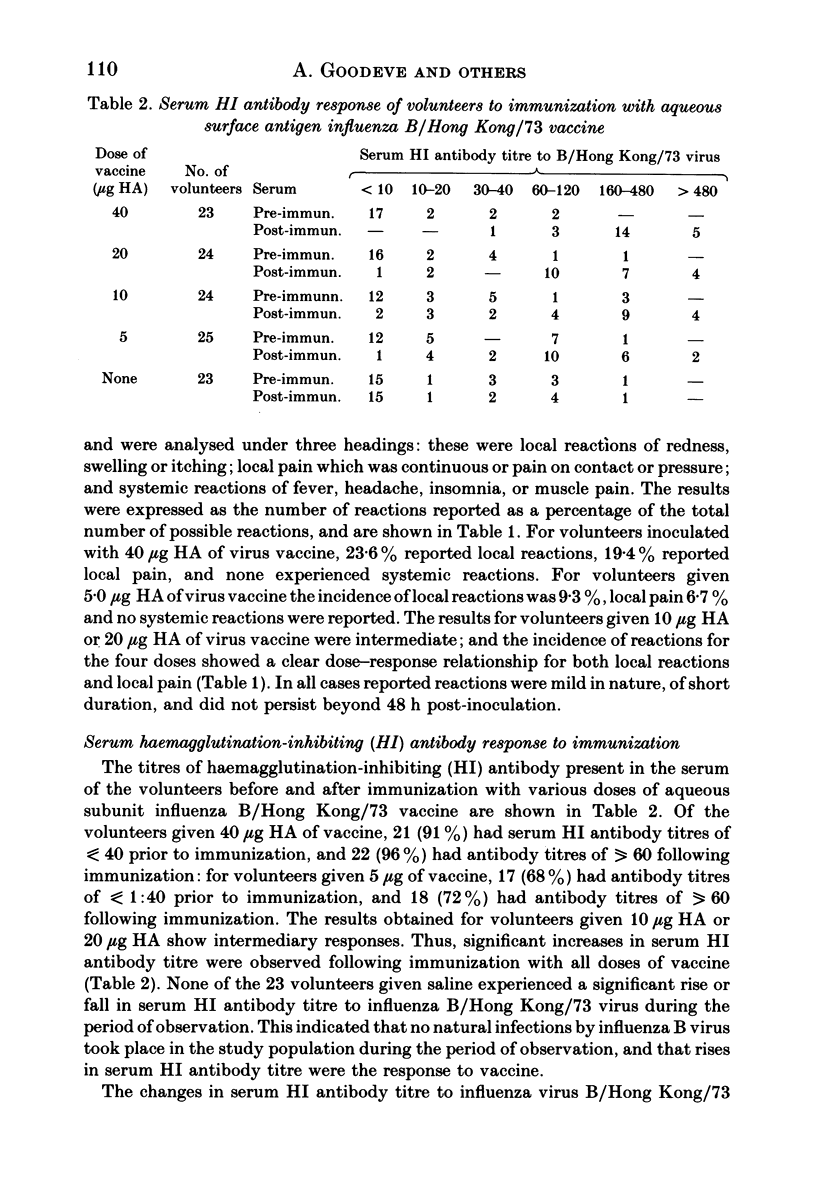
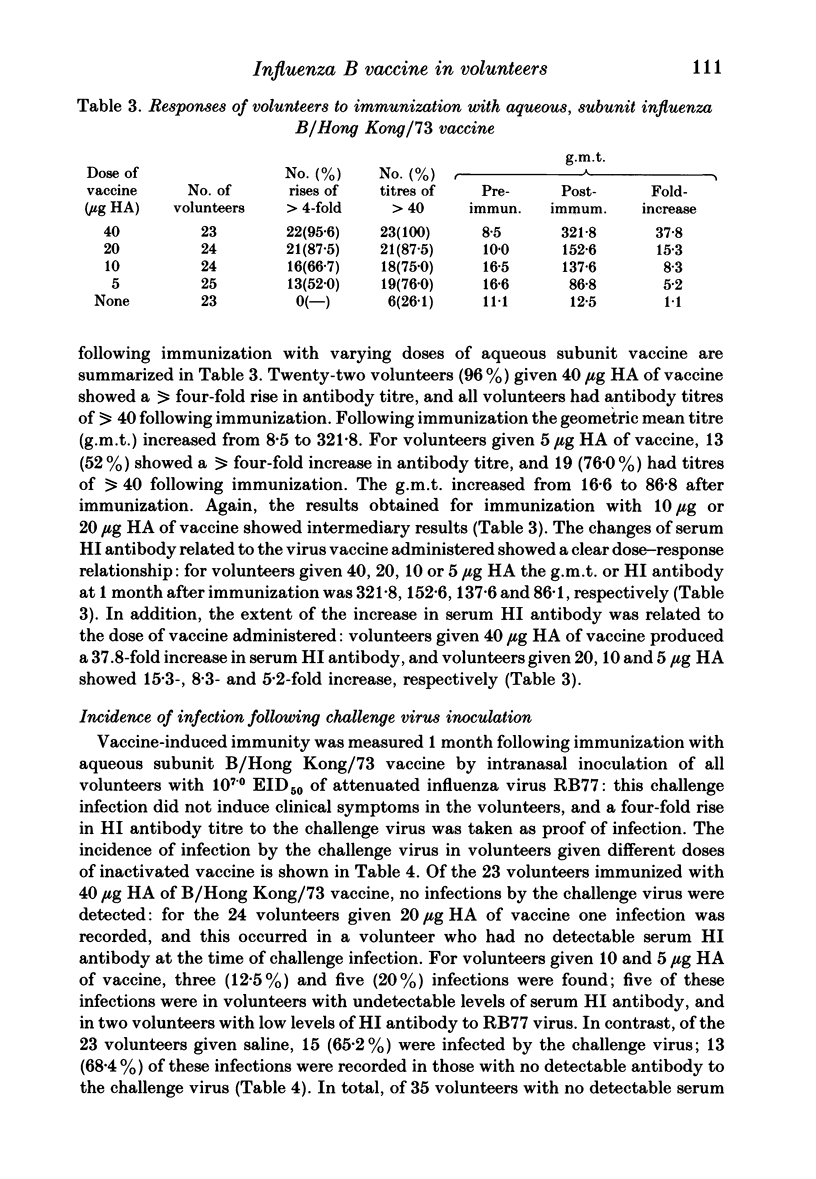

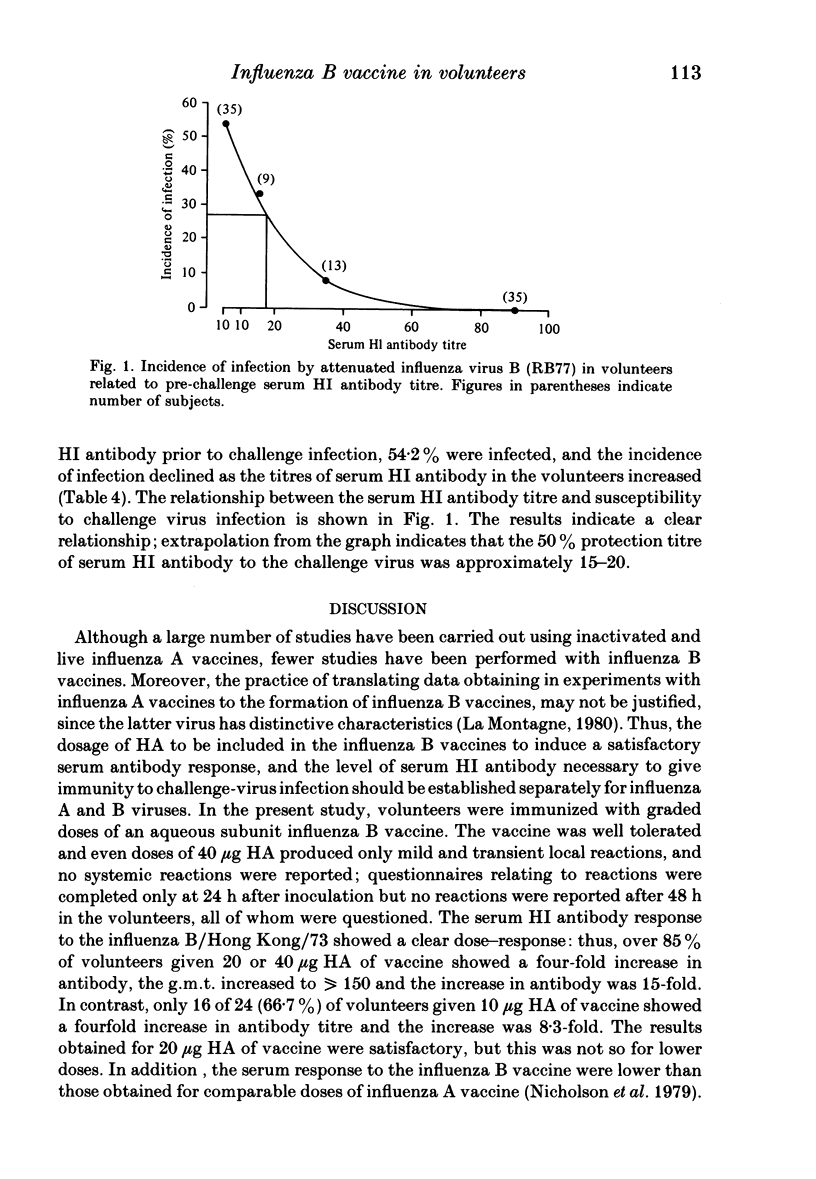


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmayer H. Selective solubilization of hemagglutinin and neuraminidase from influenza viruses. Intervirology. 1975;5(5):260–272. doi: 10.1159/000149923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings R., Clark A., Oxford J. S., Hockley D. J., Potter C. W. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of whole and ether-Tween-split influenza A virus vaccines in volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):577–586. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMontagne J. R. From the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: summary of a workshop on influenza B viruses and Reye's syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):452–465. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIKLEJOHN G., KEMPE C. H., THALMAN W. G., LENNETTE E. H. Evaluation of monovalent influenza vaccines. II. Observations during an influenza a-prime epidemic. Am J Hyg. 1952 Jan;55(1):12–21. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson K. G., Tyrrell D. A., Harrison P., Potter C. W., Jennings R., Clark A., Schild G. C., Wood J. M., Yetts R., Seagroatt V. Clinical studies of monovalent inactivated whole virus and subunit A/USSR/77 (H1N1) vaccine: serological responses and clinical reactions. J Biol Stand. 1979 Apr;7(2):123–136. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(79)80044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford J. S., Yetts R., Schild G. C. Quantitation and analysis of the specificity of post-immunization antibodies to influenza B viruses using single radial haemolysis. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):325–333. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., Jennings R., Nicholson K., Tyrrell D. A., Dickinson K. G. Immunity to attenuated influenza virus WRL 105 infection induced by heterologous, inactivated influenza A virus vaccines. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):321–332. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., Oxford J. S. Determinants of immunity to influenza infection in man. Br Med Bull. 1979 Jan;35(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Wood J. M., Newman R. W. A single-radial-immunodiffusion technique for the assay of influenza haemagglutinin antigen. Proposals for an assay method for the haemagglutinin content of influenza vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(2):223–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. M., Schild G. C., Newman R. W., Seagroatt V. An improved single-radial-immunodiffusion technique for the assay of influenza haemagglutinin antigen: application for potency determinations of inactivated whole virus and subunit vaccines. J Biol Stand. 1977;5(3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(77)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


