Abstract
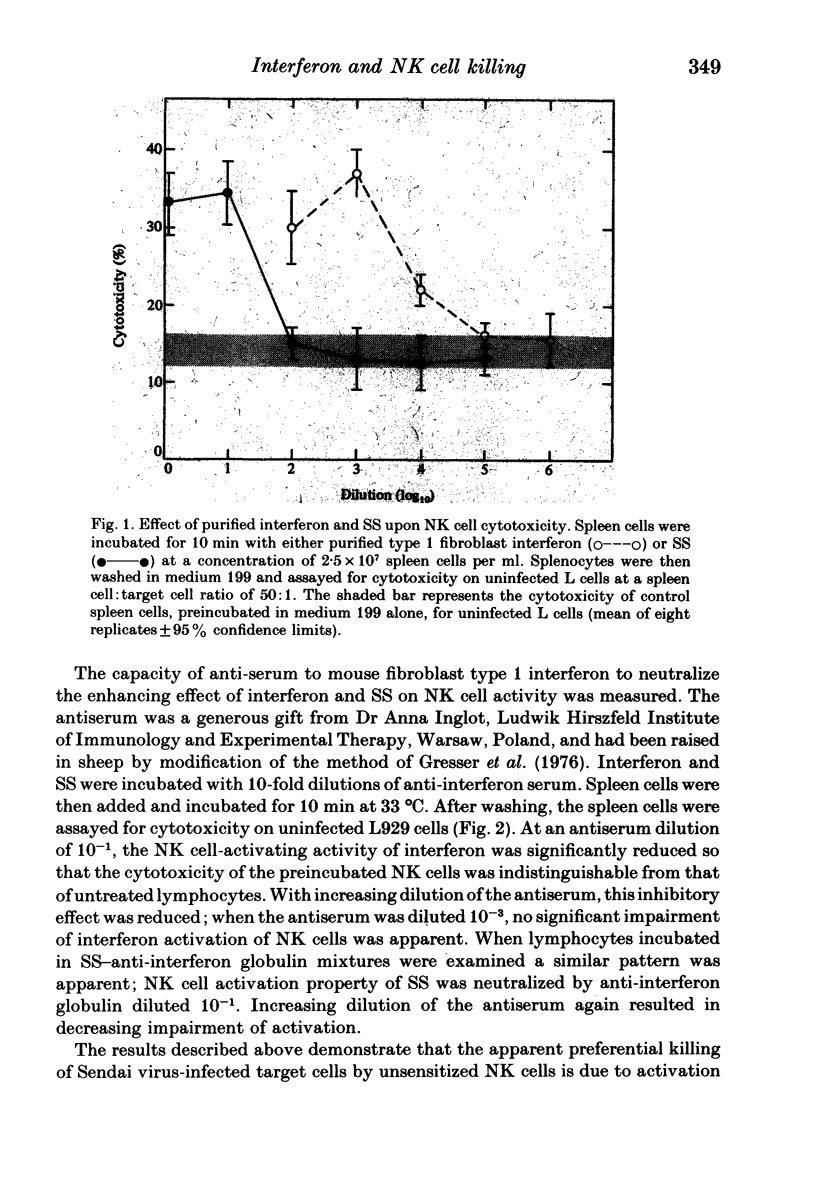
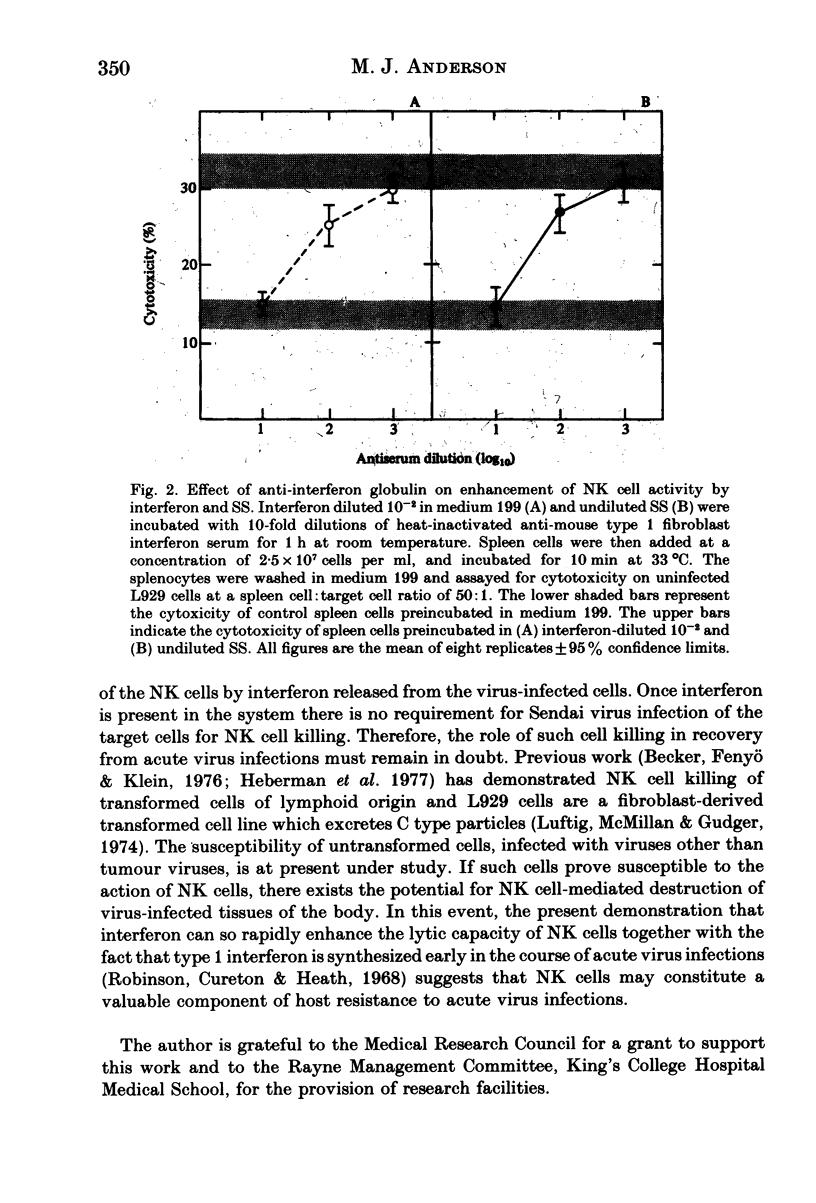
Spleen cells from uninfected CBA mice are more cytotoxic for Sendai virus-infected L929 cells than for uninfected cells and the lymphocytes responsible have the properties of NK cells. Preincubation of spleen cells with culture supernatants from Sendai virus-infected L929 cells increases the cytotoxicity for uninfected target cells. This increase in cytotoxicity can also be produced by pretreatment with purified mouse interferon. The enhancing effect of both the infected culture supernatants and purified interferon can be neutralized with anti-interferon serum. It is concluded that the preferential killing of Sendai virus-infected L929 cells by NK cells is dependent on the induction of interferon and that interferon will increase NK cell cytotoxicity for uninfected target cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Bainbridge D. R., Pattison J. R., Heath R. B. Cell-mediated immunity to Sendai virus infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.239-244.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J. Innate cytotoxicity of CBA mouse spleen cells to Sendai virus-infected L cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):608–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.608-612.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Johnston M. D., Westmacott L. M., Burke D. C. Department of Biological Sciences, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV47AL, England. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):381–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P., Knight D. Killing comes naturally. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):119–120. doi: 10.1038/278119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H., Senik A., Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):759–761. doi: 10.1038/273759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Staal S., Djeu J. Y. Augmentation of natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic target cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE S. H., OZERE R. L. PRODUCTION OF INTERFERON BY HUMAN MONONUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:190–195. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancz G. J., Johnson T. C. Temporal relationship between virus and interferon biosynthesis in L cells infected with Newcastle disease virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):266–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. B., McMillan P. N., Gudger M. Quantitation of endogenous C-type virion production in several murine cell lines. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):1017–1021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.1017-1021.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. W., Cureton R. J., Heath R. B. The pathogenesis of Sendai virus infection in the mouse lung. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):89–95. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Cytotoxic cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. I. Characterization of natural killer cell induction. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):163–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Mouse natural killer cells: induction specificity, and function. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


