Abstract
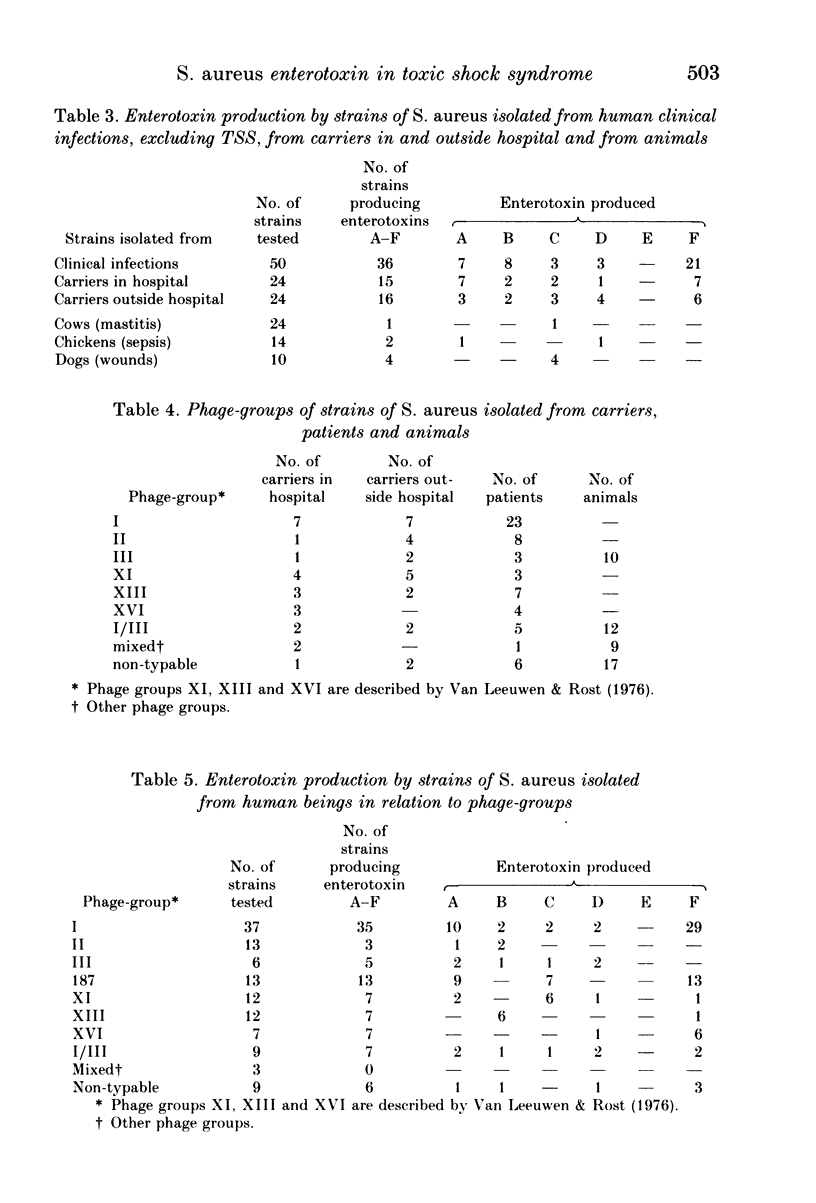
Enterotoxin production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical specimens of human and animal origin and from healthy human carriers was investigated. All nine patients admitted to hospital with symptoms of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) yielded enterotoxin-producing strains of S. aureus. Eight of these produced staphylococcal enterotoxin F (SEF). A significantly smaller proportion of strains (42% of 50 strains tested) isolated from other clinical specimens of hospitalized patients produced SEF. Production of SEF by strains isolated from clinical specimens of animal origin (48 strains) was not observed. Twenty-nine per cent of 24 S. aureus strains isolated from noses of hospital staff produced SEF. This result was not significantly different from that obtained from strains isolated from clinical specimens other than TSS. A similar percentage of strains isolated from healthy human carriers outside hospital produced SEF (25% of 24 strains tested). The results indicated that enterotoxin production, especially that of SEF, is associated with S. aureus isolated from patients suspected of TSS. There was no indication of an association between S. aureus isolated from other staphylococcal infections and SEF production. All strains were phage typed and 79% of the strains belonging to the international phage-group I produced SEF. All strains lysed by phage 187 were found to produce SEF.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird-Parker A. C. Symposium on microbial changes in foods. Factors affecting the production of bacterial food poisoning toxins. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;34(1):181–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückler J., Klima H., Schaeg W., Manz D., Blobel H. Staphylococcus aureus von Kühen mit subklinischen Euterinfektionen. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1981;28(6):494–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Issa J. A. Identification of a fourth staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1875–1882. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1875-1882.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. B., Leslie J. E., Black L. A., Lewis K. H. Serological identification of enterotoxigenic staphylococci from cheese. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1382–1387. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1382-1387.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieneke A. A. Enterotoxin production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from foods and human beings. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Oct;73(2):255–262. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


