Abstract
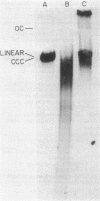
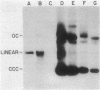
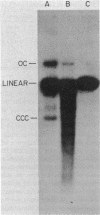
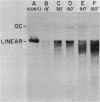
We examined the fate of plasmid DNA after uptake during transformation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. An 11.5-kilobase plasmid, pFA10, was processed to linear double-stranded DNA during uptake by competent cells, but cleavage of pFA10 was not site specific. A minority of pFA10 entered as open circles. A 42-kilobase plasmid, pFA14, was degraded into small fragments during uptake; no intracellular circular forms of pFA14 were evident. Since pFA10 DNA linearized by a restriction enzyme was not further cut during uptake, the endonucleolytic activity associated with entry of plasmid DNA appeared to act preferentially on circular DNA. Although linear plasmid DNA was taken up into a DNase-resistant state as efficiently as circular DNA, linear plasmid DNA transformed much less efficiently than circular plasmid DNA. These data suggest that during entry transforming plasmid DNA often is processed to double-stranded linear molecules; transformants may arise when some molecules are repaired to form circles. Occasional molecules which enter as intact circles may also lead to transformants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Bendler J. W., Setlow J. K. Plasmid transformation in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1099-1101.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barany F., Kahn M. E., Smith H. O. Directional transport and integration of donor DNA in Haemophilus influenzae transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G. D., Graves J. F., Sox T. E., Tenover F. C., Sparling P. F. Marker rescue by a homologous recipient plasmid during transformation of gonococci by a hybrid Pcr plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):77–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.77-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G. D., Sparling P. F. Entry of double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid during transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):638–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.638-640.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy S., Mann C., Davis R. W., Calos M. P. Deletion of plasmid sequences during Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1065–1067. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1065-1067.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contente S., Dubnau D. Marker rescue transformation by linear plasmid DNA in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):555–571. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Cirigliano C. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. Formation and properties of products isolated from transformed cells which are derived entirely from donor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):9–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. F., Biswas G. D., Sparling P. F. Sequence-specific DNA uptake in transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1071–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1071-1077.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkova R., Goodgal S. Uptake of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid by Haemophilus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):79–84. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.79-84.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Maul G., Goodgal S. H. Possible mechanism for donor DNA binding and transport in Haemophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6370–6374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korch C., Hagblom P., Ohman H., Göransson M., Normark S. Cryptic plasmid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):430–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.430-438.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Uptake of circular deoxyribonucleic acid and mechanism of deoxyribonucleic acid transport in genetic transformation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):404–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.404-409.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Keeler C. L., Jr, Jones K. R., Wood P. H. Molecular characterization of unique deletion mutants of the streptococcal plasmid, pAM beta 1. Plasmid. 1980 Jul;4(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Robbins K. E. Evolutionary analysis of the 7.1-kb beta-lactamase-specifying R-plasmid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by restriction endonucleases. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1498–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1498-1501.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Breakage prior to entry of donor DNA in Pneumococcus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahari K. Deletion plasmids from transformants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa trp cells with the RSF1010-trp hybrid plasmid and high levels of enzyme activity from the gene on the plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):312–317. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.312-317.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
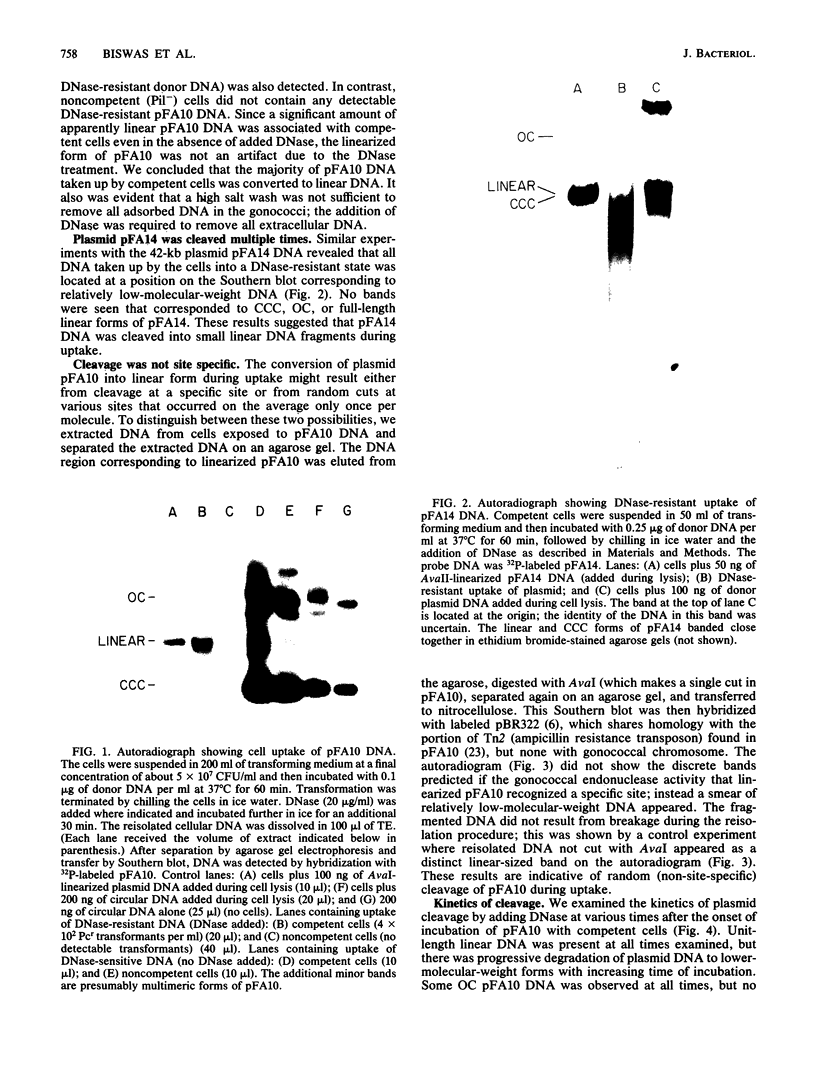
- Notani N. K., Setlow J. K., McCarthy D., Clayton N. L. Transformation of Haemophilus influenzae by plasmid RSF0885. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):812–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.812-816.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of two beta-lactamase-specifying plasmids isolated from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Guild W. R. Pathway of plasmid transformation in Pneumococcus: open circular and linear molecules are active. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):517–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.517-526.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Lopez R., Garrigan O., Tomasz A. Nucleolytic degradation of homologous and heterologous deoxyribonucleic acid molecules at the surface of competent pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.676-685.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Blackman E., Biswas G., Sparling P. F. Conjugative plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.278-286.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Sparling P. F. Transformation-derived Neisseria gonorrhoeae plasmids with altered structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.510-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]