Abstract
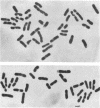
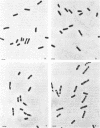
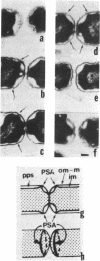
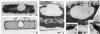
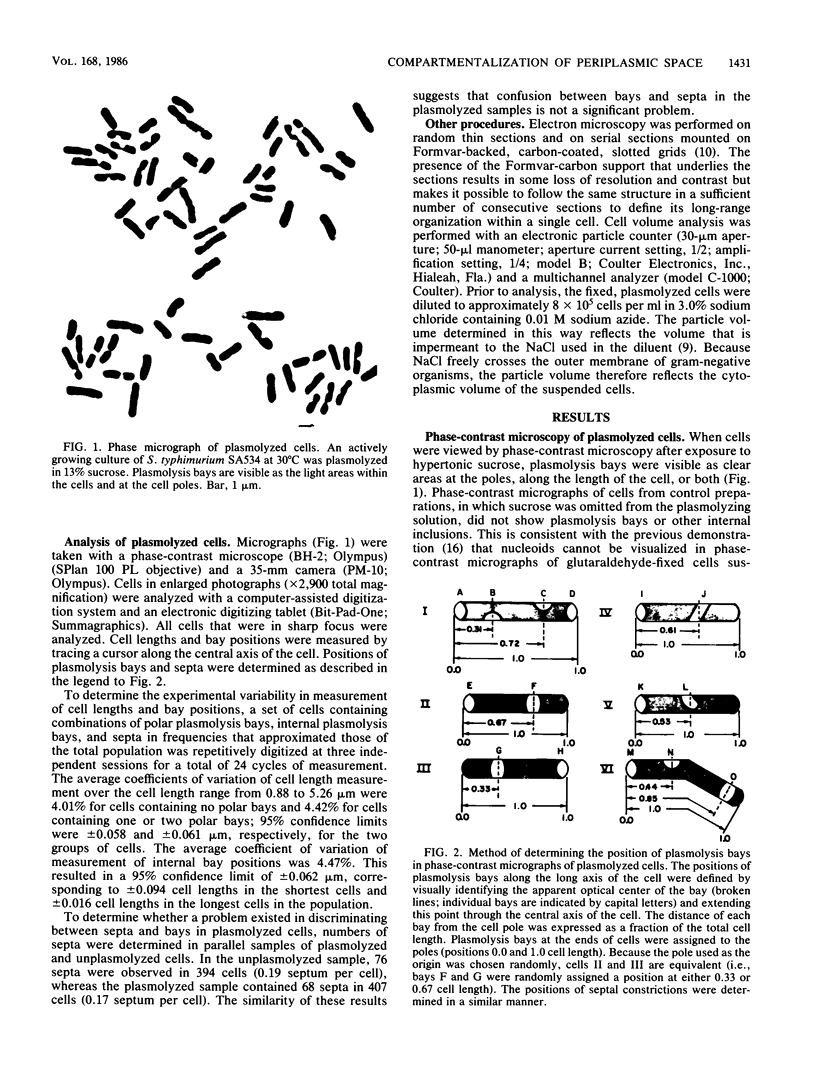
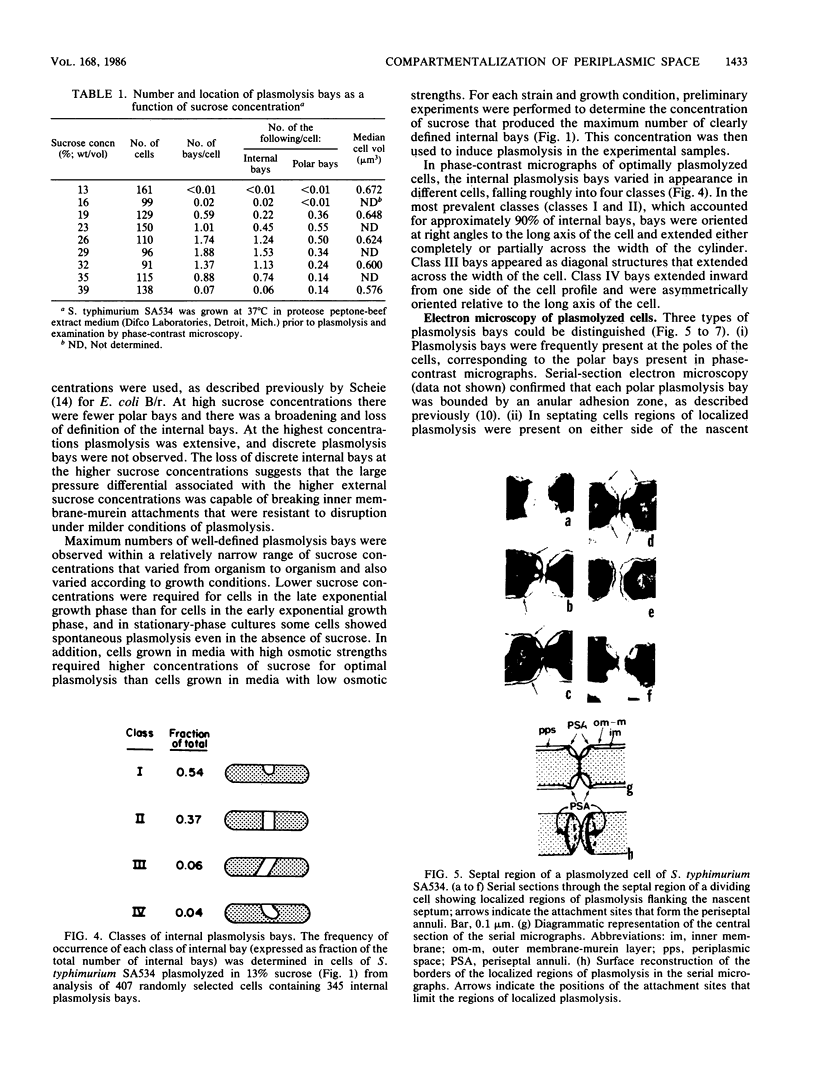
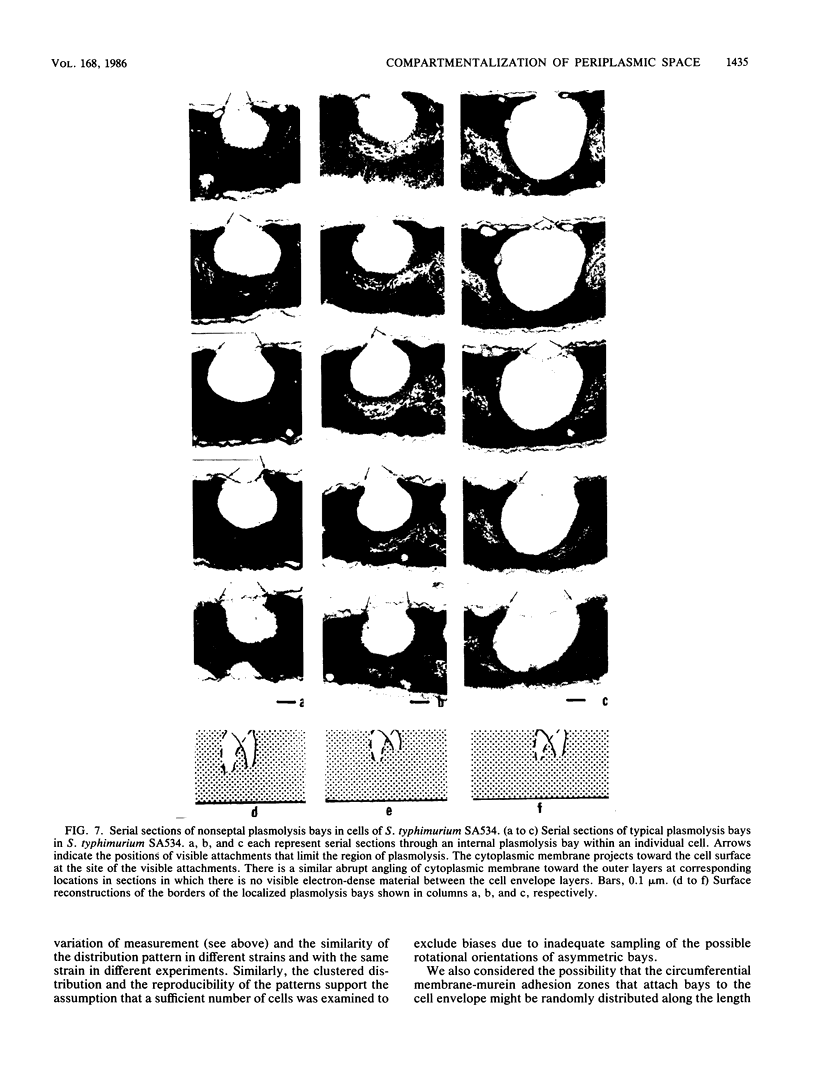
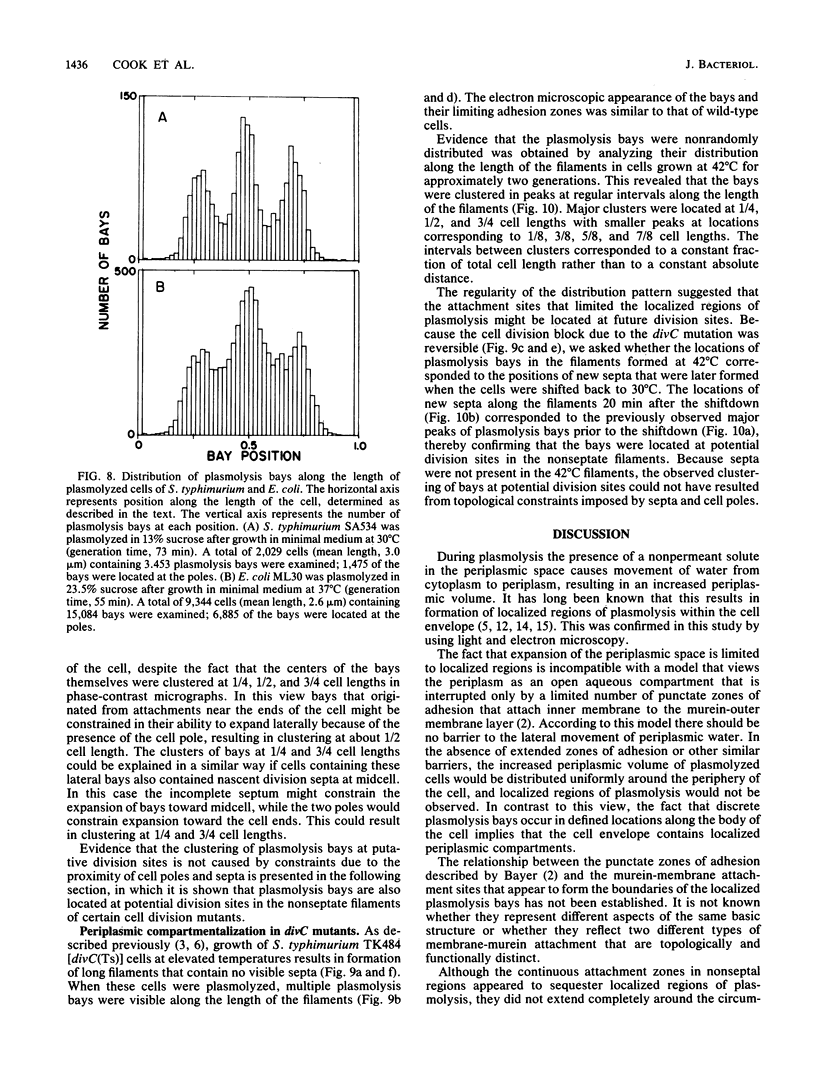
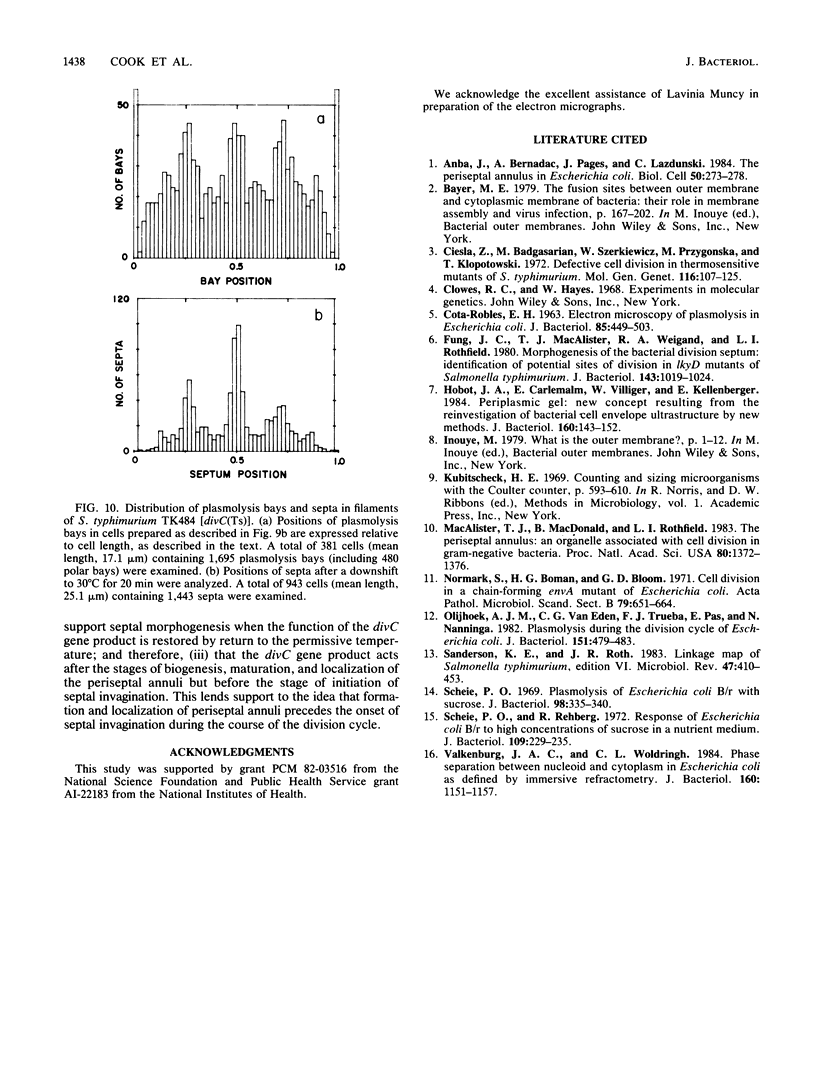
Phase-contrast and serial-section electron microscopy were used to study the patterns of localized plasmolysis that occur when cells of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli are exposed to hypertonic solutions of sucrose. In dividing cells the nascent septum was flanked by localized regions of periseptal plasmolysis. In randomly growing populations, plasmolysis bays that were not associated with septal ingrowth were clustered at the midpoint of the cell and at 1/4 and 3/4 cell lengths. The localized regions of plasmolysis were limited by continuous zones of adhesion that resembled the periseptal annular adhesion zones described previously in lkyD mutants of S. typhimurium (T. J. MacAlister, B. MacDonald, and L. I. Rothfield, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:1372-1376, 1983). When cell division was blocked by growing divC(Ts) cells at elevated temperatures, the localized regions of plasmolysis were clustered along the aseptate filaments at positions that corresponded to sites where septum formation occurred when cell division was permitted to resume by a shift back to the permissive temperature. Taken together the results are consistent with a model in which extended zones of adhesion define localized compartments within the periplasmic space, predominantly located at future sites of cell division.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anba J., Bernadac A., Pages J. M., Lazdunski C. The periseptal annulus in Escherichia coli. Biol Cell. 1984;50(3):273–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTA-ROBLES E. H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF PLASMOLYSIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:499–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.499-503.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla Z., Bagdasarian M., Szczurkiewicz W., Przygońska M., Klopotowski T. Defective cell division in thermosensitive mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):107–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00582221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., MacAlister T. J., Weigand R. A., Rothfield L. I. Morphogenesis of the bacterial division septum: identification of potential sites of division in lkyD mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1019-1024.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macalister T. J., Macdonald B., Rothfield L. I. The periseptal annulus: An organelle associated with cell division in Gram-negative bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1372–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Boman H. G., Bloom G. D. Cell division in a chain-forming envA mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Fine structure of division sites and effects of EDTA, lysozyme and ampicillin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):651–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olijhoek A. J., Van Eden C. G., Trueba F. J., Pas E., Nanninga N. Plasmolysis during the division cycle of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):479–484. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.479-484.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheie P. O. Plasmolysis of Escherichia coli B-r with sucrose. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):335–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.335-340.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheie P. O., Rehberg R. Response of Escherichia coli B-r to high concentrations of sucrose in a nutrient medium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):229–235. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.229-235.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkenburg J. A., Woldringh C. L. Phase separation between nucleoid and cytoplasm in Escherichia coli as defined by immersive refractometry. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1151-1157.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]