Abstract
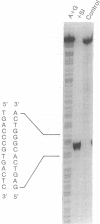
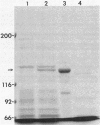
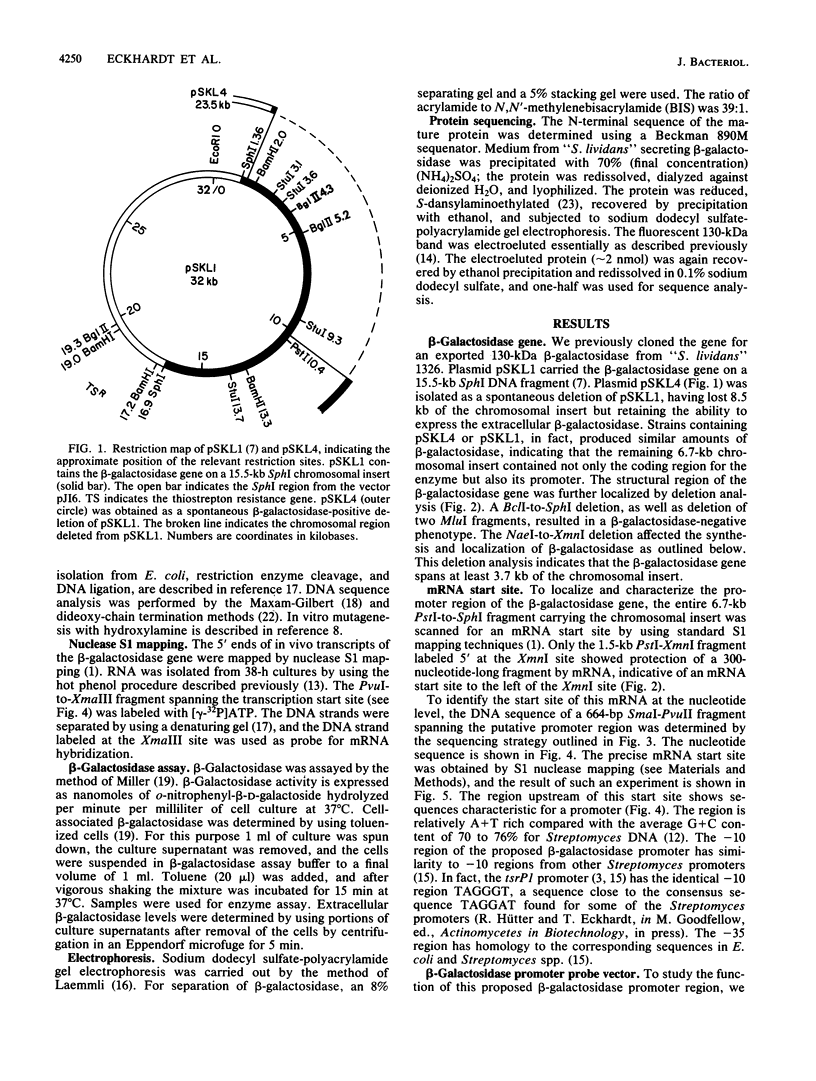
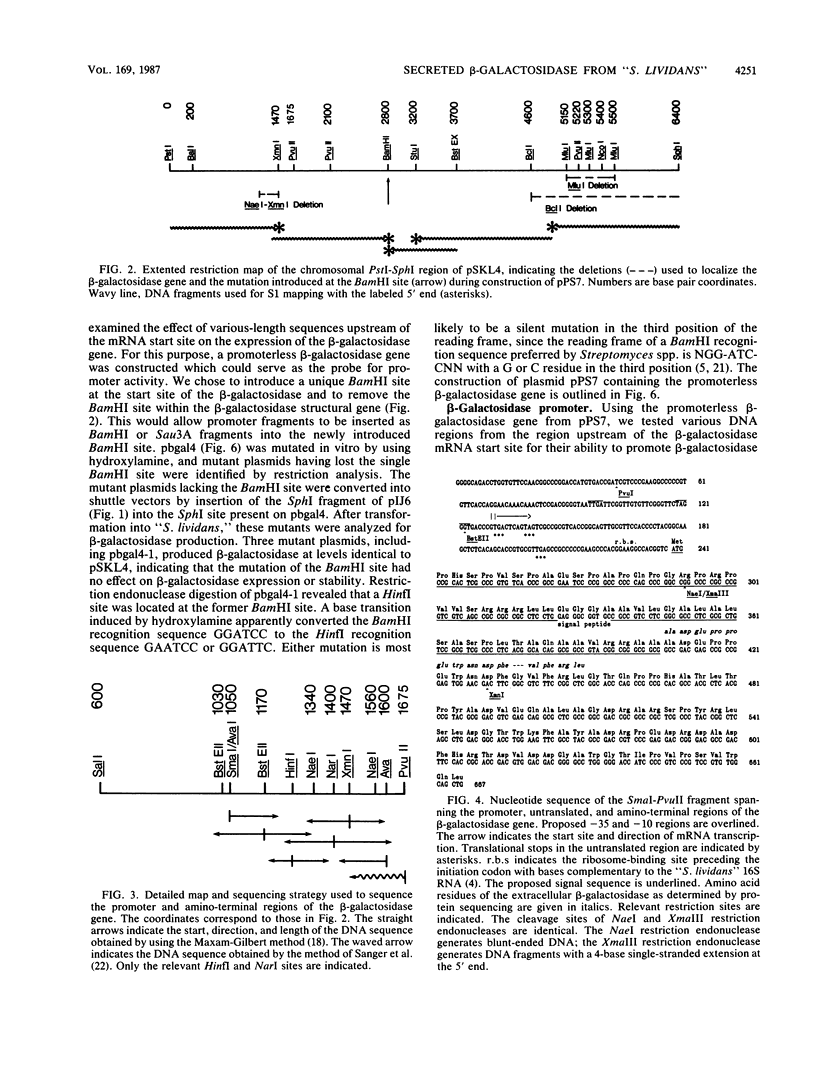
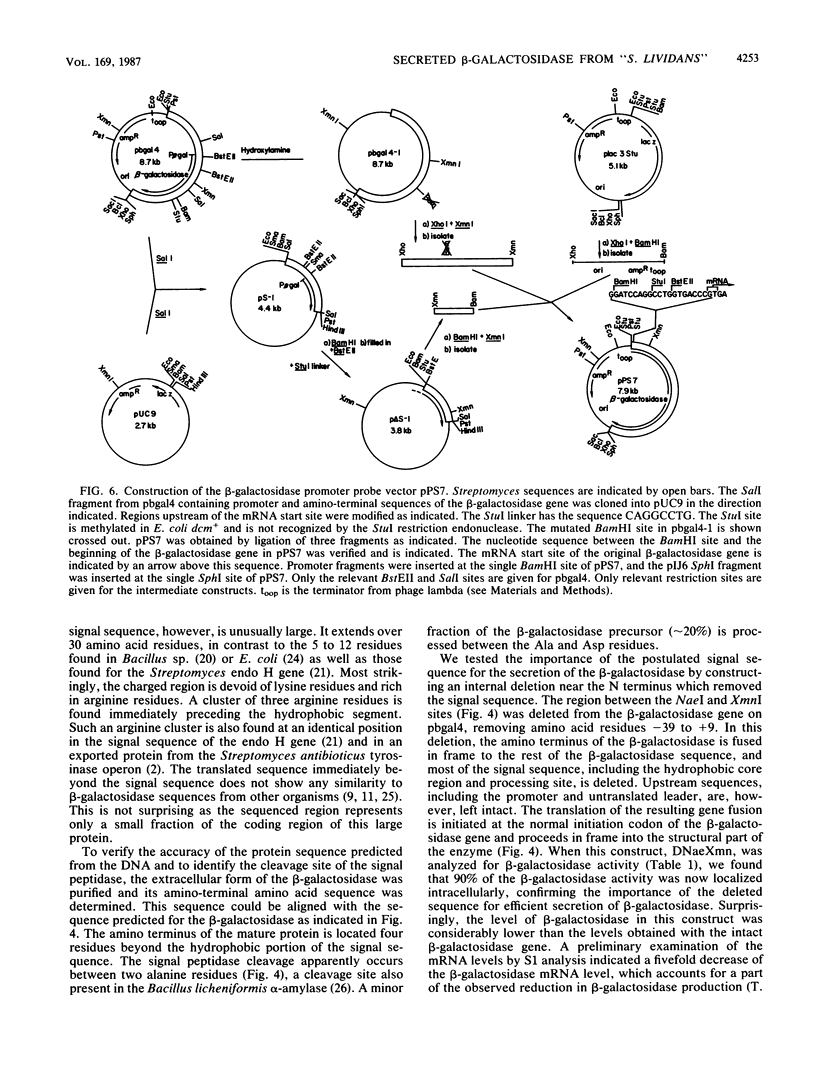
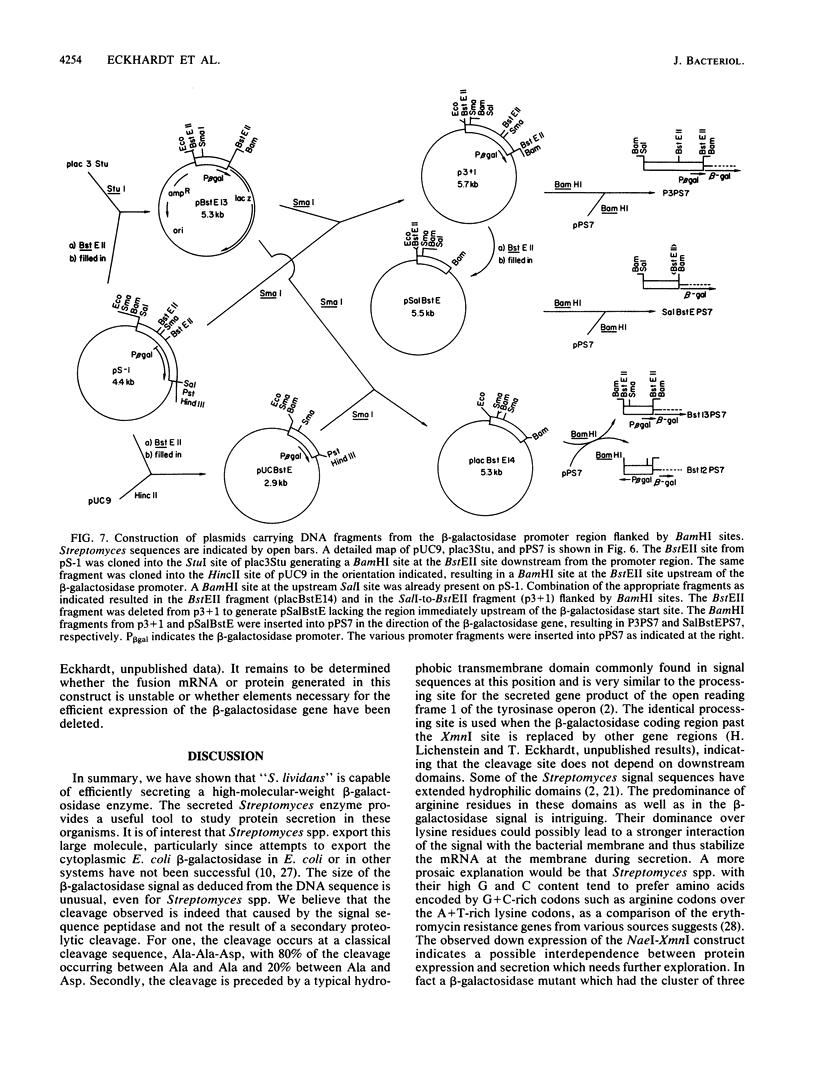
The gene for a secreted 130-kilodalton beta-galactosidase from "Streptomyces lividans" has been cloned, its promoter, signal sequence, and amino terminal region have been localized, and their nucleotide sequence has been determined. The signal sequence extends over 56 amino acids and shows the characteristic-features of signal sequences, including a hydrophilic amino terminus followed by a hydrophobic core near the signal cleavage site. The secretion of beta-galactosidase depends on the presence of the signal sequence. beta-Galactosidase is the major protein in culture supernatants and extracts of strains expressing the cloned beta-galactosidase gene and represents a valuable tool in the study of protein secretion in Streptomyces spp.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernan V., Filpula D., Herber W., Bibb M., Katz E. The nucleotide sequence of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus and characterization of the gene product. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Bibb M. J., Ward J. M., Cohen S. N. Nucleotide sequences encoding and promoting expression of three antibiotic resistance genes indigenous to Streptomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):26–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00327505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Irani M., Crombrugghe B. Isolation of mutant promoters in the Escherichia coli galactose operon using local mutagenesis on cloned DNA fragments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buvinger W. E., Riley M. Nucleotide sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae lac genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):850–857. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.850-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Schauer I., Hansen W., Esmon P., Schekman R. Invertase beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins fail to be transported from the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2347–2355. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. V., Zabin I. Amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase. XI. Peptide ordering procedures and the complete sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5521–5525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N., McConnell D. J., Cantwell B. A. The DNA sequence of the gene and genetic control sites for the excreted B. subtilis enzyme beta-glucanase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5355–5367. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Trimble R. B., Wirth D. F., Hering C., Maley F., Maley G. F., Das R., Gibson B. W., Royal N., Biemann K. Primary structure of the Streptomyces enzyme endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7577–7583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Betts P. W., Hall B. G. Sequence of the ebgA gene of Escherichia coli: comparison with the lacZ gene. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):469–477. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takkinen K., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Palva I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Amino acid sequence of alpha-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Leunissen J., van Damme-Jongsten M., Overduin P. Failure of E. coli K-12 to transport PhoE-LacZ hybrid proteins out of the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama H., Weisblum B. N-Methyl transferase of Streptomyces erythraeus that confers resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics: amino acid sequence and its homology to cognate R-factor enzymes from pathogenic bacilli and cocci. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]