Abstract
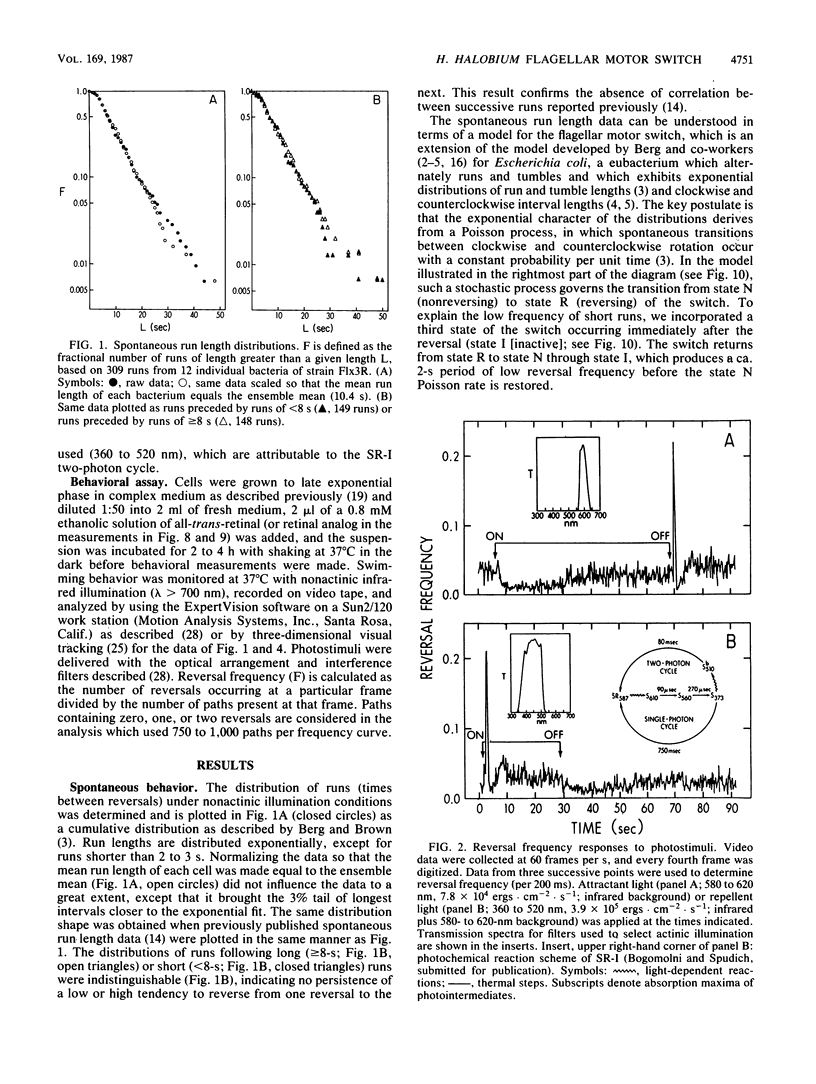
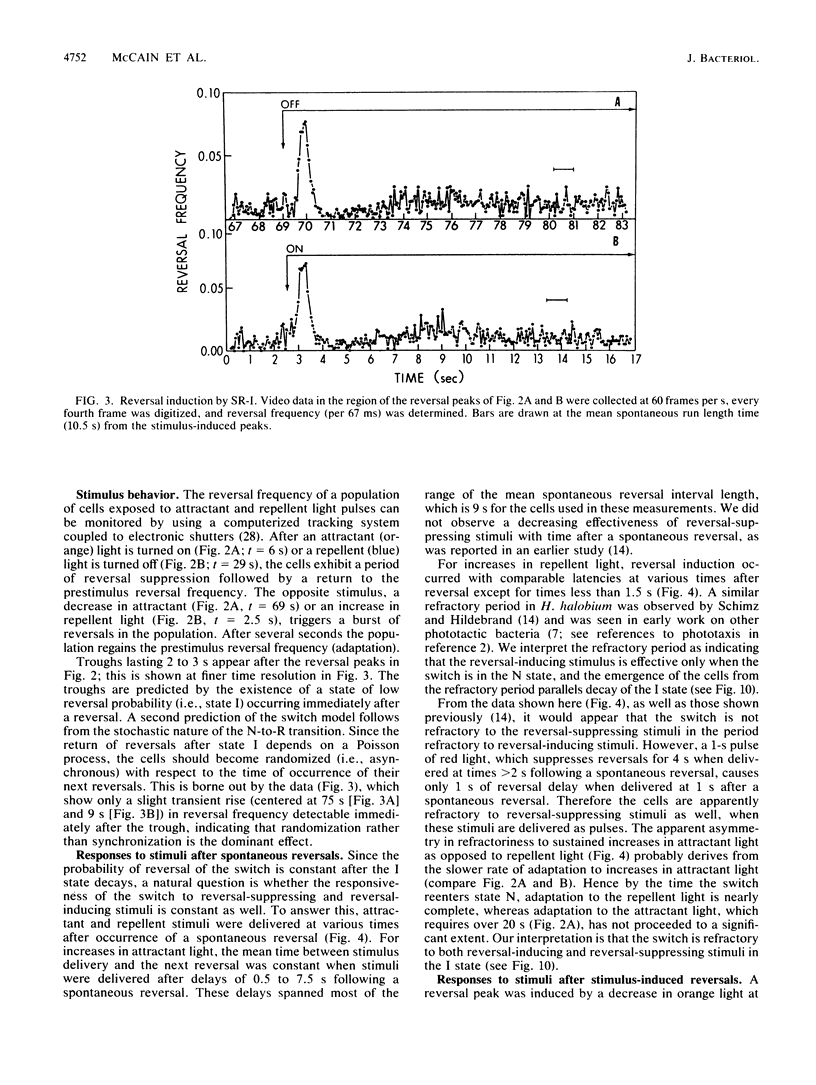
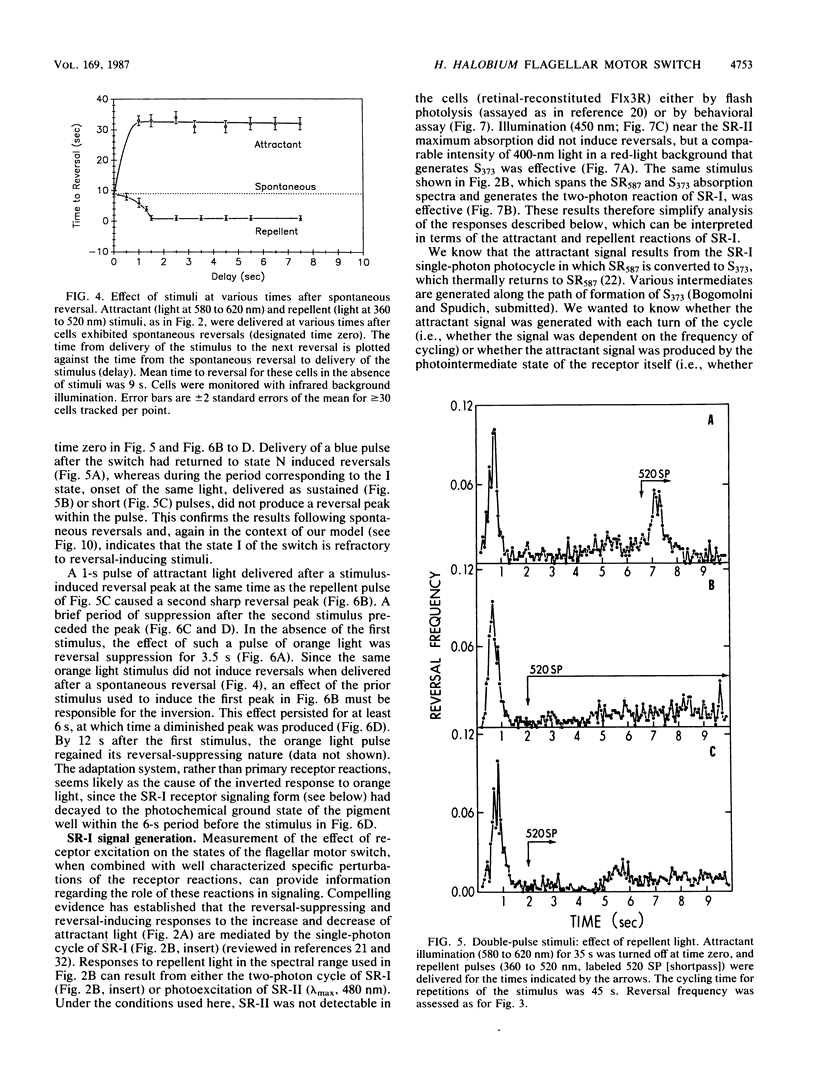
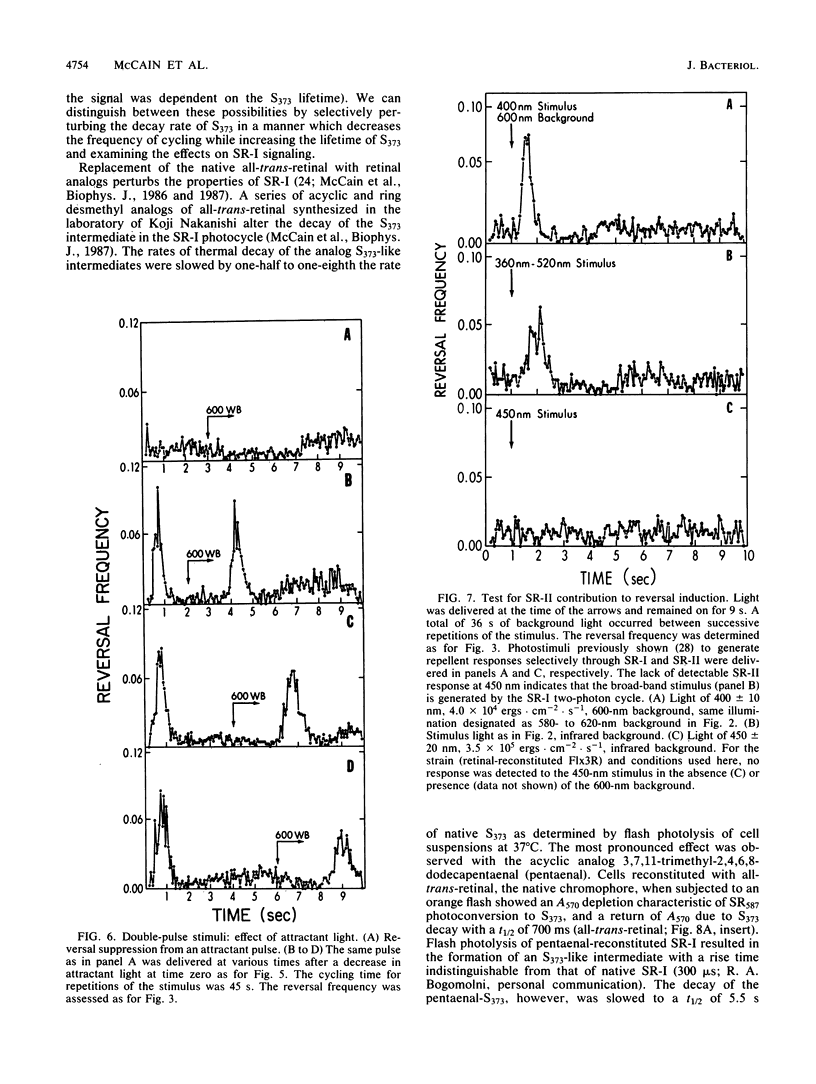
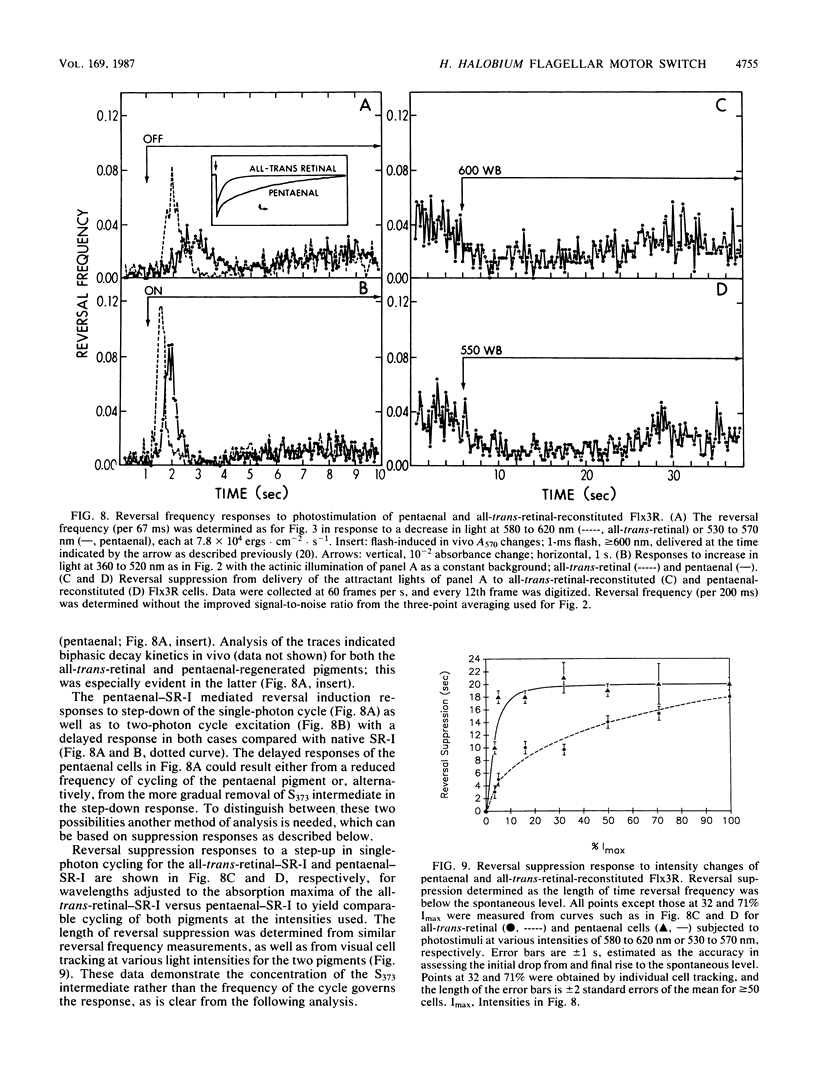
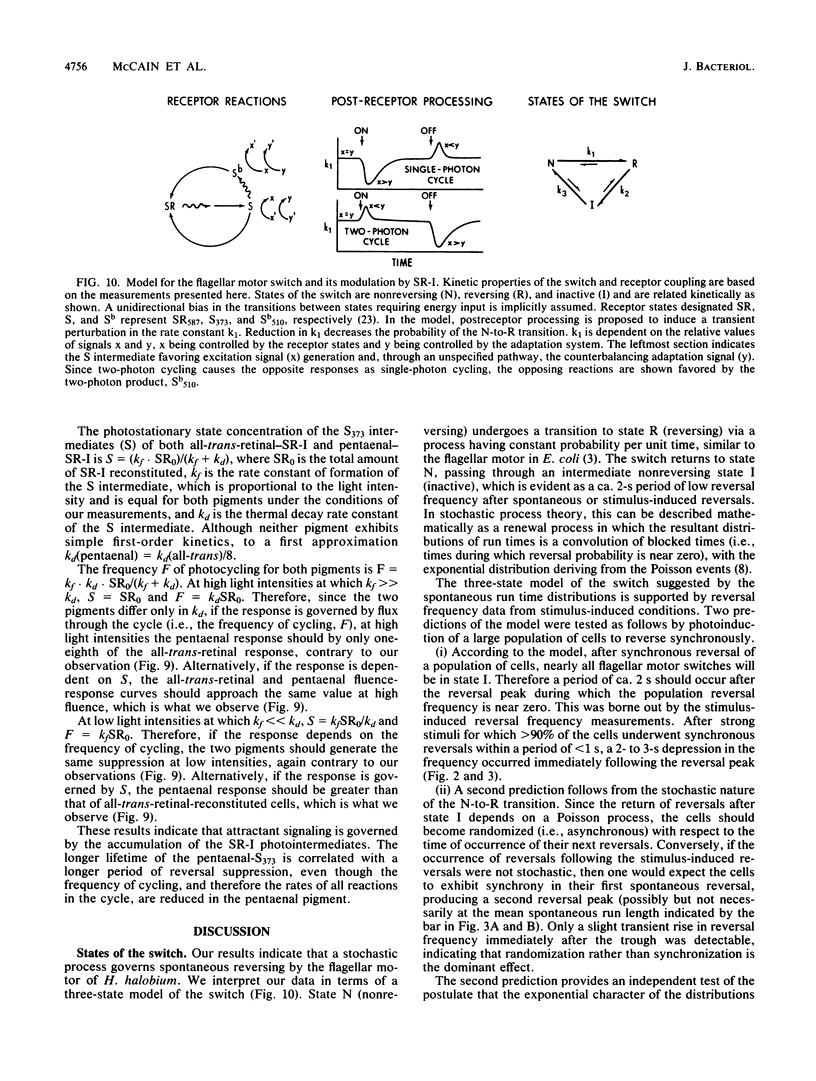
Spontaneous switching of the rotation sense of the flagellar motor of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium and modulation of the switch by attractant and repellent photostimuli were analyzed by using a computerized cell-tracking system with 67-ms resolution coupled to electronic shutters. The data fit a three-state model of the switch, in which a Poisson process governs the transition from state N (nonreversing) to state R (reversing). After a reversal, the switch returns to state N, passing through an intermediate state I (inactive), which produces a ca. 2-s period of low reversal frequency before the state N Poisson rate is restored. The stochastic nature of the H. halobium switch reveals a close similarity to Escherichia coli flagellar motor properties as elucidated previously. Sensory modulation of the switch by both photoattractant and photorepellent signals can be interpreted in terms of modulation of the single forward rate constant of the N to R transition. Insight into the mechanism of modulation by the phototaxis receptor sensory rhodopsin I (SR-I) was gained by increasing the lifetime of the principal photointermediate of the SR-I photochemical reaction cycle, S373, by replacing the native chromophore, all-trans-retinal, with the acyclic analog, 3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4,6,8-dodecapentaenal. Flash photolysis of analog-containing cells revealed an eightfold decrease in the rate of thermal decay of S373, and behavioral analysis showed longer periods of reversal suppression than that of cells with the native chromophore over similar ranges of illumination intensities. This indicates that attractant signaling is governed by the lifetime of the S373 intermediate rather than by the frequency of photocycling. In this sense, SR-I is similar to rhodopsin, whose function depends on an active photoproduct (Meta-II).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):119–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Tedesco P. M. Transient response to chemotactic stimuli in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Impulse responses in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Identification of a third rhodopsin-like pigment in phototactic Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. Studies in the phototaxis of Rhodospirillum rubrum. III. Quantitative relations between stimulus and response. Arch Mikrobiol. 1953;19(2):141–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00446397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Schimz A. Role of the response oscillator in inverse responses of Halobacterium halobium to weak light stimuli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):254–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.254-259.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao B., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G., Arnaboldi M., Balogh-Nair V., Nakanishi K., Crouch R. Photochemical and functional properties of bacteriorhodopsins formed from 5,6-dihydro- and 5,6-dihydrodesmethylretinals. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):428–435. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Signal formation in the halobacterial photophobic response mediated by a fourth retinal protein (P480). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90654-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimz A., Hildebrand E. Entrainment and temperature dependence of the response oscillator in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):689–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.689-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimz A. Methylation of membrane proteins is involved in chemosensory and photosensory behavior of Halobacterium halobium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80719-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Block S. M., Berg H. C. Temporal comparisons in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Sundberg S. A., Manor D., Spudich J. L. Properties of a second sensory receptor protein in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Spectroscopic discrimination of the three rhodopsinlike pigments in Halobacterium halobium membranes. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84345-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L. Genetic demonstration of a sensory rhodopsin in bacteria. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;164:221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Kersulis G., Koshland D. E., Jr Neither methylating nor demethylating enzymes are required for bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Alam M., Spudich J. L. Excitation signal processing times in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):895–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Selection and properties of phototaxis-deficient mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Mochizuki Y., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Evidence that the long-lifetime photointermediate of s-rhodopsin is a receptor for negative phototaxis in Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Kamo N., Takahashi T., Kobatake Y. Photochemical intermediate of third rhodopsin-like pigment in Halobacterium halobium by simultaneous illumination with red and blue light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):989–994. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Takahashi T., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Flash spectrophotometric identification of a fourth rhodopsin-like pigment in Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff E. K., Bogomolni R. A., Scherrer P., Hess B., Stoeckenius W. Color discrimination in halobacteria: spectroscopic characterization of a second sensory receptor covering the blue-green region of the spectrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


