Abstract
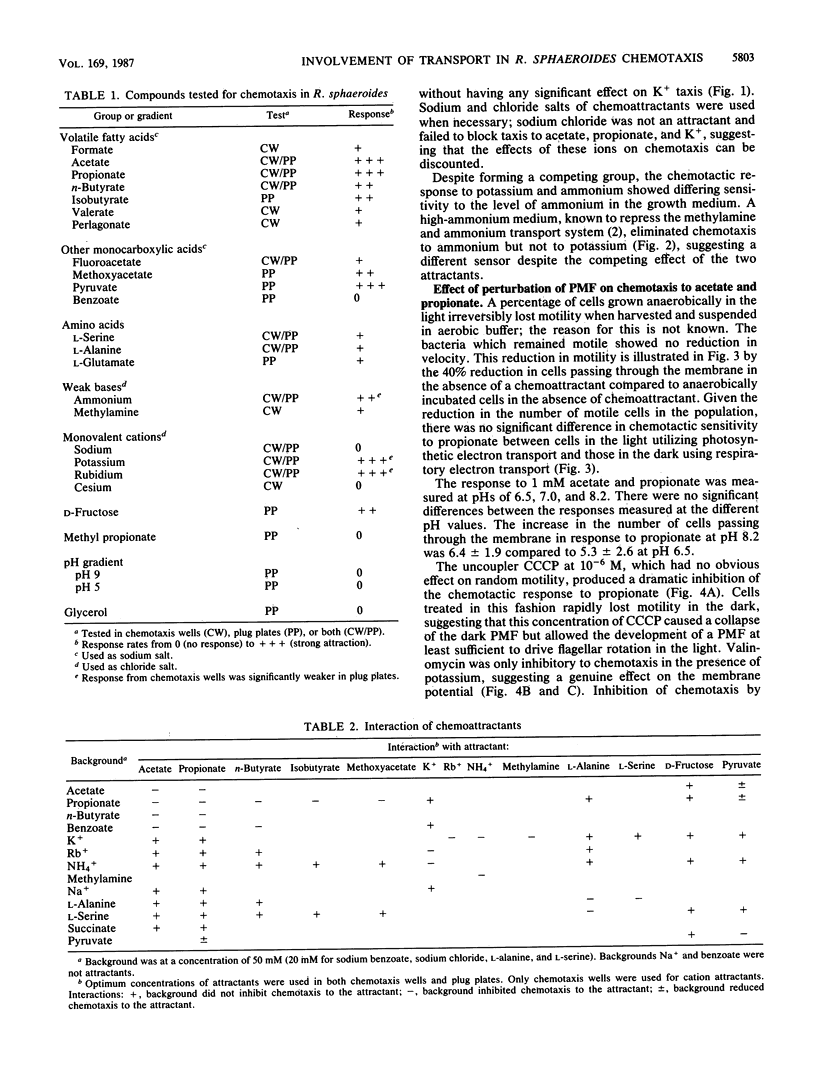
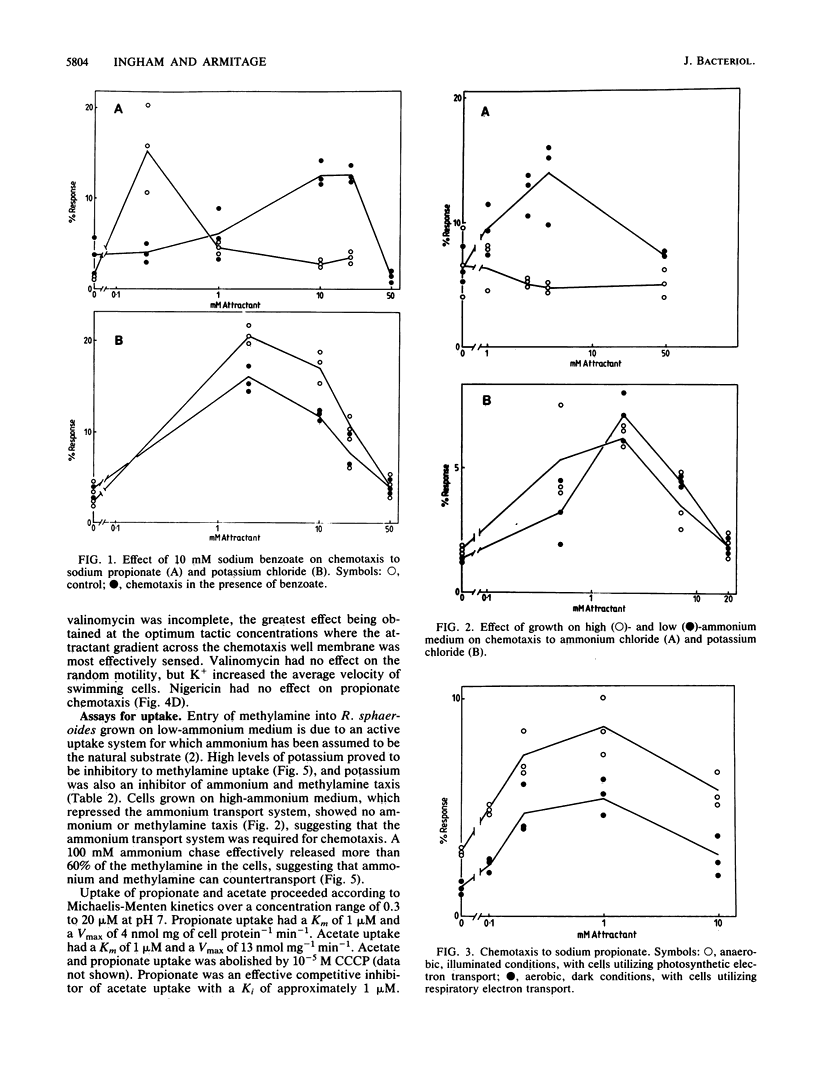
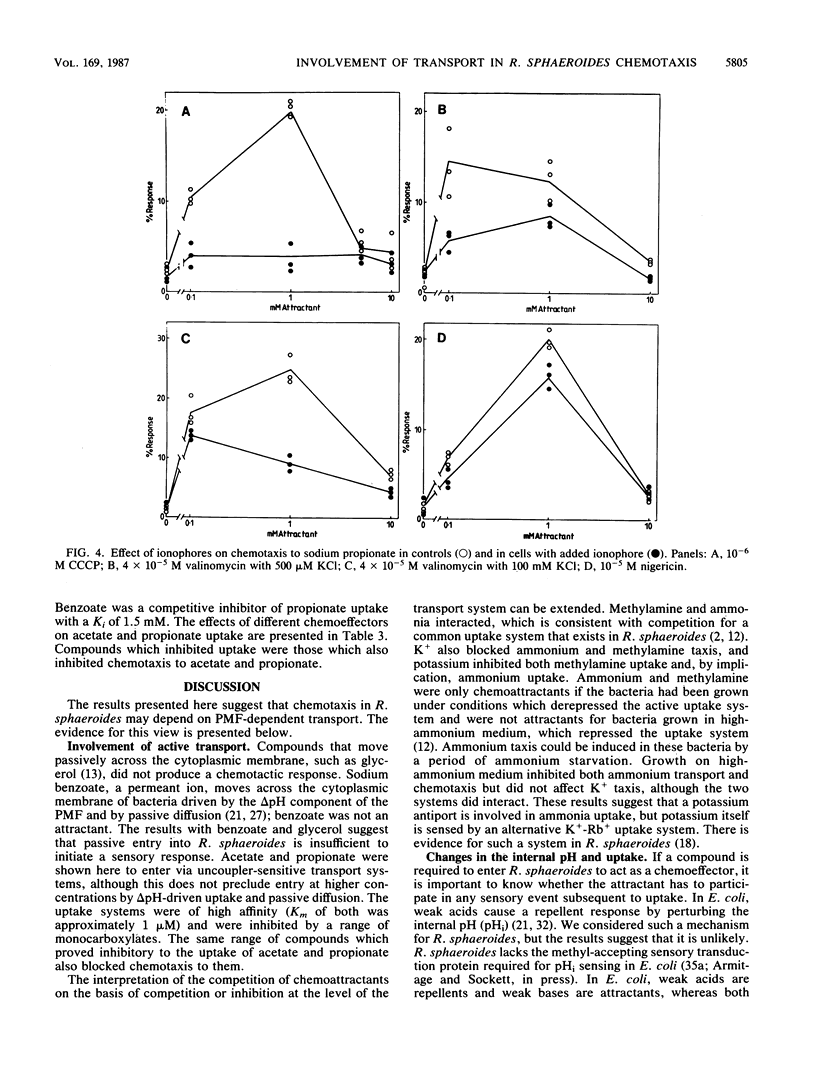
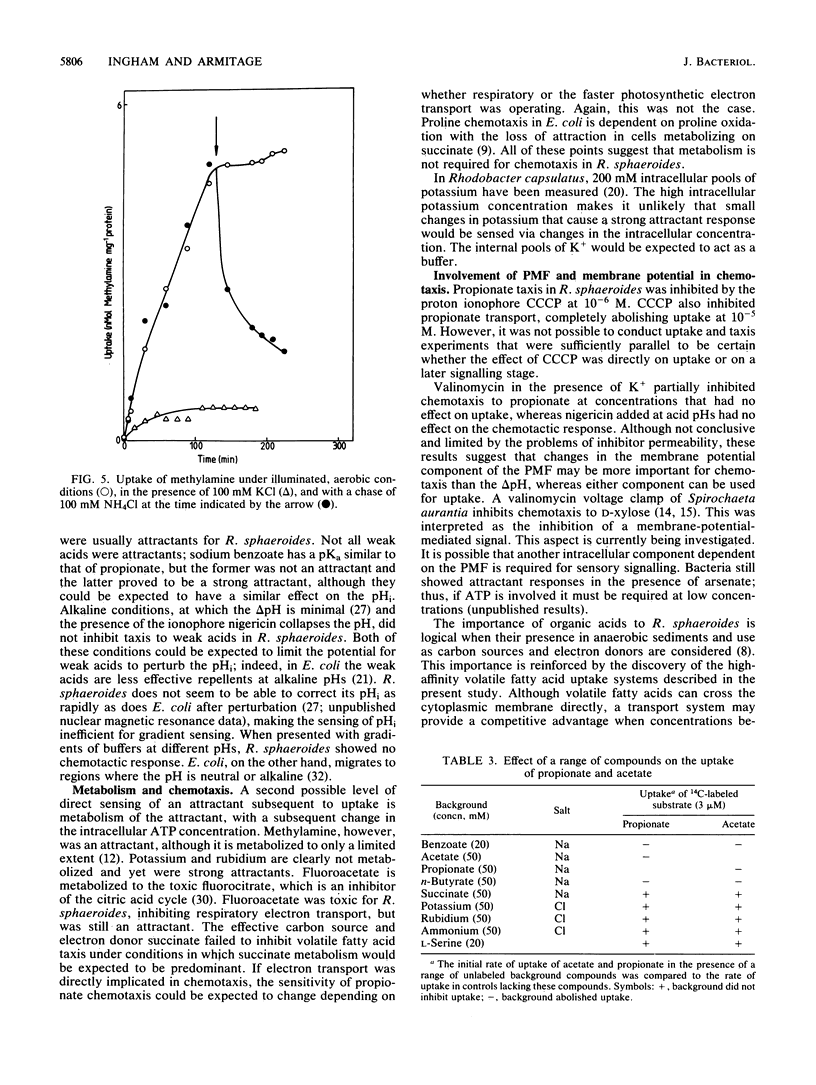
The chemotactic response to a range of chemicals was investigated in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides, an organism known to lack conventional methyl-accepting sensory transduction proteins. Strong attractants included monocarboxylic acids and monovalent cations. Results suggest that the chemotactic response required the uptake of the chemoeffector, but not its metabolism. If a chemoeffector could block the uptake of another attractant, it also inhibited chemotaxis to that attractant. Sodium benzoate was not an attractant but was a competitive inhibitor of the propionate uptake system. Binding in an active uptake system was therefore insufficient to cause a chemotactic response. At different concentrations, benzoate either blocked propionate chemotaxis or reduced the sensitivity of propionate chemotaxis, an effect consistent with its role as a competitive inhibitor of uptake. Bacteria only showed chemotaxis to ammonium when grown under ammonia-limited conditions, which derepressed the ammonium transport system. Both chemotaxis and uptake were sensitive to the proton ionophore carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, suggesting an involvement of the proton motive force in chemotaxis, at least at the level of transport. There was no evidence for internal pH as a sensory signal. These results suggest a requirement for the uptake of attractants in chemotactic sensing in R. sphaeroides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Epstein W. Phosphotransferase-system enzymes as chemoreceptors for certain sugars in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Evans M. C. Membrane potential changes during chemotaxis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80946-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Ingham C., Evans M. C. Role of proton motive force in phototactic and aerotactic responses of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):967–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.967-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Macnab R. M. Unidirectional, intermittent rotation of the flagellum of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.514-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. On the interplay of environmental factors affecting taxis and motility in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;29(2):189–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00409860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M., Madill K. A., Wood J. M. Genetic and biochemical requirements for chemotaxis to L-proline in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):902–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.902-906.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordts M. L., Gibson J. Ammonium and methylammonium transport in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1632–1638. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1632-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. Nutrient transport by anoxygenic and oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:135–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne E. A., Jr, Greenberg E. P. A voltage clamp inhibits chemotaxis of Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):916–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.916-920.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne E. A., Jr, Greenberg E. P. Chemotaxis of Spirochaeta aurantia: involvement of membrane potential in chemosensory signal transduction. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):837–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.837-844.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Iino T. Phototaxis and membrane potential in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.34-41.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Friedberg I., Lolkema J. S., Michels P. A., Konings W. N. Energy coupling of facilitated transport of inorganic ions in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1183-1191.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Crofts A. R. The high energy state in chromatophores from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(3):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper P. Potassium transport system of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1314–1322. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1314-1322.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo D. J., Taylor B. L. Aerotaxis in Salmonella typhimurium: role of electron transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):990–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.990-1001.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay K., Lolkema J., Hellingwerf K. J., Kaptein R., Konings W. N. Quantitative agreement between the values for the light-induced delta pH in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides measured with automated follow-dialysis and 31P NMR. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwano M., Taylor B. L. Novel sensory adaptation mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis to oxygen and phosphotransferase substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowlin D. M., Nettleton D. O., Ordal G. W., Hazelbauer G. L. Chemotactic transducer proteins of Escherichia coli exhibit homology with methyl-accepting proteins from distantly related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):262–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.262-266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:778–785. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Ishihara A., Berg H. C. Chemotactic signaling in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.51-59.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J., Taylor B. L. Oxygen taxis and proton motive force in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10983–10988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sockett R. E., Armitage J. P., Evans M. C. Methylation-independent and methylation-dependent chemotaxis in Rhodobacter sphaeroides and Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5808–5814. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5808-5814.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L. Role of proton motive force in sensory transduction in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:551–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


