Abstract
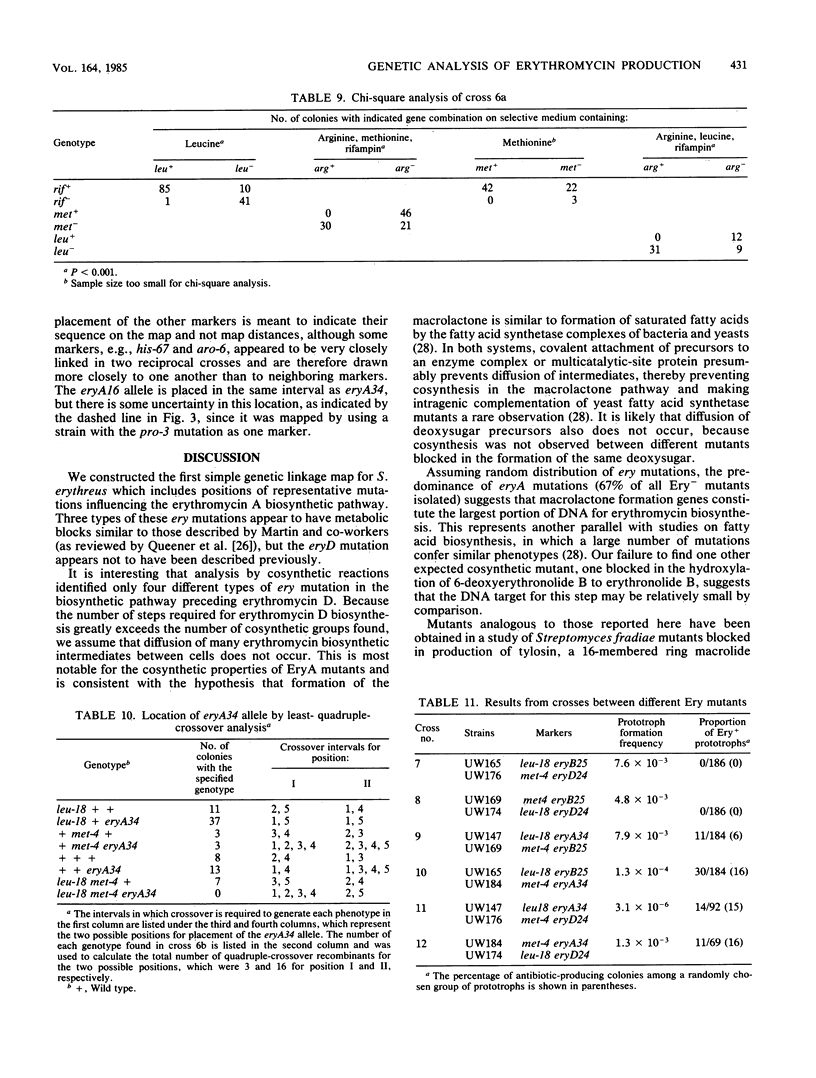
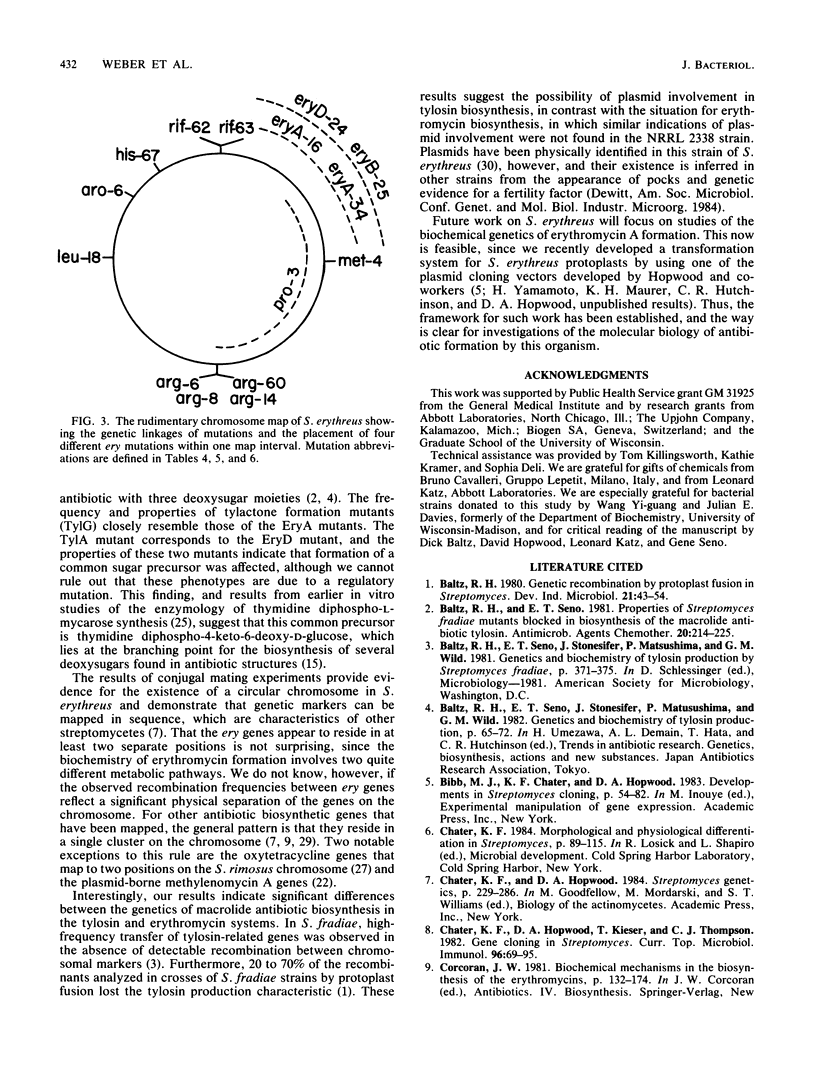
Streptomyces erythreus produces the 14-membered macrolide antibiotic erythromycin A. The properties of erythromycin A nonproducing mutants and their genetic linkage to chromosomal markers were used to establish the rudiments of genetic organization of antibiotic production. Thirty-three Ery- mutants, produced by mutagenesis of S. erythreus NRRL 2338 and affecting the formation of the macrolactone and deoxysugar intermediates of erythromycin A biosynthesis, were classified into four phenotypically different groups based on their cosynthesis behavior, the type of biosynthetic intermediate accumulated, and their ability to biotransform known biochemical intermediates of erythromycin A. Demonstration of the occurrence of natural genetic recombination during conjugal mating in S. erythreus enabled comparison of the genetic linkage relationships of three different ery mutations with seven other markers on a simple chromosome map. This established a chromosomal location for the ery mutations, which appear to be located in at least two positions within one interval of the map.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltz R. H., Seno E. T. Properties of Streptomyces fradiae mutants blocked in biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):214–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Thompson C. J. Gene cloning in Streptomyces. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:69–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delić V., Hopwood D. A., Friend E. J. Mutangenesis by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (NTG) in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mutat Res. 1970 Feb;9(2):167–182. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delić V., Pigac J., Sermonti G. Detection and study of cosynthesis of tetracycline antibiotics by an agar method. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):103–108. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L. Industrial microbiology. Science. 1981 Nov 27;214(4524):987–995. doi: 10.1126/science.6946560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harik S. I., Sharma V. K., Wetherbee J. R., Warren R. H., Banerjee S. P. Adrenergic and cholinergic receptors of cerebral microvessels. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(3):329–338. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. Genetic analysis and genome structure in Streptomyces coelicolor. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):373–403. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.373-403.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. Genetic studies with bacterial protoplasts. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:237–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Merrick M. J. Genetics of antibiotic production. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):595–635. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.595-635.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby R., Hopwood D. A. Genetic determination of methylenomycin synthesis by the SCP1 plasmid of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):239–252. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majer J., Martin J. R., Egan R. S., Corcoran J. W. Antibiotic glycosides. 8. Erythromycin D, a new macrolide antibiotic. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Mar 2;99(5):1620–1622. doi: 10.1021/ja00447a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape H., Brillinger G. U. Stoffwechselfprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 113. Biosynthese von Thymidin-diphospho-mycarose durch ein zellfreies System aus Streptomyces rimosus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(1):25–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. W., Sebek O. K., Vézina C. Mutants blocked in antibiotic synthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:593–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi-guang W., Davies J. E., Hutchinson C. R. Plasmid DNA in the erythromycin producing microorganism, Streptomyces erythreus NRRL 2338. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Mar;35(3):335–342. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


