Abstract
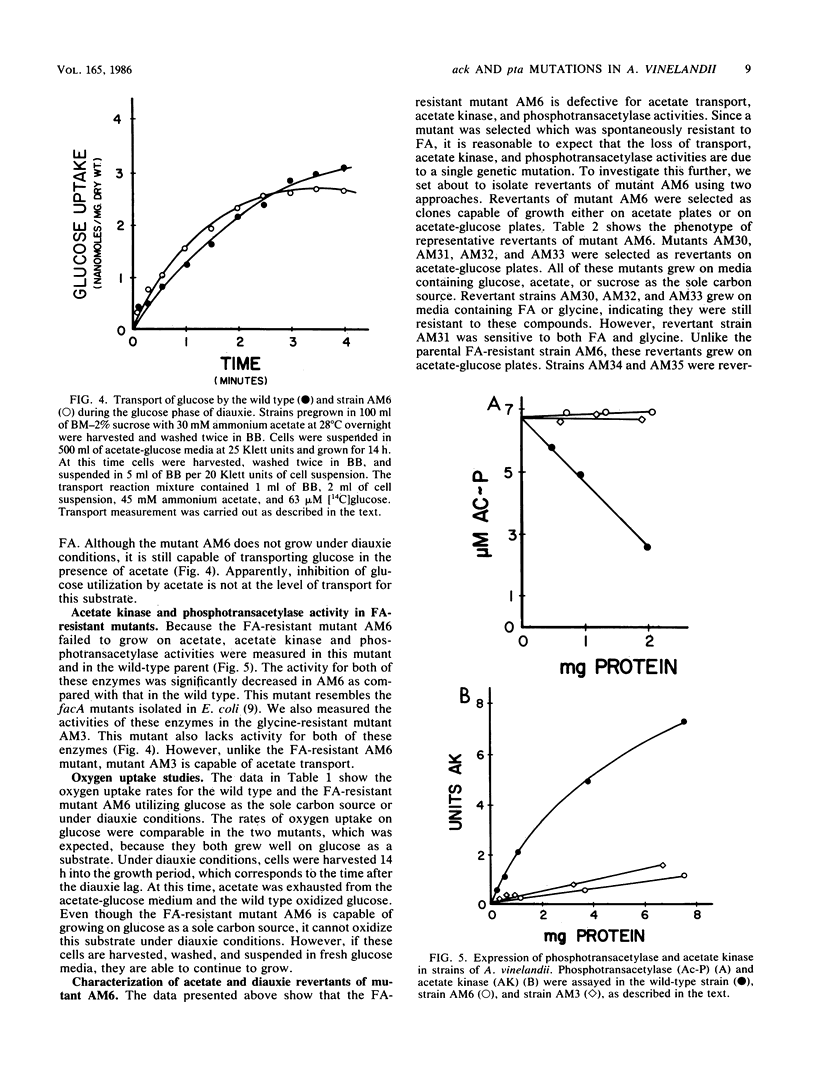
Azotobacter vinelandii mutants defective for acetate utilization that were resistant to fluoroacetate (FA) were isolated. FA-resistant mutant AM6 failed to transport [14C]acetate and lacked enzymatic activity for both acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase. Growth of wild-type A. vinelandii was sensitive to 10 mM glycine; however, all FA-resistant strains were resistant to glycine toxicity. Isolated mutants that were spontaneously resistant to glycine were also resistant to FA and lacked both acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase activity. The glycine-resistant mutant AM3, unlike mutant AM6, was capable of growth on acetate. The mutant strain AM6 was unable to growth under acetate-glucose diauxie conditions. Glucose utilization in this mutant, unlike that in wild-type A. vinelandii, was permanently arrested in the presence of acetate. Revertants of strain AM6 were selected on plates with acetate or acetate-glucose. Two classes of revertants were isolated. Class I revertant mutants AM31 and AM35 were positive for both acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase activities. These revertants were also sensitive to both FA and glycine. Class II revertant strains AM32 and AM34 still lacked acetate kinase and phophotransacetylase activity. Both of these revertants remained resistant to FA and glycine.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG P. Acyl adenylates; an enzymatic mechanism of acetate activation. J Biol Chem. 1956 Oct;222(2):991–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Jones-Mortimer M. C., Kornberg H. L. The enzymic interconversion of acetate and acetyl-coenzyme A in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Oct;102(2):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-2-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOU T. C., LIPMANN F. Separation of acetyl transfer enzymes in pigeon liver extract. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):89–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., ZAMECNIK P. C. Transformation of bacteria into L forms by amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):770–771. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.770-771.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli K12 with fumarate as terminal electron acceptor. Genetic studies with menaquinone and fluoroacetate-resistant mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Dec;115(2):259–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C. Alteration of glucose metabolism of Arthrobacter crystallopoietes by compounds which induce sphere to rod morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):526–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.526-534.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAVITT R. I., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XI. Valine inhibition of the growth of Escherichia coli strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:624–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.624-630.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVine S. M., Ardeshir F., Ames G. F. Isolation and Characterization of acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1081–1085. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1081-1085.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinthal M., Williams L. S., Umbarger H. E. Role of threonine deaminase in the regulation of isoleucine and valine biosynthesis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 21;246(151):65–68. doi: 10.1038/newbio246065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch W. H., Franklin M. Effect of temperature on diauxic growth with glucose and organic acids in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00415721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maculla E. S., Cowles P. B. The Use of Glycine in the Disruption of Bacterial Cells. Science. 1948 Apr 9;107(2780):376–377. doi: 10.1126/science.107.2780.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod J. From enzymatic adaptation to allosteric transitions. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):475–483. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3748.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. The role of the lac promotor locus in the regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1336–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quay S. C., Dick T. E., Oxender D. L. Role of transport systems in amino acid metabolism: leucine toxicity and the branched-chain amino acid transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1257-1265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. Inhibition of E. coli strains by amino-acids. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):80–81. doi: 10.1038/171080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIO-HUERTOS M., GONZALEZ-VAZQUEZ C. Morphology and pathogenicity of L forms of Clostridium tetani induced by glycine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:626–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R. The purification and properties of phosphotransacetylase. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE D. Some aspects of the hydrolysis of proline peptides by a prolineless mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):821–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., BIRGE C. H. NUCLEOTIDE ACCUMULATION INDUCED IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY GLYCINE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1124–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1124-1127.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Dawes E. A. Poly- -hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis and the regulation of glucose metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):55–66. doi: 10.1042/bj1250055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Signer E. R. Catabolite-repression-like phenomenon in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1197–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1197-1200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Amino acid biosynthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:532–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vela G. R., Rosenthal R. S. Effect of peptone on Azotobacter morphology. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):260–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.260-266.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn M. R., Niven C. F., Jr Amino Acid Interrelationships in the Nutrition of Streptococcus bovis. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jun;55(6):769–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.6.769-776.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


