Abstract
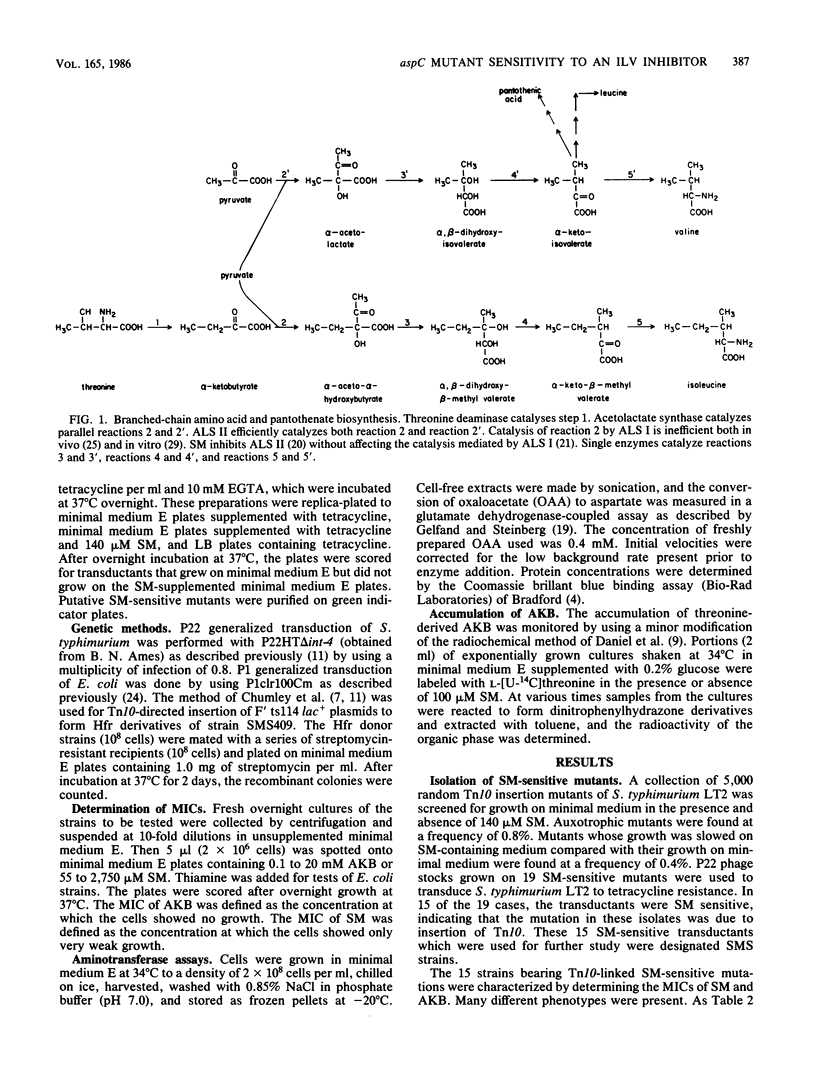
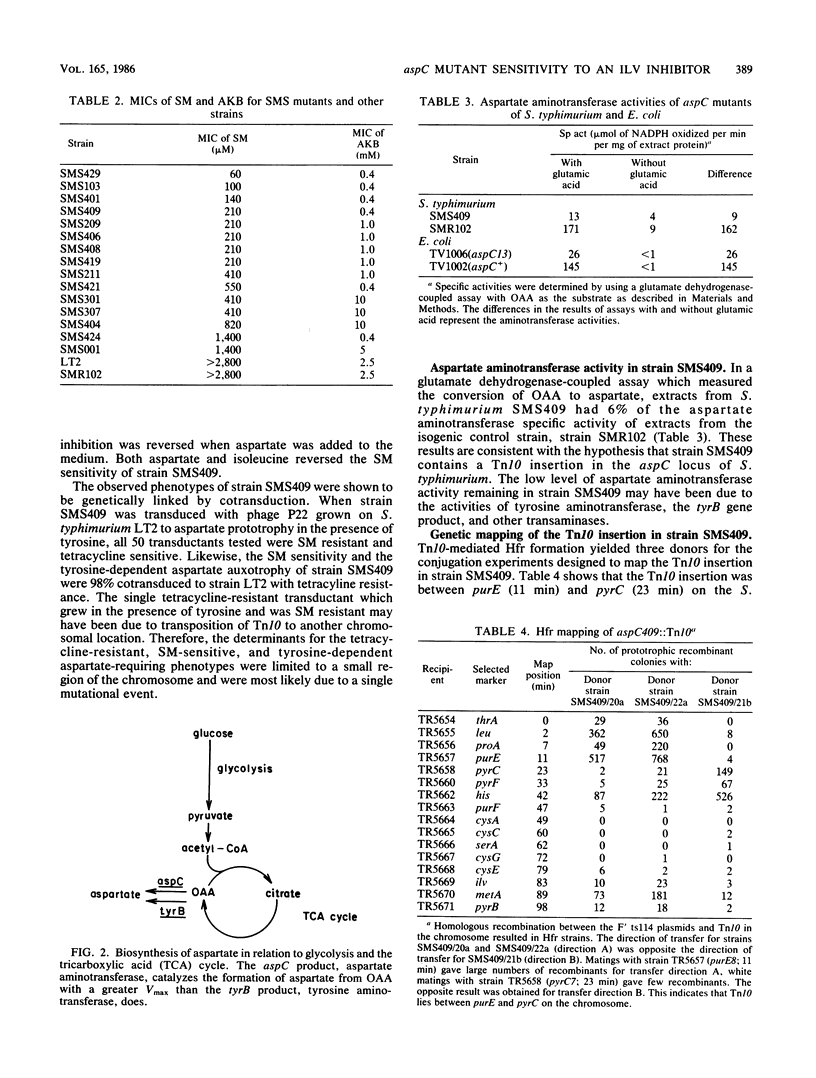
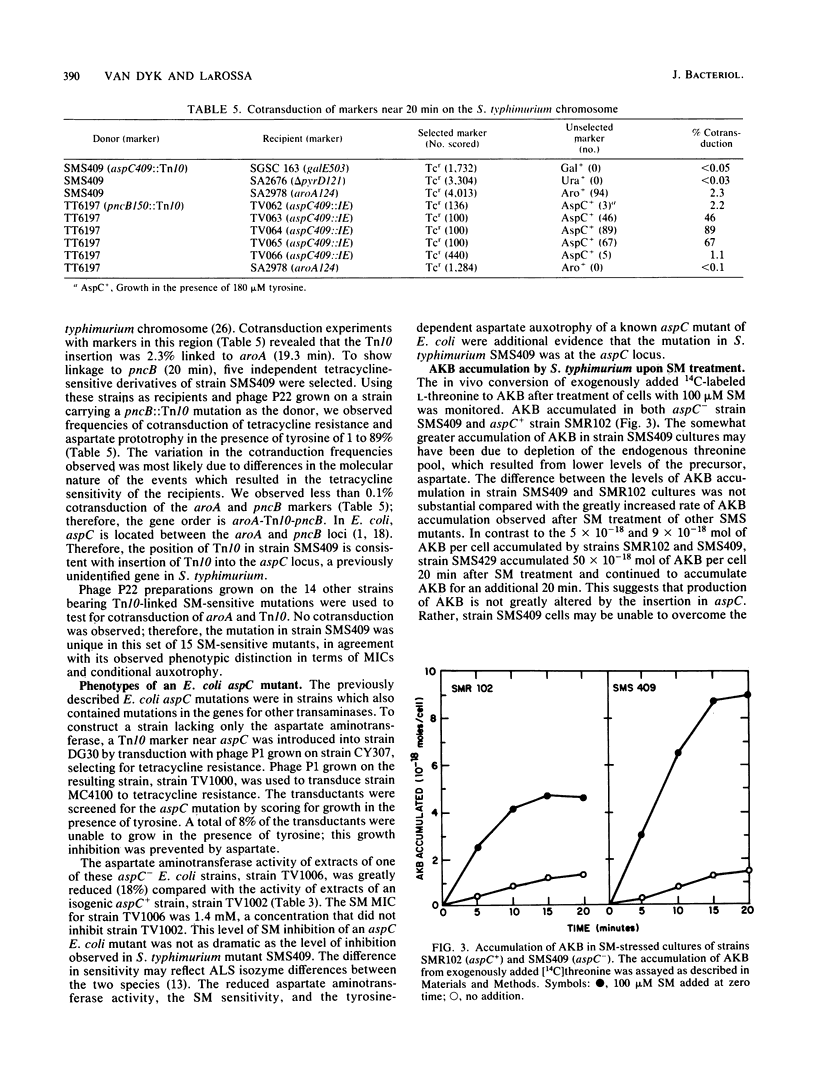
Sulfometuron methyl is a potent and specific inhibitor of acetolactate synthase II in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutant strains sensitive to sulfometuron methyl on minimal medium were isolated following mutagenesis with Tn10. A conditionally auxotrophic insertion mutant, strain SMS409, which required aspartate at high temperatures or in the presence of tyrosine, was found among the 15 mutants isolated. The Tn10 insertion in strain SMS409 was mapped by conjugation and transduction to the region between aroA and pncB at 20 min on the chromosome of S. typhimurium; this location is similar to the genetic location of aspC in Escherichia coli. The specific activity of the aspC product, aspartate aminotransferase, was severely reduced in strain SMS409. This indicated that the Tn10 insertion in strain SMS409 inactivated aspC. An aspC mutant of E. coli was also inhibited by either sulfometuron methyl or tyrosine. We present a hypothesis which relates the observed alpha-ketobutyrate accumulation in sulfometuron methyl-inhibited cultures of strain SMS409 to aspartate starvation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget P. B., Poteete A. R., Sauer R. T. Control of phage P22 tail protein expression by transcription termination. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 15;164(4):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaleff R. S., Mauvais C. J. Acetolactate synthase is the site of action of two sulfonylurea herbicides in higher plants. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1443–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4656.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danchin A., Dondon L., Daniel J. Metabolic alterations mediated by 2-ketobutyrate in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):473–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00382086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J., Dondon L., Danchin A. 2-Ketobutyrate: a putative alarmone of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(3):452–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00331076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J., Joseph E., Danchin A. Role of 2-ketobutyrate as an alarmone in E. coli K12: inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity mediated by the phosphoenolpyruvate: glycose phosphotransferase transport system. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):467–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00382085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Felice M., Guardiola J., Esposito B., Iaccarino M. Structural genes for a newly recognized acetolactate synthase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1068–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1068-1077.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eoyang L., Silverman P. M. Purification and subunit composition of acetohydroxyacid synthase I from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):184–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.184-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKASAWA T., NIKAIDO H. Galactose-sensitive mutants of Salmonella. II. Bacteriolysis induced by galactose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco S. C., Dumas K. S. Genetic analysis of mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the herbicide sulfometuron methyl. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):21–35. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P., Donegan J., Mullen J., Tsui P., Freundlich M., Eoyang L., Weber R., Silverman P. M. The ilvB locus of Escherichia coli K-12 is an operon encoding both subunits of acetohydroxyacid synthase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3979–3993. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Rudo N. Mapping of the aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferase genes tyrB and aspC. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):441–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.441-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Steinberg R. A. Escherichia coli mutants deficient in the aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):429–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.429-440.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R. A., Schloss J. V. The sulfonylurea herbicide sulfometuron methyl is an extremely potent and selective inhibitor of acetolactate synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8753–8757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R. A., Smulski D. R. ilvB-encoded acetolactate synthase is resistant to the herbicide sulfometuron methyl. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):391–394. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.391-394.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther R. P., Calhoun D. H., Adams C. W., Hauser C. A., Gray J., Hatfield G. W. Molecular basis of valine resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):922–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primerano D. A., Burns R. O. Metabolic basis for the isoleucine, pantothenate or methionine requirement of ilvG strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1202–1211. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1202-1211.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Van Dyk D. E., Vasta J. F., Kutny R. M. Purification and properties of Salmonella typhimurium acetolactate synthase isozyme II from Escherichia coli HB101/pDU9. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4952–4959. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Berg C. M., Sobol T. J. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in acetohydroxy acid synthases I and II. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1258–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1258-1263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Berg C. M. Substrate channeling: alpha-ketobutyrate inhibition of acetohydroxy acid synthase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1509–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1509-1512.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Levinthal M., Williams L. S. Synthesis of the isoleucyl- and valyl-tRNA synthetases and the isoleucine-valine biosynthetic enzymes in a threonine deaminase regulatory mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 5;175(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. H., De Felice M., Devereux J., Calvo J. M. Molecular structure of ilvIH and its evolutionary relationship to ilvG in Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5299–5313. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hauser C. A., Hatfield G. W. The nucleotide sequence of the ilvBN operon of Escherichia coli: sequence homologies of the acetohydroxy acid synthase isozymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3995–4010. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Wiesmeyer H., Kalckar H. M., Jordan E. HEREDITARY DEFECTS IN GALACTOSE METABOLISM IN ESCHERICHIA COLI MUTANTS, II. GALACTOSE-INDUCED SENSITIVITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1786–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Felice M., Lago C. T., Squires C. H., Calvo J. M. Acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


