Abstract
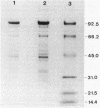
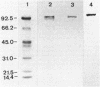
We confirmed an earlier report (B. B. Buchanan, J. Bacteriol. 119:1066-1068, 1974) that the nonsulfur purple photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum contains pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase (EC 2.7.9.1) activity that is absolutely dependent upon all three substrates by performing enzyme assays in both the forward (phosphoenolpyruvate formation) and reverse (ATP formation) directions. Of the various carbon sources tested, photoheterotrophic growth on DL-lactate plus bicarbonate proved to be best for the production of dikinase activity units. A four-step protocol, which included batch DEAE-cellulose processing, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and chromatography on hydroxylapatite and Blue A Dyematrex gels, was devised for partially purifying the enzyme from such cells. The protein was purified about 80-fold to an apparent electrophoretic purity of about 60% and a final specific activity of 3.6 U/mg of protein, with about a 35% overall recovery of activity units. Estimations of native and monomeric relative molecular weights by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, high-pressure liquid chromatography-based size exclusion chromatography, denaturing electrophoresis, and immunoblotting suggested that the holoenzyme was most likely a homodimer of 92.7-kilodalton subunits. The results are compared with related previous data on the nonphotosynthetic bacterial dikinase and the C4 mesophyll chloroplast enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Burnell J. N., Hatch M. D. Regulation of C4 photosynthesis: inactivation of pyruvate, Pi dikinase by ADP-dependent phosphorylation and activation by phosphorolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):492–503. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benziman M. Pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase from Acetobacter sylinum. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:192–199. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B. Orthophosphate requirement for the formation of phosphoenolpyruvate from pyruvate by enzyme preparations from photosynthetic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1066–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1066-1068.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budde R. J., Holbrook G. P., Chollet R. Studies on the dark/light regulation of maize leaf pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase by reversible phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss N. H., Evans C. T., Wood H. G. Pyruvate phosphate dikinase: sequence of the histidyl peptide, the pyrophosphoryl and phosphoryl carrier. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5805–5809. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss N. H., Wood H. G. Covalent chemistry of pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;87:51–66. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)87007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson C. A., Smith W. W., Eisenberg D., Hartman F. C. Preliminary structural studies of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11594–11596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Subunit dissociation and reconstitution of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Chromatium vinosum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Feb 1;236(2):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90651-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum, and evidence for phosphate, ribose and an adenine-like unit covalently bound to the iron protein. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):251–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1750251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner Y., Michaels G., Wood H. G. Pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase of Bacteroides symbiosus and Propionibacterium shermanii. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:199–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner Y., Wood H. G. Steady state and exchange kinetics of pyruvate, phosphate dikinase from Propionibacterium shermanii. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7920–7928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. F., Goss N. H., Wood H. G. Modification of pyruvate, phosphate dikinase with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate: evidence for a catalytically critical lysine residue. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2518–2523. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Proton-Translocating Inorganic Pyrophosphatase in Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Tonoplast Vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):46–52. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahashi K., Hayakawa S., Sugiyama T. Cold lability of pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase in the maize leaf. Plant Physiol. 1978 Nov;62(5):826–830. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.5.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T. Purification, molecular, and catalytic properties of pyruvate phosphate dikinase from the maize leaf. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 17;12(15):2862–2868. doi: 10.1021/bi00739a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Perrot B., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. The structure of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3251–3270. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]