Abstract
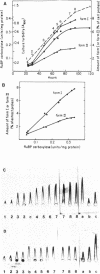
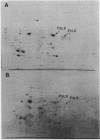
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBPC-O) activity was greatly enhanced when Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides was grown in a mineral salts medium supplied with 1.5% CO2 in hydrogen. Analysis of cell extracts by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that cells growing on 1.5% CO2 in H2 specifically accumulated RuBPC-O polypeptides. Quantitative immunological determinations revealed that accumulation of form I and form II RuBPC-O closely correlates with the increase of specific activity. However, the two enzymes appeared to be derepressed at different levels. Upon transfer from heterotrophic to autotrophic (1.5% CO2) growth conditions, the intracellular form I RuBPC-O concentration was augmented 17-fold, whereas the form II RuBPC-O content increased only fourfold. As a result, the form I-form II ratio changed from 0.5 to about 2.0. Since this change in the RuBPC-O ratio occurred in the early stage of growth, it suggests that form I RuBPC-O is required for growth under drastic CO2 limitation. The difference in the extent of derepression of form I and form II RuBPC-O also indicates that the synthesis of each enzyme is regulated somewhat independently of the other.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassett C. L., Rinehart C. A., Rawson J. R. Immunological determination of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and the large and small subunits of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in leaves of the c(4) plant pearl millet. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):828–832. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braatz J. A., McIntire K. R. A rapid and effecient method for the isolation of proteins from polyacrylamide cells. Prep Biochem. 1977;7(6):495–509. doi: 10.1080/00327487708065516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornari C. S., Kaplan S. Identification of nitrogenase and carboxylase genes in the photosynthetic bacteria and cloning of a carboxylase gene from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Characterization of antiserum directed against form II ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):1020–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.1020-1022.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Isolation and preliminary characterization of two forms of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):818–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.818-823.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Structural differences in the catalytic subunits of form I and form II ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1188–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1188-1193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller E. D., Chory J., Kaplan S. Cloning and characterization of the gene product of the form II ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):469–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.469-472.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumley F. G., Schmidt G. W. Rocket and crossed immunoelectrophoresis of proteins solubilized with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):86–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quivey R. G., Jr, Tabita F. R. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the form II ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase gene from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles L. S., Tabita F. R. Derepression of the synthesis of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):458–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.458-464.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Phares E. F., Long M. V., Norton I. L., Stringer C. D., Hartman F. C. Isolation, characterization, and crystallization of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase from autotrophically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):490–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.490-501.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Davidson E., Marrs B. L. Depression of the synthesis of the intermediate and large forms of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Jul;138(3):233–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00402127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Caruso P., Whitman W. Facile assay of enzymes unique to the Calvin cycle in intact cells, with special reference to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):462–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters C. A one-step biuret assay for protein in the presence of detergent. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):695–698. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver K. E., Tabita F. R. Isolation and partial characterization of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides mutants defective in the regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):507–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.507-515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W., Tabita F. R. Inhibition of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1034–1039. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90758-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]