Abstract
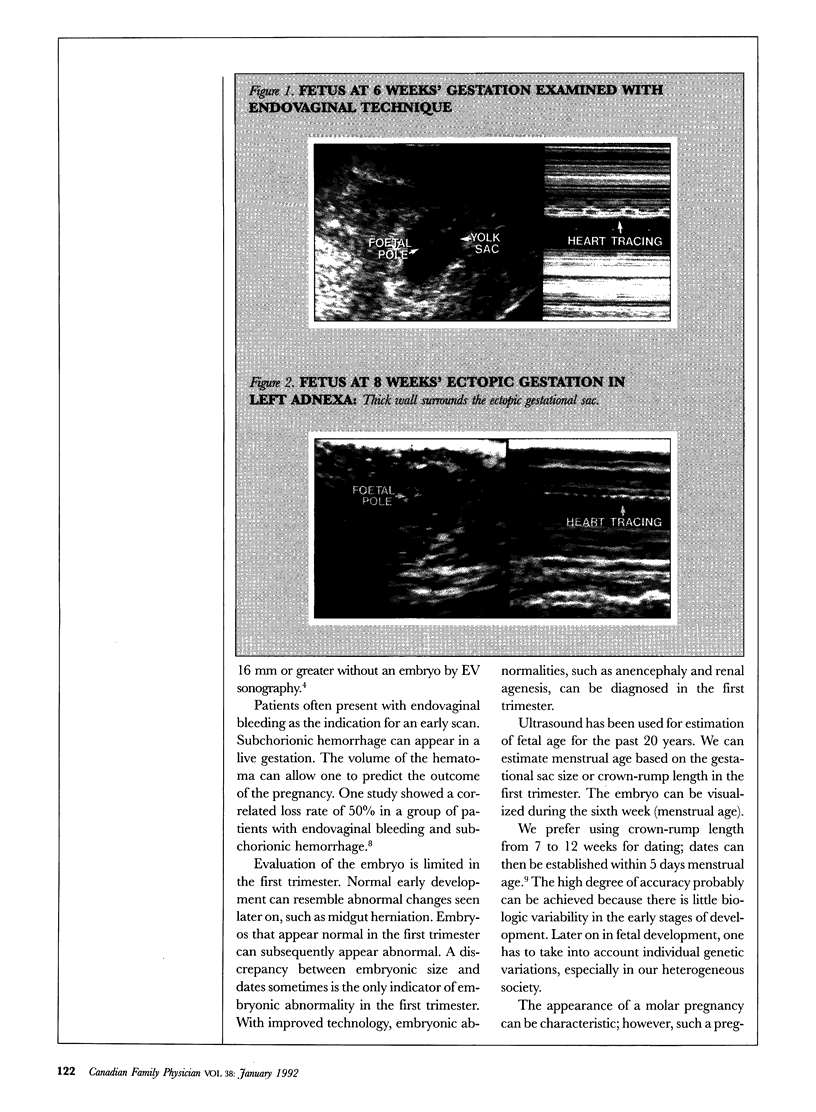
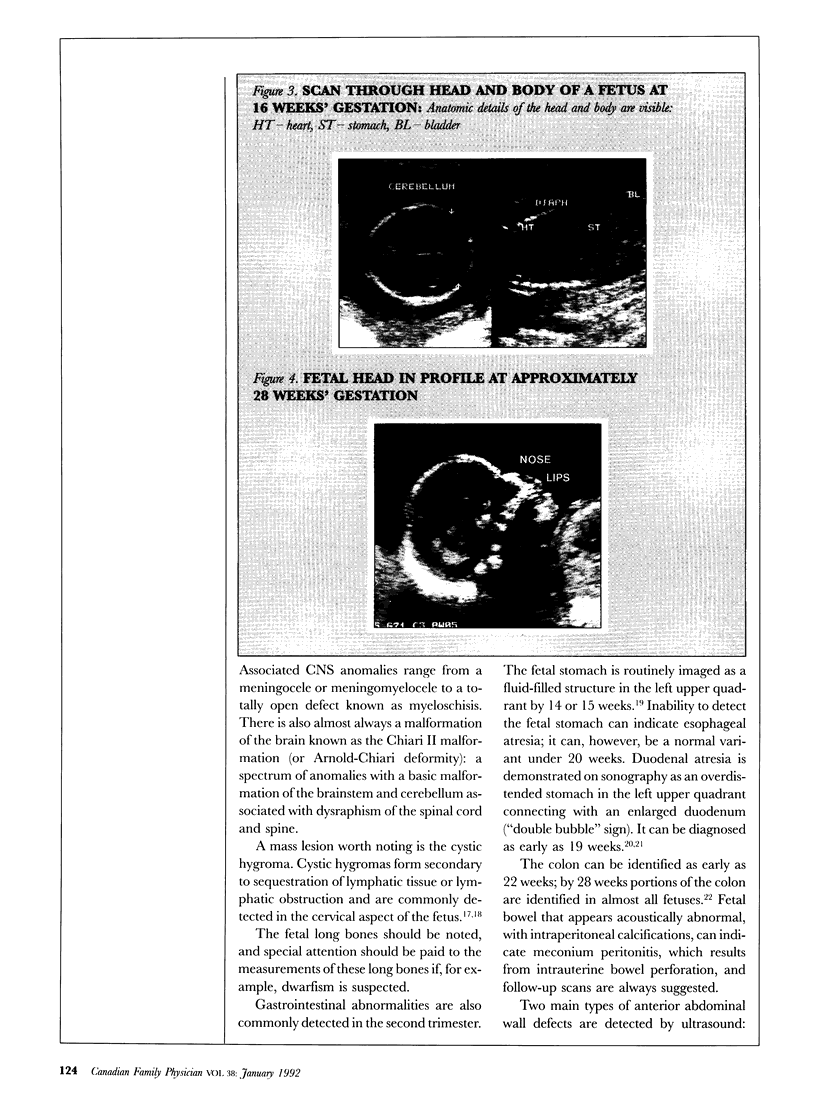
First-trimester ultrasound examination is of value to establish dates or assess fetal viability in cases of bleeding but provides limited information on the well-being of the fetus. At between 16 and 20 weeks' gestation, examination of fetal anatomy allows many abnormalities to be detected. Third-trimester ultrasound examination is predominantly for follow up of growth and normal development or of any abnormalities seen earlier.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barss V. A., Benacerraf B. R., Frigoletto F. D., Jr Antenatal sonographic diagnosis of fetal gastrointestinal malformations. Pediatrics. 1985 Sep;76(3):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacciatore B. Can the status of tubal pregnancy be predicted with transvaginal sonography? A prospective comparison of sonographic, surgical, and serum hCG findings. Radiology. 1990 Nov;177(2):481–484. doi: 10.1148/radiology.177.2.2217789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman B. G., Grumbach K., Arger P. H., Mintz M. C., Arenson R. L., Mennuti M., Gabbe S. G. Twin gestations: monitoring of complications and anomalies with US. Radiology. 1987 Nov;165(2):449–453. doi: 10.1148/radiology.165.2.3310098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald I. Ultrasonic echo sounding in obstetrical and gynecological diagnosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Dec 1;93(7):935–941. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(65)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman S. F. Deaths from ectopic pregnancy, United States, 1979 to 1980. Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Sep;62(3):334–338. doi: 10.1097/00006250-198309000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filly R. A. Ectopic pregnancy: the role of sonography. Radiology. 1987 Mar;162(3):661–668. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.3.3544031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grignon A., Filion R., Filiatrault D., Robitaille P., Homsy Y., Boutin H., Leblond R. Urinary tract dilatation in utero: classification and clinical applications. Radiology. 1986 Sep;160(3):645–647. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.3.3526402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks C. H. Twinning in relation to birth weight, mortality, and congenital anomalies. Obstet Gynecol. 1966 Jan;27(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouppila P., Kirkinen P. Problems associated with the ultrasonic diagnosis of abruptio placentae. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1982 Feb;20(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0020-7292(82)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouppila P., Kirkinen P. Ultrasonic and clinical aspects in the diagnosis and prognosis of congenital gastrointestinal anomalies. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1984 Jul-Aug;10(4):465–472. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(84)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knab D. R. Abruptio placentae. An assessment of the time and method of delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Nov;52(5):625–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C. S., Lyons E. A., Lindsay D. J. Early diagnosis of nonviable pregnancy with endovaginal US. Radiology. 1988 May;167(2):383–385. doi: 10.1148/radiology.167.2.3282258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C. S., Lyons E. A., Lindsay D. J. Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy. Radiol Clin North Am. 1990 Jan;28(1):19–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C. S., Lyons E. A., Zheng X. H., Lindsay D. J., Holt S. C. Endovaginal US: demonstration of cardiac activity in embryos of less than 5.0 mm in crown-rump length. Radiology. 1990 Jul;176(1):71–74. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.1.2191372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony B. S., Filly R. A., Callen P. W. Amnionicity and chorionicity in twin pregnancies: prediction using ultrasound. Radiology. 1985 Apr;155(1):205–209. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.1.3883418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning F. A., Platt L. D., Sipos L. Antepartum fetal evaluation: development of a fetal biophysical profile. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Mar 15;136(6):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz M. C., Kurtz A. B., Arenson R., Arger P. H., Coleman B. G., Wapner R. J., Goldberg B. B. Abruptio placentae: apparent thickening of the placenta caused by hyperechoic retroplacental clot. J Ultrasound Med. 1986 Jul;5(7):411–413. doi: 10.7863/jum.1986.5.7.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg D. A., Cyr D. R., Mack L. A., Wilson D. A., Shuman W. P. Sonographic spectrum of placental abruption. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Jan;148(1):161–164. doi: 10.2214/ajr.148.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg D. A., Filly R. A., Filho D. L., Laing F. C., Mahony B. S. Abnormal pregnancy: early diagnosis by US and serum chorionic gonadotropin levels. Radiology. 1986 Feb;158(2):393–396. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.2.3510444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg D. A., Laing F. C., Filly R. A. Threatened abortion: sonographic distinction of normal and abnormal gestation sacs. Radiology. 1986 Feb;158(2):397–400. doi: 10.1148/radiology.158.2.3510445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. F., Cefalo R. C., Bair D. G. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of fetal cystic hygroma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Oct 15;138(4):464–466. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips H. E., McGahan J. P. Intrauterine fetal cystic hygromas: sonographic detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Apr;136(4):799–802. doi: 10.2214/ajr.136.4.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius D. H., Drose J. A., Manco-Johnson M. L. Fetal lateral ventricular ratio determination during the second trimester. J Ultrasound Med. 1986 Mar;5(3):121–124. doi: 10.7863/jum.1986.5.3.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius D. H., Gosink B. B., Clautice-Engle T., Leopold G. R., Minnick C. M. Sonographic evaluation of the fetal stomach: significance of nonvisualization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Nov;151(5):987–989. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.5.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbrei E. E., Pham D. H. Placental abruption and subchorionic hemorrhage in the first half of pregnancy: US appearance and clinical outcome. Radiology. 1986 Jul;160(1):109–112. doi: 10.1148/radiology.160.1.3520643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S. F., Siu C. M., Switzer P. J. Sonographic demonstration of heterotopic pregnancy: report of two cases. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1989 Dec;40(6):316–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirt B. A., Oliphant M., Gordon L. P. Fetal central nervous system abnormalities. Radiol Clin North Am. 1990 Jan;28(1):59–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox A. J., Weinberg C. R., O'Connor J. F., Baird D. D., Schlatterer J. P., Canfield R. E., Armstrong E. G., Nisula B. C. Incidence of early loss of pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 28;319(4):189–194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807283190401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wladimiroff J. W., Campbell S. Fetal urine-production rates in normal and complicated pregnancy. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):151–154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H. C., Goodman J. D., Carr L., Rabinowitz J. G. Intradecidual sign: a US criterion of early intrauterine pregnancy. Radiology. 1986 Nov;161(2):463–467. doi: 10.1148/radiology.161.2.3532191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]