Abstract
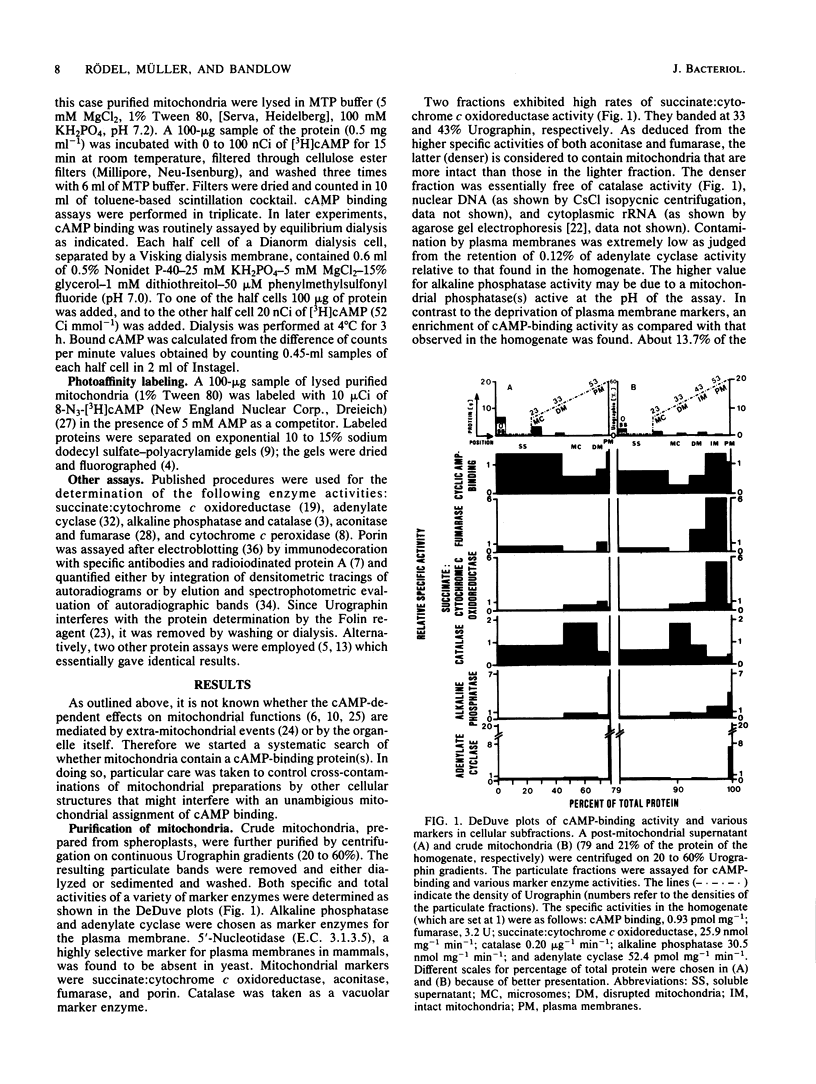
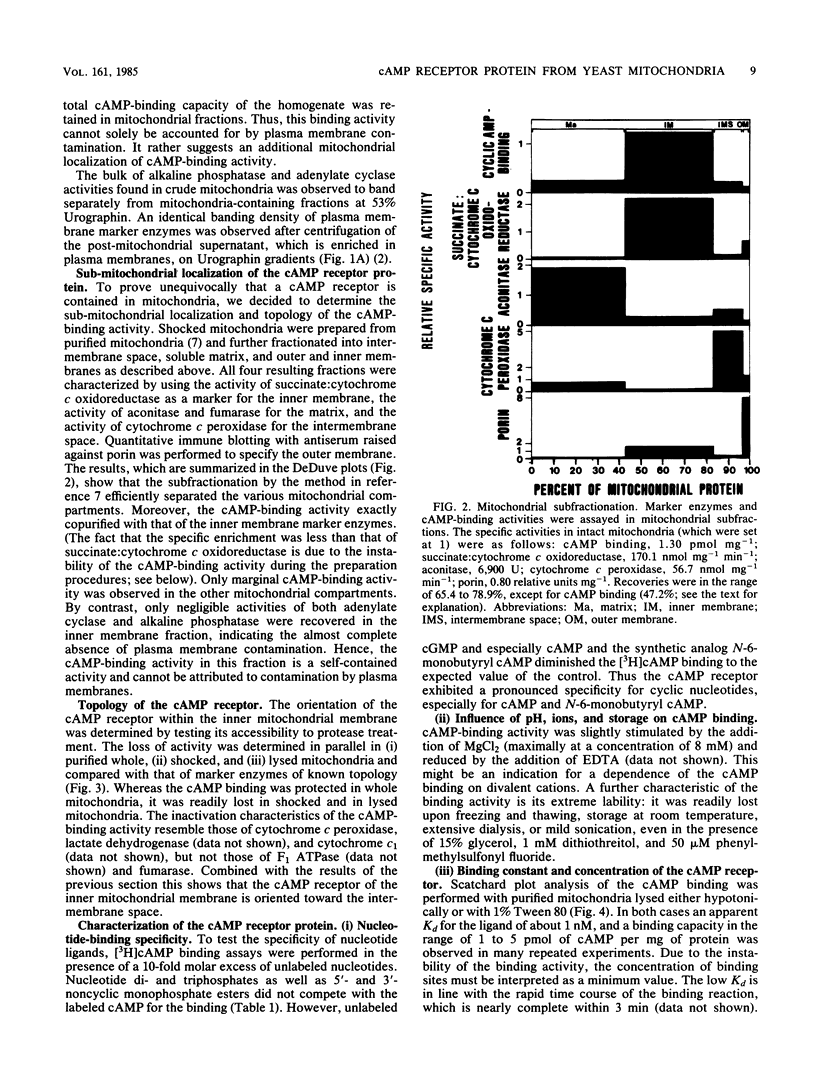
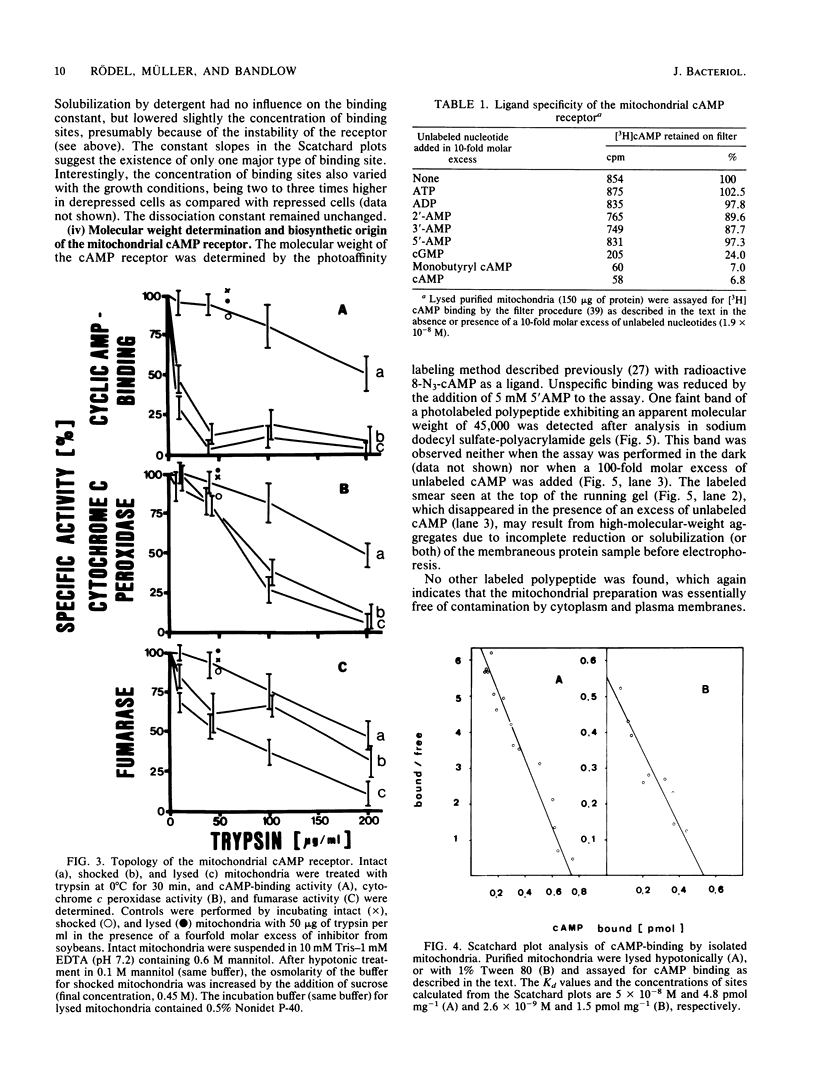
We have identified and characterized a cyclic AMP receptor protein in mitochondria of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The binding is specific for cyclic nucleotides, particularly for cyclic AMP which is bound with high affinity (Kd of 10(-9) M) at 1 to 5 pmol/mg of mitochondrial protein. The mitochondrial cyclic AMP receptor is synthesized on cytoplasmic ribosomes and has an apparent molecular weight of 45,000 as determined by photoaffinity labeling. It is localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane and faces the intermembrane space. Cross-contamination of mitochondrial inner membranes by plasma membranes or soluble cytoplasmic proteins is excluded.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandlow W., Bauer P. Separation and some properties of the inner and outer membranes of yeast mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:311–333. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60962-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandlow W. Membrane separation and biogenesis of the outer membrane of yeast mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):105–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran K., Jayaraman J. Effect of cyclic AMP on the biogenesis of cytochrome oxidase in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):52–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djavadi-Ohaniance L., Rudin Y., Schatz G. Identification of enzymically inactive apocytochrome c peroxidase in anaerobically grown Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., Butow R. A. Variant forms of mitochondrial translation products in yeast: evidence for location of determinants on mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1083–1086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang M., Butow R. A. Nucleotide reversal of mitochondrial repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1579–1583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. In vitro studies on the biogenesis of the outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3427–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson T., Jergil B. Protein kinase activity and endogenous phosphorylation in subfractions of rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 11;588(3):380–391. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson C. S., Krebs E. G. Characterization of a cyclic AMP-binding protein from bakers' yeast. Identification as a regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2137–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes P. K., McDonough J. P., Mahler H. R. Identification of cAMP binding proteins associated with the plasma membrane of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Racker E. Purification and characterization of two protein kinases from bovine heart mitochondrial membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4547–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlicki W., Grankowski N., Gasior E. Isolation and properties of two protein kinases from yeast which phosphorylate casein and some ribosomal proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):493–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B., Burger G., Bandlow W. Activity of reduced ubiquinone: cytochrome c oxidoreductase with various ubiquinol-isoprenologues as substrate and corresponding inhibitory effect of antimycin in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 18;368(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens D., Lustig A., Rabinowitz M. Purification of mitochondrial RNA polymerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1474–1481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Jaynes P. K., McDonough J. P., Hanson D. K. Catabolite repression in yeast: mediation by cAMP. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:455–474. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Lin C. C. Exogenous adenosine 3': 5'-monophosphate can release yeast from catabolite repression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91500-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):462–480. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.462-480.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz A. H., Rudolph S. A., Haley B. E., Greengard P. Photoaffinity labeling of a protein kinase from bovine brain with 8-azidoadenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3858–3862. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Spectrophotometric measurements of the enzymatic formation of fumaric and cis-aconitic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigobello M. P., Carignani G., Pinna L. A. Esolation and partial characterization of a membrane bound protein kinase from mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1400–1406. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riquelme P. T., Hosey M. M., Marcus F., Kemp R. G. Phosphorylation of muscle phosphofructokinase by the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1480–1487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):530–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Garren L. D. An assay for adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate based on the association of the nucleotide with a partially purified binding protein. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 13;9(21):4223–4229. doi: 10.1021/bi00823a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plaat J. B. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate stimulates trehalose degradation in baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):580–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90643-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]