Abstract
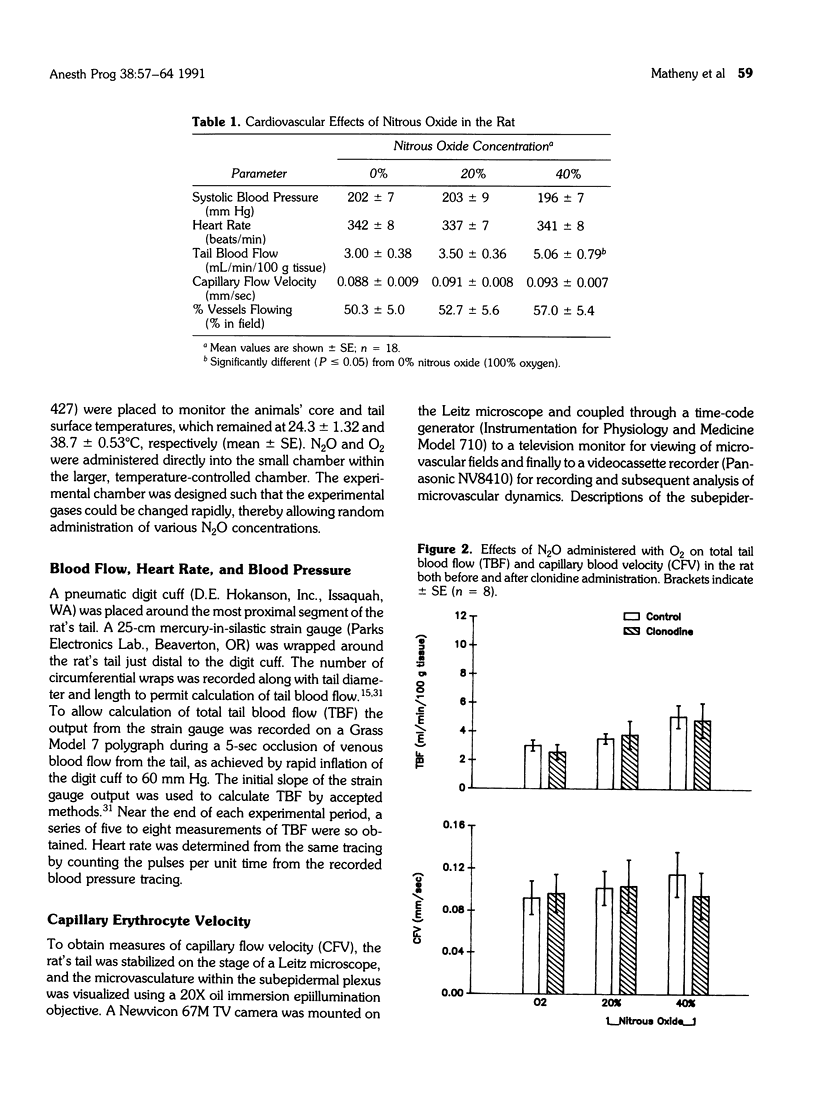
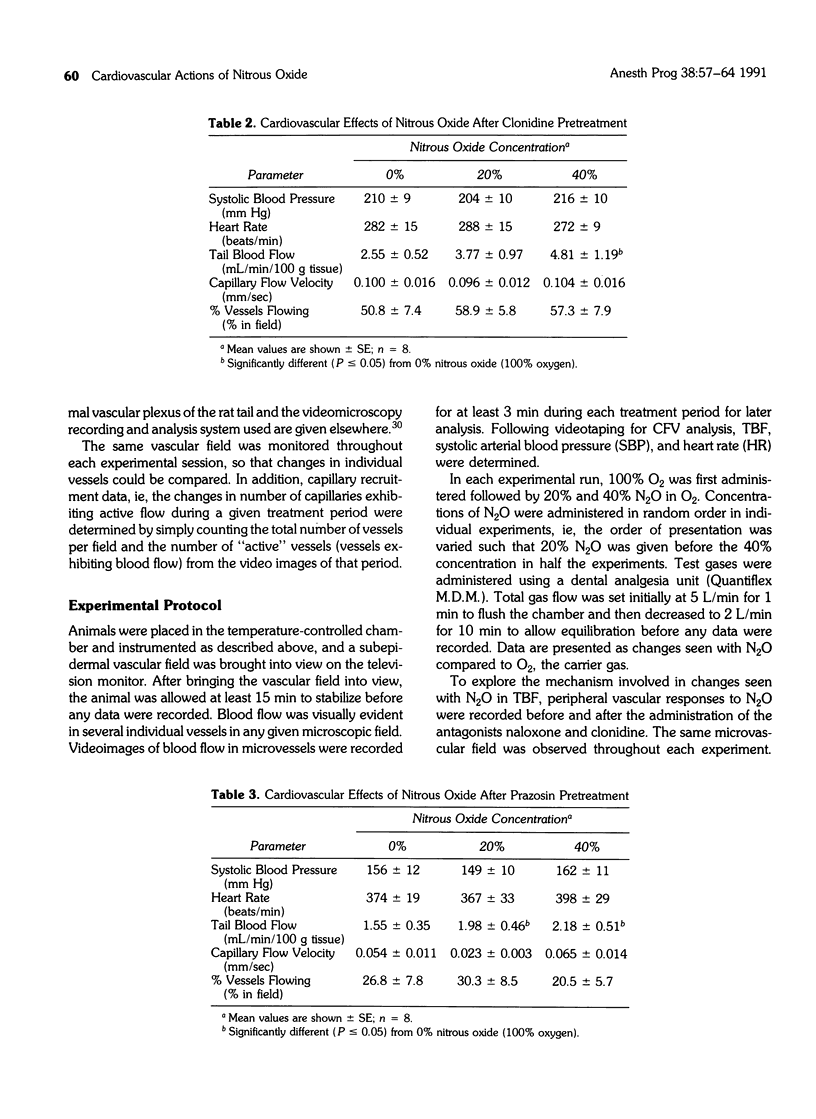
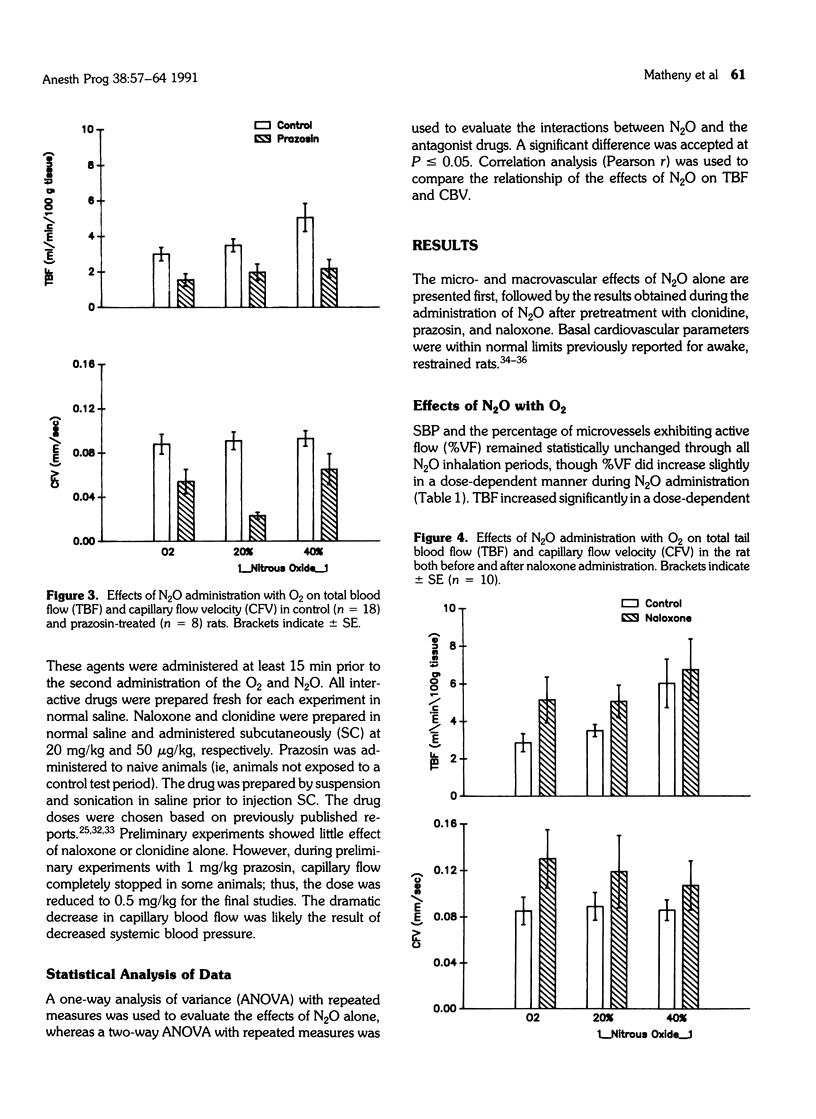
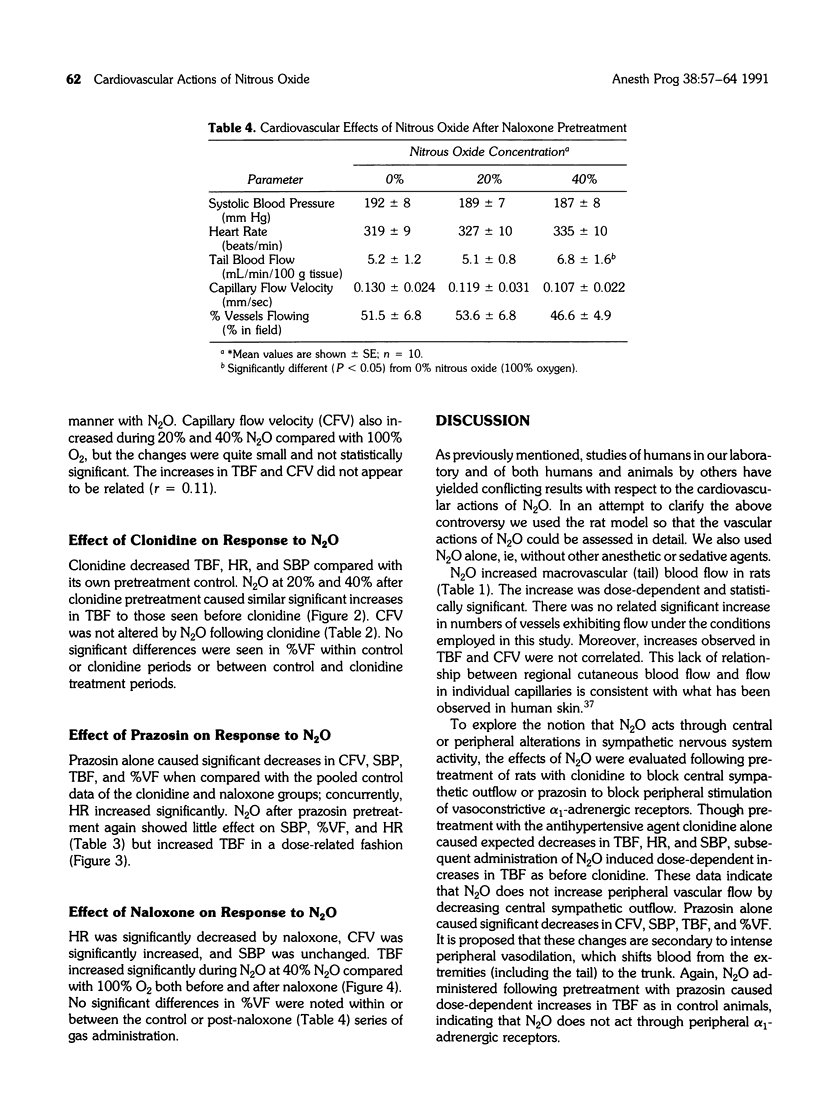
The aims of this study were: (1) to determine the macro- and microvascular actions of nitrous oxide (N2O) in the rat, and (2) to determine whether the vascular actions of N2O involved specific interaction with alpha-adrenergic receptors or opioid receptors. Systolic blood pressure, heart rat, total tail blood flow, blood cell velocity in subepidermal capillaries of the tail, and percentage of capillaries exhibiting flow were monitored in conscious rats during the administration of N2O before and after administration of clonidine (an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist), prazosin (an alpha 1-adrenergic antagonist) or naloxone (an opioid antagonist). Total tail blood flow increased significantly in a dose-dependent manner with N2O at 20% and 40% with oxygen. This action of N2O was not blocked by clonidine, prazosin, or naloxone. Capillary flow velocity increased during 20% and 40% N2O compared to 100% O2, but the changes were not statistically significant nor did they correlate with the changes in tail blood flow. These data suggest that the peripheral vascular action of N2O does not involve specific actions at alpha-adrenergic receptors or opioid receptors and may be the result of direct actions on the peripheral vasculature.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J., Luthi P., Sonnay M., Boillat N. Effect of acute administration of prazosin on blood pressure, heart rate and plasma renin level in the conscious normotensive rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1986 Jul;13(7):535–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1986.tb00936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron B. A., Van Loon G. R. Role of sympathoadrenomedullary system in cardiovascular response to stress in rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1989 Nov;28(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(89)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman V. L., Hoffman W. E., Miletich D. J., Albrecht R. F. Cerebrovascular and cerebral metabolic effects of N2O in unrestrained rats. Anesthesiology. 1990 Aug;73(2):269–272. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199008000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Finck A. D., Ngai S. H. Nitrous oxide analgesia: reversal by naloxone and development of tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Dec;203(3):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Ngai S. H., Finck A. D. Nitrous oxide "analgesia": resemblance to opiate action. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):967–968. doi: 10.1126/science.982058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. C., Quock R. M. A study of central opioid receptor involvement in nitrous oxide analgesia in mice. Anesth Prog. 1990 Jul;37(4):181–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daras C., Cantrill R. C., Gillman M. A. [3H]naloxone displacement: evidence for nitrous oxide as opioid receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90626-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. R., Chinyanga H. M. Cardiovascular collapse associated with nitrous oxide anaesthetic: a case report. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1982 Sep;29(5):484–488. doi: 10.1007/BF03009414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch G., Samra S. K. Effects of nitrous oxide on global and regional cortical blood flow. Stroke. 1990 Sep;21(9):1293–1298. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.9.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on pre- and postsynaptically located alpha-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;36(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond J. C., Scheller M. S., Todd M. M. The effect of nitrous oxide on cortical cerebral blood flow during anesthesia with halothane and isoflurane, with and without morphine, in the rabbit. Anesth Analg. 1987 Nov;66(11):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele J. H., Smith N. T. Cardiovascular effects of 40 percent nitrous oxide in man. Anesth Analg. 1972 Nov-Dec;51(6):956–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga A. F., Epstein R. M. Sympathetic excitation during nitrous-oxide-halothane anesthesia in the cat. Anesthesiology. 1973 Jul;39(1):23–36. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197307000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillman M. A., Kok L., Lichtigfeld F. J. Paradoxical effect of naloxone on nitrous oxide analgesia in man. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan 25;61(2):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. M., Stephenson W. H., Pettinger W. A. Pharmacological evidence for a functional role of the prejunctional alpha-adrenoreceptor in noradrenergic neurotransmission in the conscious rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;311(2):129–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00510251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Abboud F. M. Factors that influence blood flow in skeletal muscle and skin. Anesthesiology. 1974 Aug;41(2):139–156. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197408000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. J., Quock R. M. Cardiovascular influences of nitrous oxide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Anesth Prog. 1989 May-Jun;36(3):88–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobes D. R., Kennell E. M., Bush G. L., Mull T. D., Lecky J. H., Behar M. G., Wollman H. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism during morphine--nitrous oxide anesthesia in man. Anesthesiology. 1977 Jul;47(1):16–18. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197707000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Mattson M., Newman A. H., Rice K. C., Skolnick P. Stereospecific reversal of nitrous oxide analgesia by naloxone. Life Sci. 1989;44(11):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Graczak L. M. Influence of narcotic antagonist drugs upon nitrous oxide analgesia in mice. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 2;440(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Kouchich F. J., Tseng L. F. Does nitrous oxide induce release of brain opioid peptides? Pharmacology. 1985;30(2):95–99. doi: 10.1159/000138056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quock R. M., Walczak C. K., Henry R. J., Chen D. C. Effect of subtype-selective opioid receptor blockers on nitrous oxide antinociception in rats. Pharmacol Res. 1990 May-Jun;22(3):351–357. doi: 10.1016/1043-6618(90)90733-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. R., Shepherd S., McSorley T. Evaluation of the role of skin temperature in the response of cutaneous capillary blood flow to indirect heat. Microcirc Endothelium Lymphatics. 1988 Dec;4(6):447–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. I., Matheny J. L., Falace D. A., O'Reilly J. E., Norton J. C. Effect of age on the digit blood flow response to sedative concentrations of nitrous oxide. Anesth Prog. 1984 Jan-Feb;31(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. H., Rees J. M. The effects of naloxone on the analgesic activities of general anaesthetics. Experientia. 1981 Mar 15;37(3):289–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01991660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuebner E. A. Nitrous oxide--analgesia or anesthesia. Dent Clin North Am. 1973 Apr;17(2):235–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY R. J. The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):1–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLMAN H., ALEXANDER C., COHEN P. J., SMITH T. C., CHASE P. E., VANDERMOLEN R. CEREBRAL CIRCULATION DURING GENERAL ANESTHESIA AND HYPERVENTILATION IN MAN.: THIOPENTAL INDUCTION TO NITROUS OXIDE AND D-TUBOCURARINE. Anesthesiology. 1965 May-Jun;26:329–334. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196505000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga J. R., Joseph S. A., Knigge K. M. The effects of nitrous oxide on the central endogenous pro-opiomelanocortin system in the rat. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 8;420(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga J. R., Joseph S. A., Knigge K. M. The effects of nitrous oxide on the secretory activity of pro-opiomelanocortin peptides from basal hypothalamic cells attached to cytodex beads in a superfusion in vitro system. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 8;420(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


