Abstract
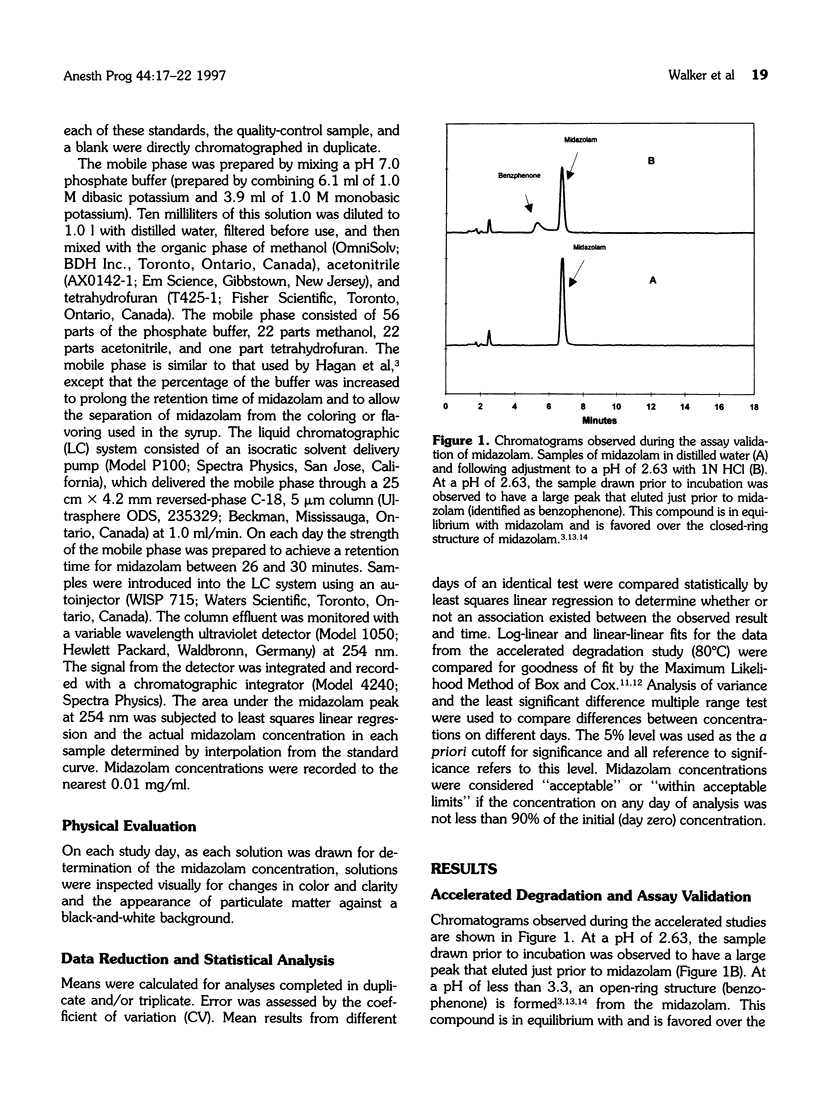
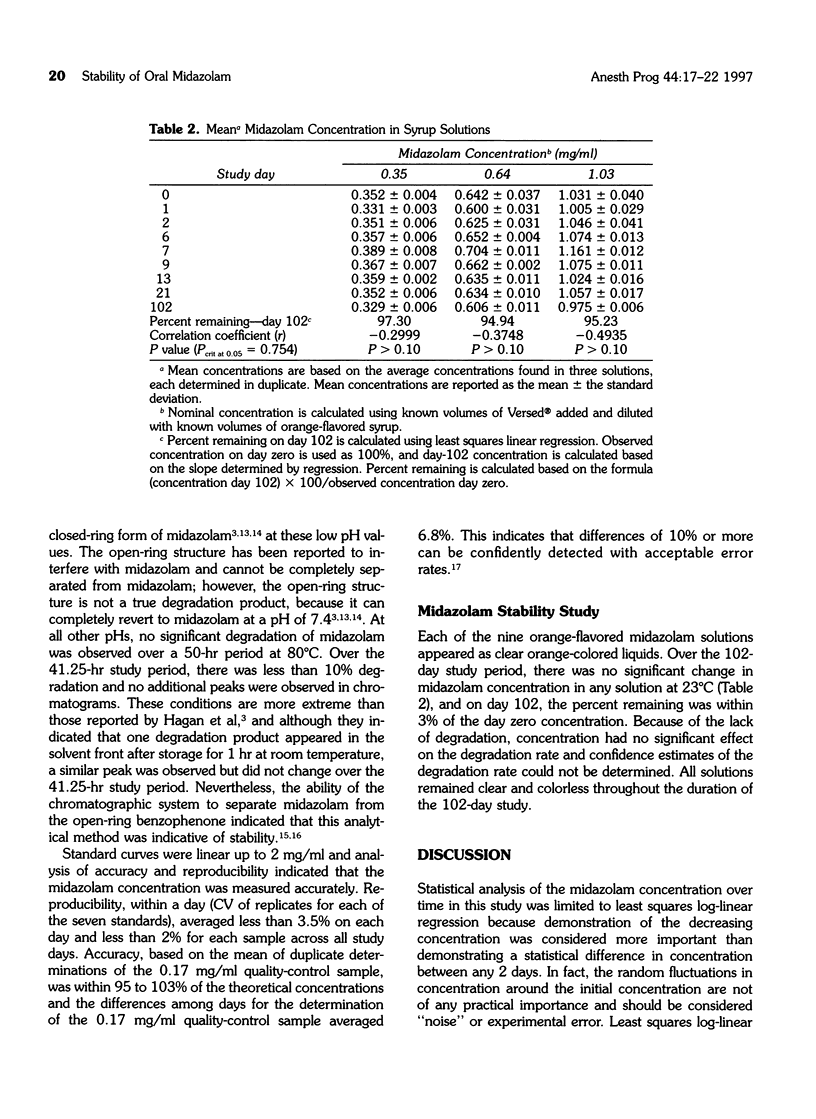
Midazolam is increasingly being used for oral sedation in pediatric dentistry. Unfortunately, it is available only as a parenteral formulation in Canada and the United States. Preparation of the parenteral solution for oral use is not uniform and leads the clinician to question the stability of this drug when used in conjunction with these vehicles. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the chemical stability of parenteral midazolam as an oral formulation to determine its expiry date. This was evaluated using a validated stability-indicating liquid chromatographic method. Midazolam was diluted in orange-flavored syrup to yield concentrations of 0.35, 0.64, and 1.03 mg/ml and then stored at room temperature. Samples were drawn on each of 9 study days (0, 1, 2, 6, 7, 9, 13, 21, and 102) and chromatographed. On each study day, solutions were inspected visually for changes in color, clarity, and appearance of particulate matter. Midazolam concentrations were considered within acceptable limits if they were not less than 90% of the initial concentration. Over the 102-day study period, there was no significant change in concentration in any of the solutions. On day 102, the remaining midazolam was within 7% of the day zero concentration. Therefore, these formulations of midazolam are stable at room temperature for a period of 102 days and would be suitable for clinical use.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersin R. Solubility and acid-base behaviour of midazolam in media of different pH, studied by ultraviolet spectrophotometry with multicomponent software. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1991;9(6):451–455. doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(91)80246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt-Mehta V., Johnson C. E., Kostoff L., Rosen D. A. Stability of midazolam hydrochloride in extemporaneously prepared flavored gelatin. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1993 Mar;50(3):472–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt-Mehta V., Rosen D. A., King R. S., Maksym C. J. Stability of midazolam hydrochloride in parenteral nutrient solutions. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1993 Feb;50(2):285–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. F., Koestner J. A., Tobias J. D. Stability of midazolam prepared for oral administration. South Med J. 1993 Jul;86(7):771-2, 776. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199307000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan R. L., Jacobs L. F., 3rd, Pimsler M., Merritt G. J. Stability of midazolam hydrochloride in 5% dextrose injection or 0.9% sodium chloride injection over 30 days. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1993 Nov;50(11):2379–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan C. O., Spahr-Schopfer I. A., Sikich N., Hartley E., Lerman J. Premedication of children with oral midazolam. Can J Anaesth. 1992 Jul;39(6):545–550. doi: 10.1007/BF03008315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soy D., Lopez M. C., Salvador L., Parra L., Roca M., Chabas E., Codina C., Modamio P., Mariño E. L., Ribas J. Stability of an oral midazolam solution for premedication in paediatric patients. Pharm World Sci. 1994 Dec 2;16(6):260–264. doi: 10.1007/BF02178567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steedman S. L., Koonce J. R., Wynn J. E., Brahen N. H. Stability of midazolam hydrochloride in a flavored, dye-free oral solution. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1992 Mar;49(3):615–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolley P. D., Strom B. L. Sample size calculations for clinical pharmacology studies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 May;39(5):489–490. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissel L. A. Avoiding common flaws in stability and compatibility studies of injectable drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1983 Jul;40(7):1159–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissel L. A., Flora K. P. Stability studies: five years later. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1988 Jul;45(7):1569–1571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


