Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the ability of low-dose fentanyl to produce analgesia when administered via the periodontal ligament injection in teeth with symptomatic, inflamed pulps. All subjects presented for emergency treatment with moderate to severe pain and had a posterior tooth with a clinical diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis. Twenty subjects randomly received either 10 micrograms fentanyl citrate or saline placebo via the periodontal ligament injection in a double-blind manner. The subjects rated their pain prior to injection and rated pain intensity and pain half gone for 59 min postinjection. Low-dose fentanyl delivered via the periodontal ligament injection in inflamed teeth provided significantly greater analgesia than the saline placebo (P < 0.05). Since the dose of fentanyl used was less than the dose required to provide analgesia by a central mechanism, the results of this study may be consistent with a peripheral opioid mechanism of action.
Full text
PDF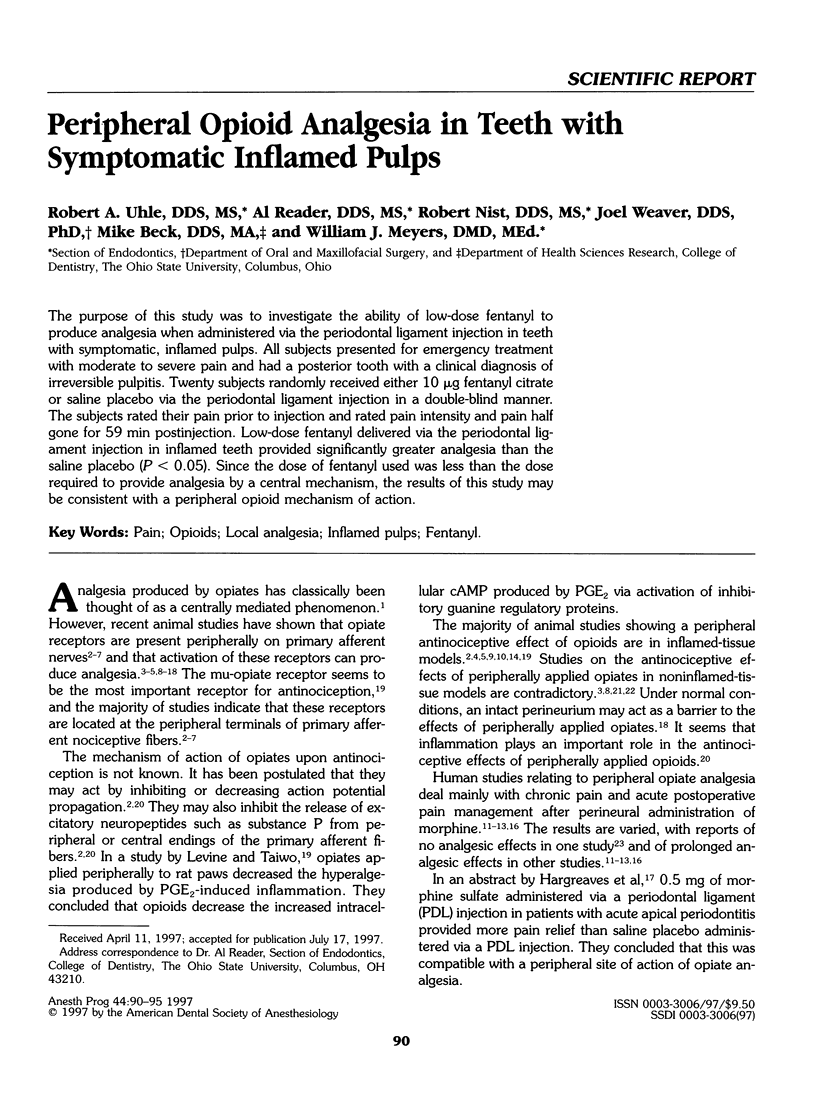




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonijevic I., Mousa S. A., Schäfer M., Stein C. Perineurial defect and peripheral opioid analgesia in inflammation. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):165–172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00165.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G. A., Newton S. H., Starr J. Evidence for an action of morphine and the enkephalins on sensory nerve endings in the mouse peritoneum. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;73(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower S., Hull C. J. Comparative pharmacokinetics of fentanyl and alfentanil. Br J Anaesth. 1982 Aug;54(8):871–877. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.8.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullingham R., O'Sullivan G., McQuay H., Poppleton P., Rolfe M., Evans P., Moore A. Perineural injection of morphine fails to relieve postoperative pain in humans. Anesth Analg. 1983 Feb;62(2):164–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Reader A., Fertel R., Beck M., Meyers W. J. A radioimmunoassay determination of the concentrations of prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha in painful and asymptomatic human dental pulps. J Endod. 1985 Aug;11(8):330–335. doi: 10.1016/s0099-2399(85)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. A. Models for clinical assessment of oral analgesics. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 14;75(5A):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne R. A., Cooper S. A. Evaluation of preoperative ibuprofen for postoperative pain after removal of third molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978 Jun;45(6):851–856. doi: 10.1016/s0030-4220(78)80004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer W. P., van Heerden J. D., de V Joubert J. J. The route of periodontal ligament injection of local anesthetic solution. J Endod. 1983 Nov;9(11):471–474. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(83)80161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Molina N., Vettore O. Prostaglandin hyperalgesia, V: a peripheral analgesic receptor for opiates. Prostaglandins. 1982 Jan;23(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Nakamura M. I - Prostaglandin hyperalgesia, a cAMP/Ca2+ dependent process. Prostaglandins. 1979 Aug;18(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Emson P. C., Leigh B. K., Gilbert R. F., Iversen L. L. Multiple opiate receptor sites on primary afferent fibres. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):351–353. doi: 10.1038/284351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B., Sudha T. S. Effects of enkephalin, applied intracellularly, on action potentials in vertebrate A and C nerve fibre axons. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Jan;26(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhs Q. M., Walker W. A., 3rd, Gough R. W., Schindler W. G., Hartman K. S. The periodontal ligament injection: histological effects on the periodontium in dogs. J Endod. 1983 Oct;9(10):411–415. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(83)80254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay G. K., Kowalski S. R., Plummer J. L., Cousins M. J., Armstrong P. J. Fentanyl blood concentration-analgesic response relationship in the treatment of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg. 1988 Apr;67(4):329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. F., Chapman C. R., Saeger L. S., Bjurstrom R., Walter M. H., Schoene R. B., Kippes M. Steady-state infusions of opioids in human. II. Concentration-effect relationships and therapeutic margins. Pain. 1990 Oct;43(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90051-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris J. L., Dubner R., Hargreaves K. M. Opioid analgesia at peripheral sites: a target for opioids released during stress and inflammation? Anesth Analg. 1987 Dec;66(12):1277–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser V., Gobeaux D., Lombard M. C., Guilbaud G., Besson J. M. Potent and long lasting antinociceptive effects after injection of low doses of a mu-opioid receptor agonist, fentanyl, into the brachial plexus sheath of the rat. Pain. 1990 Aug;42(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91165-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Taiwo Y. O. Involvement of the mu-opiate receptor in peripheral analgesia. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):571–575. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays K. S., Lipman J. J., Schnapp M. Local analgesia without anesthesia using peripheral perineural morphine injections. Anesth Analg. 1987 May;66(5):417–420. doi: 10.1213/00000539-198705000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza M. M., Reader A., Meyers W. J., Foreman D. W. An ultrastructural investigation of the human apical pulp in irreversible pulpitis. I. Nerves. J Endod. 1987 Jun;13(6):267–276. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(87)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza M. M., Reader A., Meyers W. J., Marquard J. V. An ultrastructural investigation of the human apical pulp in irreversible pulpitis. II. Vasculature and connective tissue. J Endod. 1987 Jul;13(7):318–327. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(87)80113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H., Sanchez R., Knudsen F. Perineural morphine for the relief of chronic pain. Anaesthesia. 1986 Jul;41(7):768–769. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1986.tb12872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. J., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Opiates inhibit the discharges of fine afferent units from inflamed knee joint of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 23;76(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELTZER S., BENDER I. B., ZIONTZ M. THE DYNAMICS OF PULP INFLAMMATION: CORRELATIONS BETWEEN DIAGNOSTIC DATA AND ACTUAL HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS IN THE PULP. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963 Aug;16:969–977. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(63)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez R., Nielsen H., Heslet L., Iversen A. D. Neuronal blockade with morphine. A hypothesis. Anaesthesia. 1984 Aug;39(8):788–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb06525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleder J. R., Reader A., Beck M., Meyers W. J. The periodontal ligament injection: a comparison of 2% lidocaine, 3% mepivacaine, and 1:100,000 epinephrine to 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine in human mandibular premolars. J Endod. 1988 Aug;14(8):397–404. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(88)80124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senami M., Aoki M., Kitahata L. M., Collins J. G., Kumeta Y., Murata K. Lack of opiate effects on cat C polymodal nociceptive fibers. Pain. 1986 Oct;27(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. N., Pashley D. H. Periodontal ligament injection: evaluation of systemic effects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983 Dec;56(6):571–574. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(83)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. N., Walton R. E. Periodontal ligament injection: distribution of injected solutions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983 Mar;55(3):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(83)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Buchan P. Peripheral opioid receptors located on the rat saphenous nerve. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Gramsch C., Herz A. Intrinsic mechanisms of antinociception in inflammation: local opioid receptors and beta-endorphin. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1292–1298. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01292.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Hassan A. H., Przewłocki R., Gramsch C., Peter K., Herz A. Opioids from immunocytes interact with receptors on sensory nerves to inhibit nociception in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5935–5939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Millan M. J., Shippenberg T. S., Herz A. Peripheral effect of fentanyl upon nociception in inflamed tissue of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jan 22;84(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90412-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. Peripheral analgesic actions of opioids. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1991 Apr;6(3):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0885-3924(91)90960-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. J., Reader A., Beck M., Meyers W. J. The periodontal ligament injection: a comparison of the efficacy in human maxillary and mandibular teeth. J Endod. 1988 Oct;14(10):508–514. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(88)80109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuge O., Matsumoto M., Kitahata L. M., Collins J. G., Senami M. Direct opioid application to peripheral nerves does not alter compound action potentials. Anesth Analg. 1985 Jul;64(7):667–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


