Abstract
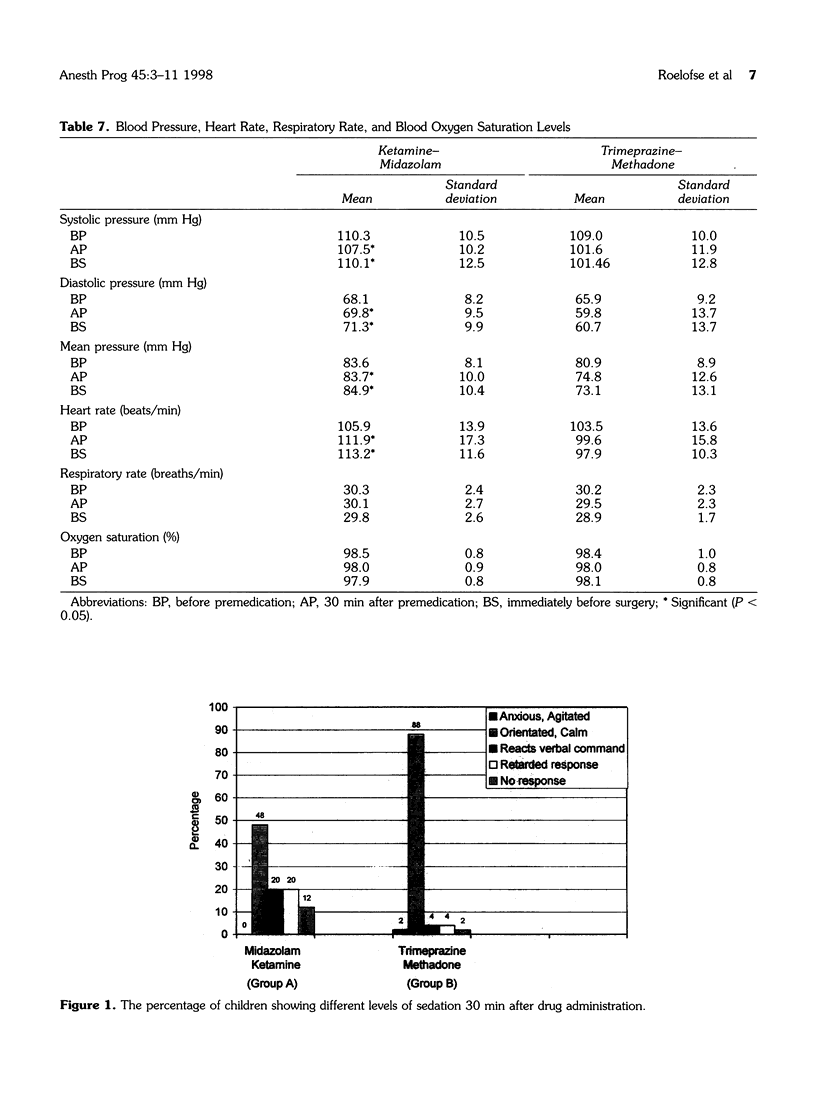
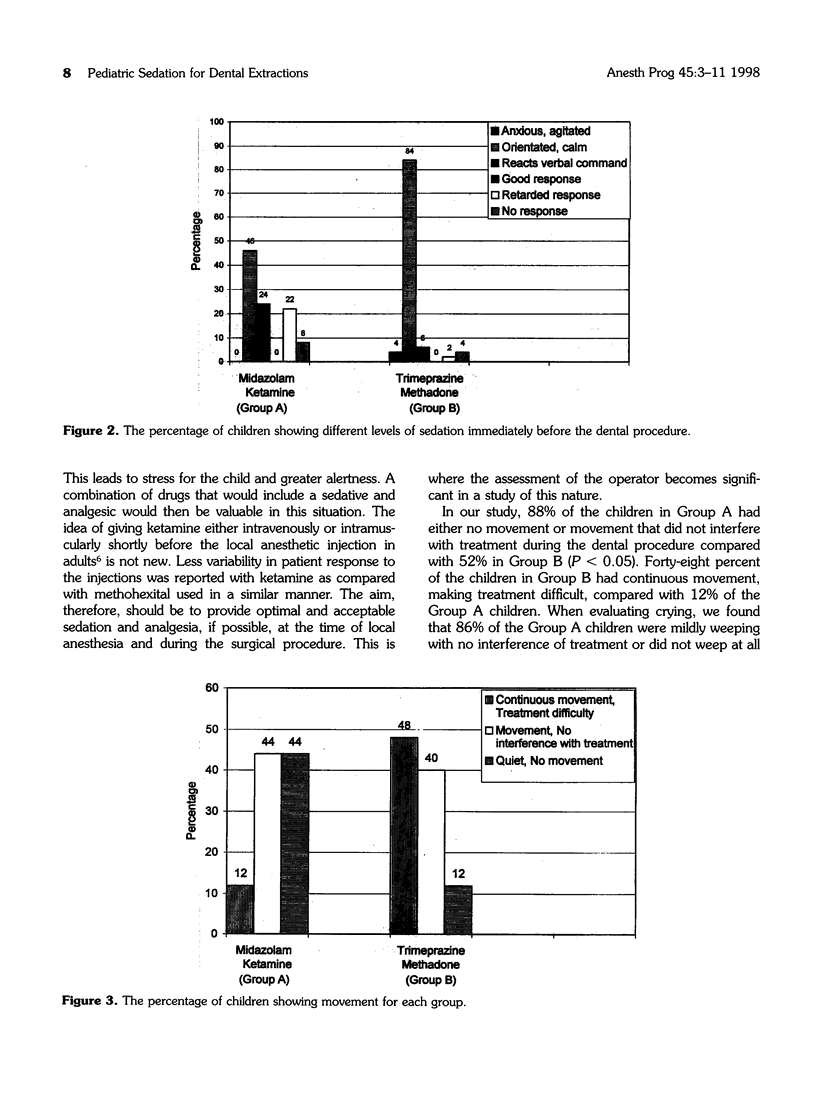
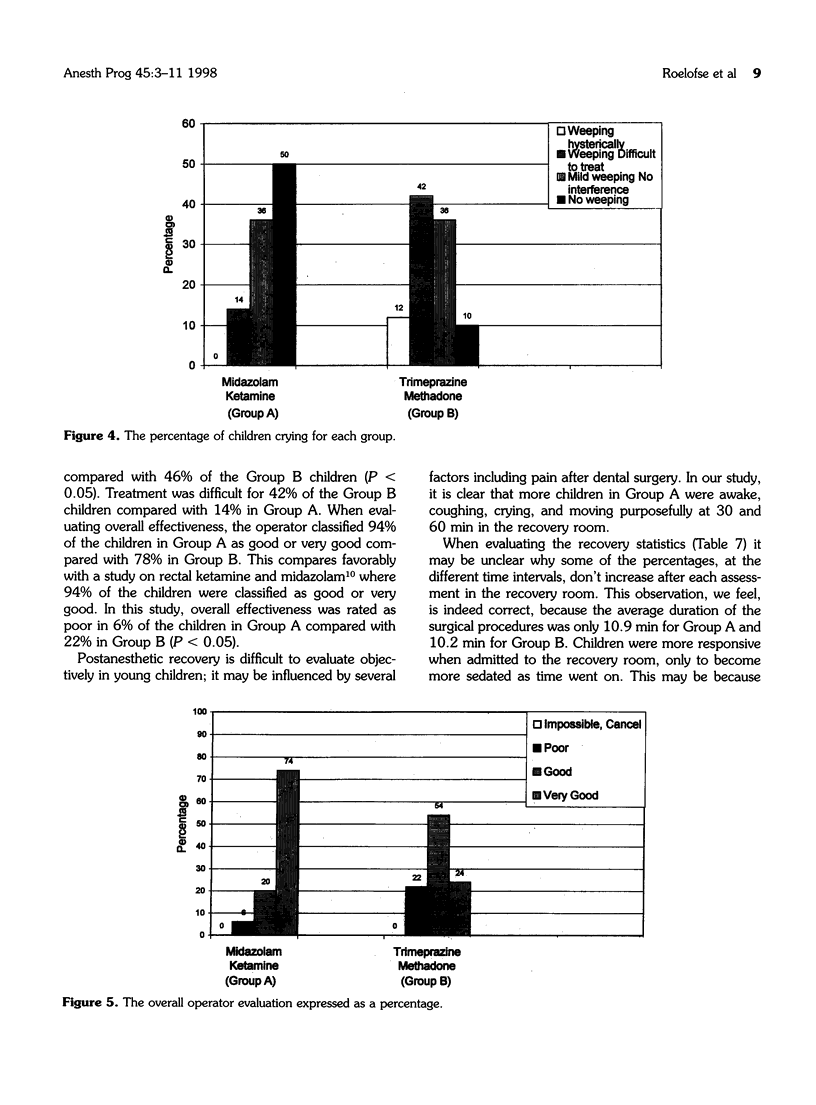
The safety and efficacy of an oral sedation technique for children having minor oral surgical procedures under local anesthesia were studied. One hundred healthy children between the ages of 2 and 7 yr received either a combination of midazolam (0.35 mg/kg) and ketamine (5 mg/kg) (Group A), or a combination of trimeprazine (3 mg/kg) and methadone (0.2 mg/kg) (Group B) 30 min preoperatively. Hemodynamic parameters, adverse reactions, postoperative recovery, and behavior were evaluated. More children were asleep, but rousable to verbal commands, 30 min after drug administration in Group A (40%) than in Group B (8%). Immediately before the dental procedure, 46% of children in Group A were asleep in contrast to 8% of children in group B. Significantly more children in Group A were awake, coughing, crying, and moving purposefully 30 and 60 min after admission to the recovery room. Two children (4%) in Group A vomited. Ten (20%) children in Group A hallucinated compared to none in Group B. The surgeon rated the procedure as good or very good in 94% of children in Group A compared to 78% in Group B. Our results show that the combination of midazolam and ketamine, administered orally, is a safe, effective, and practical approach to managing children for minor oral surgical procedures under local anesthesia.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badini Confalonieri F., Cassarino G. L'uso della ketamina per os in odontostomatologia. Esperienze cliniche in chirurgia estrattiva e pedodonzia ambulatoriale. Minerva Stomatol. 1983 Nov-Dec;32(6):915–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankstein K. C., Anderson J. A. A double-blind comparison of low-dose intravenous ketamine and methohexital in adults. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991 May;49(5):468–475. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(91)90169-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulthard P., Rood J. P. Objective measurement of the analgesic effect of midazolam in humans. Anesth Prog. 1993;40(2):35–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan W. K., Pruhs R. J., Ashrafi M. H., Post A. C. Chloral hydrate and other drugs used in sedating young children: a survey of American Academy of Pedodontics Diplomates. Pediatr Dent. 1983 Dec;5(4):252–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld L. H., Negus J. B., White P. F. Oral midazolam preanesthetic medication in pediatric outpatients. Anesthesiology. 1990 Nov;73(5):831–834. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199011000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. M., Johnson N. E. Ketamine sedation for pediatric procedures: Part 2, Review and implications. Ann Emerg Med. 1990 Sep;19(9):1033–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)82569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutstein H. B., Johnson K. L., Heard M. B., Gregory G. A. Oral ketamine preanesthetic medication in children. Anesthesiology. 1992 Jan;76(1):28–33. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199201000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houpt M. I., Weiss N. J., Koenigsberg S. R., Desjardins P. J. Comparison of chloral hydrate with and without promethazine in the sedation of young children. Pediatr Dent. 1985 Mar;7(1):41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafft T. C., Krämer N., Kunzelmann K. H., Hickel R. Experience with midazolam as sedative in the dental treatment of uncooperative children. ASDC J Dent Child. 1993 Jul-Oct;60(4-5):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryshtalskyj B., Direnfeld V. N., Johnson T. W. Use of low-dose ketamine hydrochloride in outpatient oral surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990 Apr;69(4):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(90)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay M. A., Savege T. M., Simpson B. R., Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 22;2(5920):656–659. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5920.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofse J. A., Joubert J. J., Swart L. C., Stander I., Roelofse P. G. An evaluation of the effect of oral ketamine and standard oral premedication in the sedation of paediatric dental patients. J Dent Assoc S Afr. 1996 Apr;51(4):197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofse J. A., van der Bijl P., Stegmann D. H., Hartshorne J. E. Preanesthetic medication with rectal midazolam in children undergoing dental extractions. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990 Aug;48(8):791–797. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(90)90333-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward D. J. A simplified scoring system for the post-operative recovery room. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1975 Jan;22(1):111–113. doi: 10.1007/BF03004827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. R. A comparative evaluation of ketamine anesthesia in children and adults. Anesthesiology. 1974 May;40(5):459–464. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197405000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner D. L., Cabaret J., Velling D. Ketamine plus midazolam, a most effective paediatric oral premedicant. Paediatr Anaesth. 1995;5(5):293–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.1995.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


