Abstract
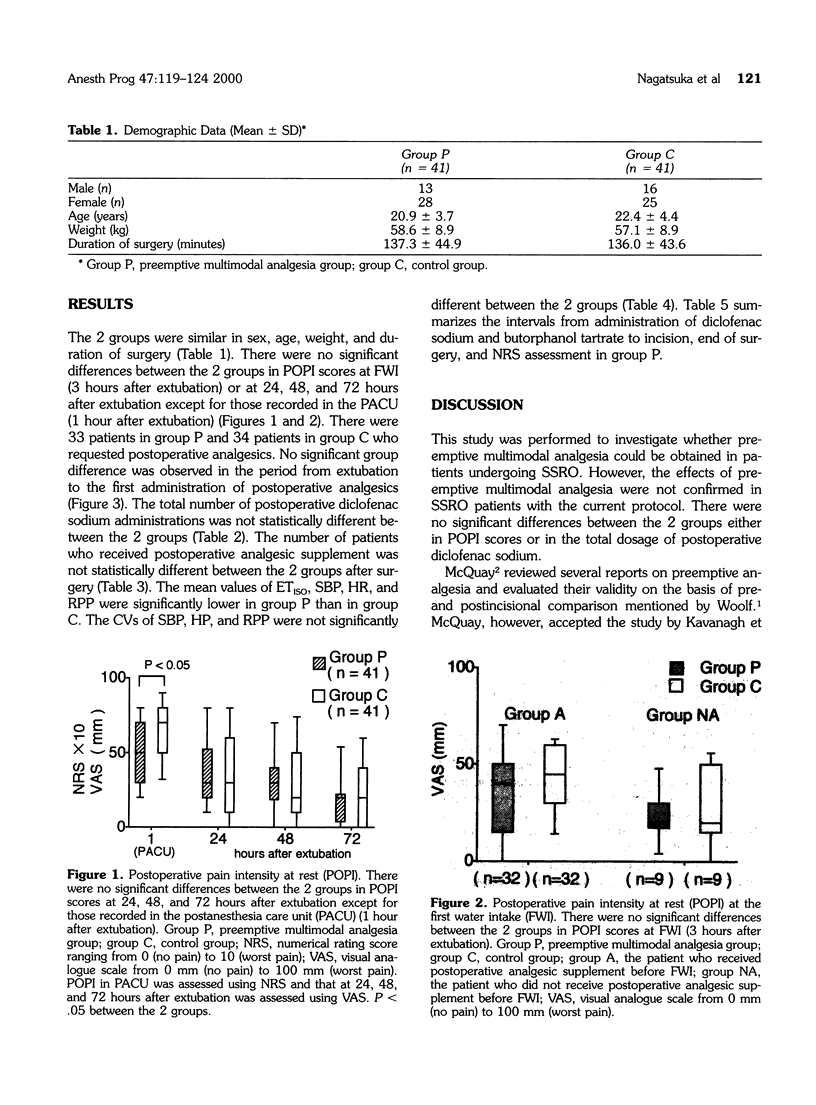
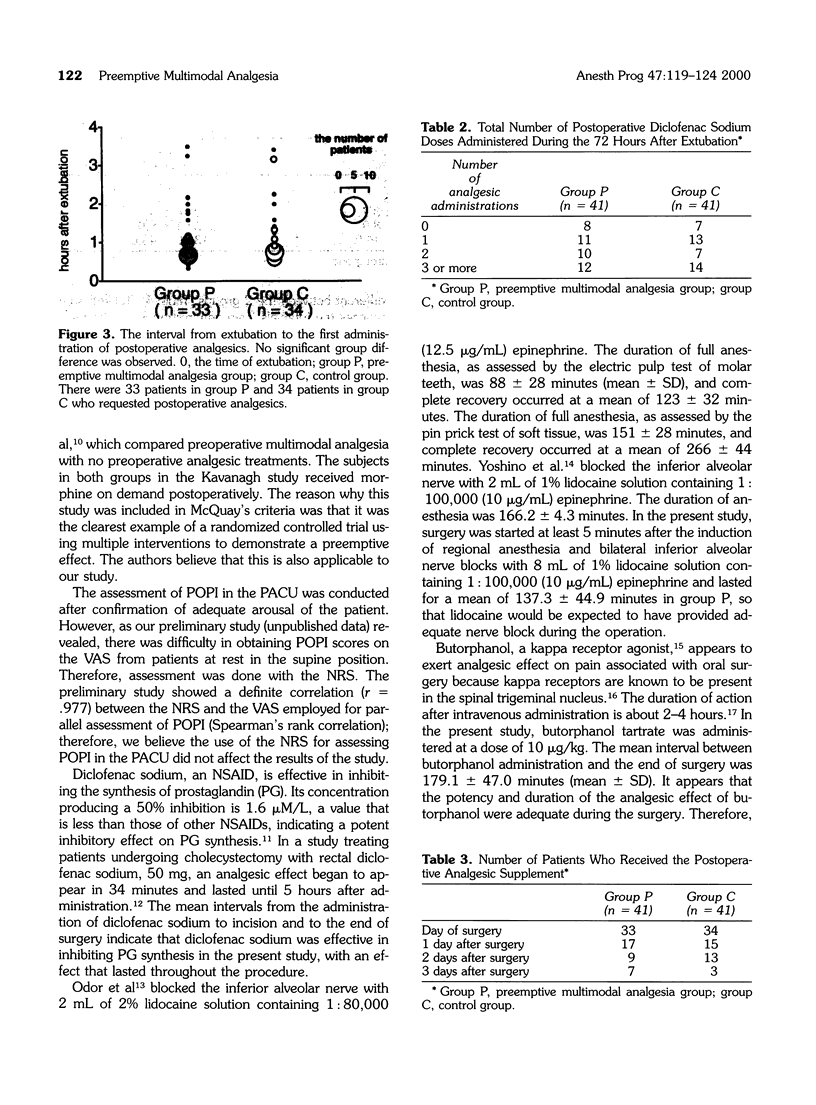
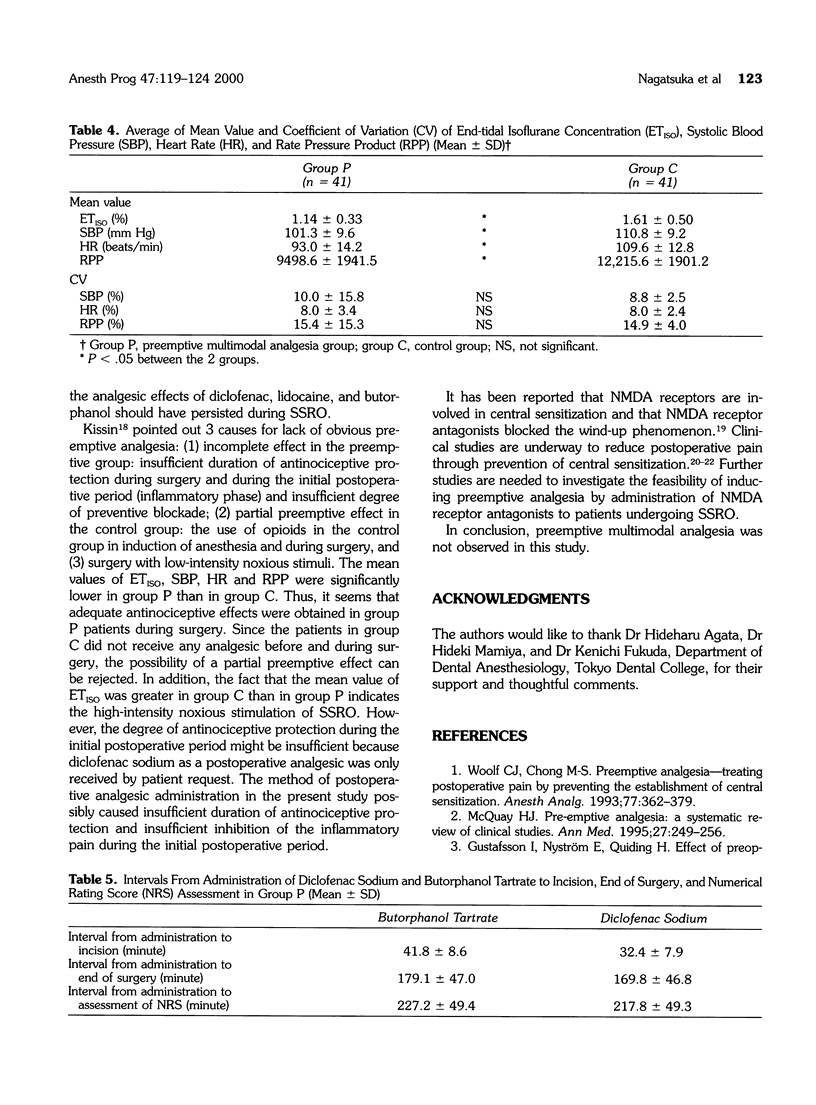
The aim of the study was to investigate whether preemptive multimodal analgesia (diclofenac, butorphanol, and lidocaine) was obtained during sagittal split ramus osteotomy (SSRO). Following institutional approval and informed consent, 82 healthy patients (ASA-I) undergoing SSRO were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 groups, the preemptive multimodal analgesia group (group P, n = 41) and the control group (group C, n = 41). This study was conducted in a double-blind manner. Patients in group P received 50 mg rectal diclofenac sodium, 10 micrograms/kg intravenous 0.1% butorphanol tartrate, and 1% lidocaine solution containing 10 micrograms/mL epinephrine for regional anesthesia and for bilateral inferior alveolar nerve blocks before the start of surgery. Postoperative pain intensity at rest (POPI) was assessed on a numerical rating score (NRS) in the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) and on a visual analogue scale (VAS) at the first water intake (FWI) and at 24, 48, and 72 hours after extubation. POPI in the PACU was significantly lower in group P than in group C, whereas there were no significant differences at FWI, 24, 48, and 72 hours after extubation in both groups. Preemptive multimodal analgesia was not observed in this study.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridgman J. B., Gillgrass T. G., Zacharias M. The absence of any pre-emptive analgesic effect for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996 Oct;34(5):428–431. doi: 10.1016/s0266-4356(96)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. I., Kendrick R. W. Pre-emptive analgesia using local anaesthesia: a study in bilaterally symmetrical surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1997 Nov;79(5):657–659. doi: 10.1093/bja/79.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flath R. K., Hicks M. L., Dionne R. A., Pelleu G. B., Jr Pain suppression after pulpectomy with preoperative flurbiprofen. J Endod. 1987 Jul;13(7):339–347. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(87)80116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu E. S., Miguel R., Scharf J. E. Preemptive ketamine decreases postoperative narcotic requirements in patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 1997 May;84(5):1086–1090. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199705000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaw S. P., Makimura M., Oh K. W., Hoskins B., Ho I. K. Involvement of kappa-opioid receptors in opioid dependence/withdrawal: studies using butorphanol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 May 12;257(1-2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90707-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh B. P., Katz J., Sandler A. N., Nierenberg H., Roger S., Boylan J. F., Laws A. K. Multimodal analgesia before thoracic surgery does not reduce postoperative pain. Br J Anaesth. 1994 Aug;73(2):184–189. doi: 10.1093/bja/73.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissin I. Preemptive analgesia. Why its effect is not always obvious. Anesthesiology. 1996 May;84(5):1015–1019. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199605000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Menassé R., Riesterer L., Pericin C., Ruegg M., Ziel R. The pharmacology of diclofenac sodium (Voltarol). Rheumatol Rehabil. 1979;Suppl 2:11–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Fox C. A., Burke S., Meng F., Thompson R. C., Akil H., Watson S. J. Mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol. 1994 Dec 15;350(3):412–438. doi: 10.1002/cne.903500307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuay H. J. Pre-emptive analgesia: a systematic review of clinical studies. Ann Med. 1995 Apr;27(2):249–256. doi: 10.3109/07853899509031967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odor T. M., Pitt Ford T. R., McDonald F. Effect of inferior alveolar nerve block anaesthesia on the lower teeth. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1994 Jun;10(3):144–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.1994.tb00540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roytblat L., Korotkoruchko A., Katz J., Glazer M., Greemberg L., Fisher A. Postoperative pain: the effect of low-dose ketamine in addition to general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1993 Dec;77(6):1161–1165. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199312000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisk A. L., Grover B. J. A comparison of preoperative and postoperative naproxen sodium for suppression of postoperative pain. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990 Jul;48(7):674–678. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(90)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisk A. L., Mosley R. O., Martin R. P. Comparison of preoperative and postoperative diflunisal for suppression of postoperative pain. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989 May;47(5):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(89)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang J., Hayes S. R. Butorphanol tartrate (stadol): a review. J Post Anesth Nurs. 1991 Apr;6(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. S., Lu C. C., Cherng C. H., Ho S. T. Pre-emptive analgesia with ketamine, morphine and epidural lidocaine prior to total knee replacement. Can J Anaesth. 1997 Jan;44(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF03014321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf C. J., Chong M. S. Preemptive analgesia--treating postoperative pain by preventing the establishment of central sensitization. Anesth Analg. 1993 Aug;77(2):362–379. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199377020-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf C. J., Thompson S. W. The induction and maintenance of central sensitization is dependent on N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activation; implications for the treatment of post-injury pain hypersensitivity states. Pain. 1991 Mar;44(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90100-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


