Abstract
The synthesis of IGF-II mRNA in sheep foetal tissues is considerably higher than IGF-I. IGF-II probably has a paracrine role in the foetus; however it is likely that IGF-I originates mainly from the foetal liver and has an endocrine function. Although in the adult system IGF-I is tightly bound to serum carrier proteins it is potentially biologically active. Galactopoiesis in the goat mammary gland provides a useful model for demonstrating the importance of circulating IGF-I as a mediator of GH action. Ligand-receptor interactions involved in the stimulation of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts by IGF-I, II and insulin were examined. It was found that the potency of binding to type I receptors was IGF-I greater than IGF-II much greater than insulin by competitive binding assays and chemical cross-linking studies, and that some cell lines secrete an IGF binding protein which is specific for IGF-I and II and which acts as an inhibitor in cellular binding assays. Maximal stimulation of DNA synthesis induced by IGF-I, II and insulin in the presence of synergising mitogens were similar. While the actions of the IGFs were consistent with type I receptor binding insulin appeared to act through its own receptor. The reduction of EGF receptor affinity following the addition of IGF-I and insulin to 3T3 cells may involve a protein kinase that is not sensitive to phorbol esters. 3T3 cell nuclei contain endogenous inositol phospholipids and their corresponding kinases and monoesterases.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. M. Lactogenic hormones: binding sites, mammary growth, secretory cell differentiation, and milk biosynthesis in ruminants. J Dairy Sci. 1985 Feb;68(2):501–519. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(85)80849-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Zaltsman Z., Turtle J. R. Immunoreactive somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein in human milk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Jun;58(6):955–959. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-6-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Brown K. D. Characterization of an epithelioid cell line derived from rat small intestine: demonstration of cytokeratin filaments. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1984 Jul;8(7):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(84)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Van Wyk J. J. Evidence for a functional role of endogenously produced somatomedinlike peptides in the regulation of DNA synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts and porcine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1172/JCI111906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco L., Gilmour R. S., Ognibene A., Letcher A. J., Manzoli F. A., Irvine R. F. Synthesis of polyphosphoinositides in nuclei of Friend cells. Evidence for polyphosphoinositide metabolism inside the nucleus which changes with cell differentiation. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):765–770. doi: 10.1042/bj2480765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Misra P., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Effect of an anti-insulin-like growth factor I receptor antibody on insulin-like growth factor II stimulation of DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., de Ruiz Galaretta C. M., Fanjul L. F., Mojsilovic L., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin but not phorbol ester treatment increases phosphorylation of vinculin by protein kinase C in BC3H-1 myocytes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
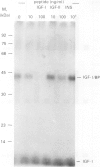
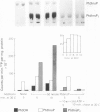
- Corps A. N., Brown K. D. Ligand-receptor interactions involved in the stimulation of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts by insulin-like growth factors and insulin. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):119–125. doi: 10.1042/bj2520119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corps A. N., Brown K. D. Stimulation of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation in culture by growth factors in human and ruminant mammary secretions. J Endocrinol. 1987 May;113(2):285–290. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1130285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Applewhite G. T., Underwood L. E. Evidence that somatomedin is synthesized by multiple tissues in the fetus. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I-binding proteins in human amniotic fluid and in fetal and postnatal blood: evidence of immunological homology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):612–617. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Blethen S. L. Inhibition of access of bound somatomedin to membrane receptor and immunobinding sites: a comparison of radioreceptor and radioimmunoassay of somatomedin in native and acid-ethanol-extracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):781–788. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. R., Collier R. J., McNamara J. P., Head H. H., Sussman W. Effects of thyroxine and growth hormone treatment of dairy cows on milk yield, cardiac output and mammary blood flow. J Anim Sci. 1988 Jan;66(1):70–79. doi: 10.2527/jas1988.66170x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. R., Gluckman P. D., Hart I. C., Henderson H. V. Effects of injecting growth hormone or thyroxine on milk production and blood plasma concentrations of insulin-like growth factors I and II in dairy cows. J Endocrinol. 1987 Jul;114(1):17–24. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1140017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Fredrikson G., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Acute regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression by growth hormone during adipose cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4011–4016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ethier S. P., Kudla A., Cundiff K. C. Influence of hormone and growth factor interactions on the proliferative potential of normal rat mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jul;132(1):161–167. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer J., Forbes J. M., Hart I. C., Robinson J. S., Thorburn G. D. Somatomedin-like activity in plasma after foetal hypophysectomy or nephrectomy and in experimental intra-uterine growth retardation in sheep. J Endocrinol. 1979 Oct;83(1):119–127. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0830119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Usher P., Moses A. C. Monoclonal antibody to the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) receptor blocks IGF-I receptor-mediated DNA synthesis: clarification of the mitogenic mechanisms of IGF-I and insulin in human skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Van Obberghen E. Protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2350001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Butler J. H., Comline R., Fowden A. The effects of pancreatectomy on the plasma concentrations of insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 in the sheep fetus. J Dev Physiol. 1987 Feb;9(1):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Lund P. K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3563497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Pierce S. B., Morgan D. O., Sara V., Smith M. C., Roth R. A. The receptor for insulin-like growth factor II mediates an insulin-like response. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3367–3371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Blakeley D. M., Brown K. D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J. Effects of bombesin and insulin on inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate and inositol (1,3,4)trisphosphate formation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Milner R. D. Somatomedins and fetal growth. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;86:124–151. doi: 10.1002/9780470720684.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D. Insulin, glucagon and the receptor-mediated control of cyclic AMP concentrations in liver. Twenty-second Colworth medal lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Apr;14(2):183–193. doi: 10.1042/bst0140183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa W., Spencer E. M., Larson L., Nandi S. Somatomedin-C substitutes for insulin for the growth of mammary epithelial cells from normal virgin mice in serum-free collagen gel cell culture. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2695–2699. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoli F. A., Capitani S., Mazzotti G., Barnabei O., Maraldi N. M. Role of chromatin phospholipids on template availability and ultrastructure of isolated nuclei. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1982;20:247–262. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(82)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9343–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell G. H., Hart I. C., Kirby A. C. Local intra-arterial infusion of growth hormone into the mammary glands of sheep and goats: effects on milk yield and composition, plasma hormones and metabolites. Aust J Biol Sci. 1987;40(2):181–189. doi: 10.1071/bi9870181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mepham T. B., Lawrence S. E., Peters A. R., Hart I. C. Effects of exogenous growth hormone on mammary function in lactating goats. Horm Metab Res. 1984 May;16(5):248–253. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser C. G., Sankaran L., Hennighausen L., Topper Y. J. Comparison of the roles of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in casein gene expression and in the development of alpha-lactalbumin and glucose transport activities in the mouse mammary epithelial cell. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1411–1416. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanus J. A., Rabinovitch A., Rechler M. M. Neonatal rat islet cell cultures synthesize insulin-like growth factor I. Diabetes. 1985 Jul;34(7):696–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.7.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Mendoza S. A. Synergistic signals in mitogenesis: role of ion fluxes, cyclic nucleotides and protein kinase C in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;3:229–242. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_3.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Spencer E. M. Local injections of human or rat growth hormone or of purified human somatomedin-C stimulate unilateral tibial epiphyseal growth in hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2563–2567. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMON W. D., Jr, DAUGHADAY W. H. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiwiller E., Guler H. P., Merryweather J., Scandella C., Maerki W., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth restoration of insulin-deficient diabetic rats by recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):169–171. doi: 10.1038/323169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Hauri C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Comparison of in vivo effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II and of growth hormone in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Feb;108(2):167–174. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1080167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skottner A., Clark R. G., Robinson I. C., Fryklund L. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor: testing the somatomedin hypothesis in hypophysectomized rats. J Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;112(1):123–132. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1120123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stracke H., Schulz A., Moeller D., Rossol S., Schatz H. Effect of growth hormone on osteoblasts and demonstration of somatomedin-C/IGF I in bone organ culture. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Sep;107(1):16–24. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1070016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally M., Li C. H., Hall K. IGF-2 stimulated growth mediated by the somatomedin type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):811–816. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90948-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Graves D. C., Casella S. J., Jacobs S. Evidence from monoclonal antibody studies that insulin stimulates deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis through the type I somatomedin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):639–643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Jagars G., Sand I., Grunwald J., Froesch E. R. Inhibition of the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity on isolated rat fat cells by binding to its carrier protein. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI109377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]