Abstract
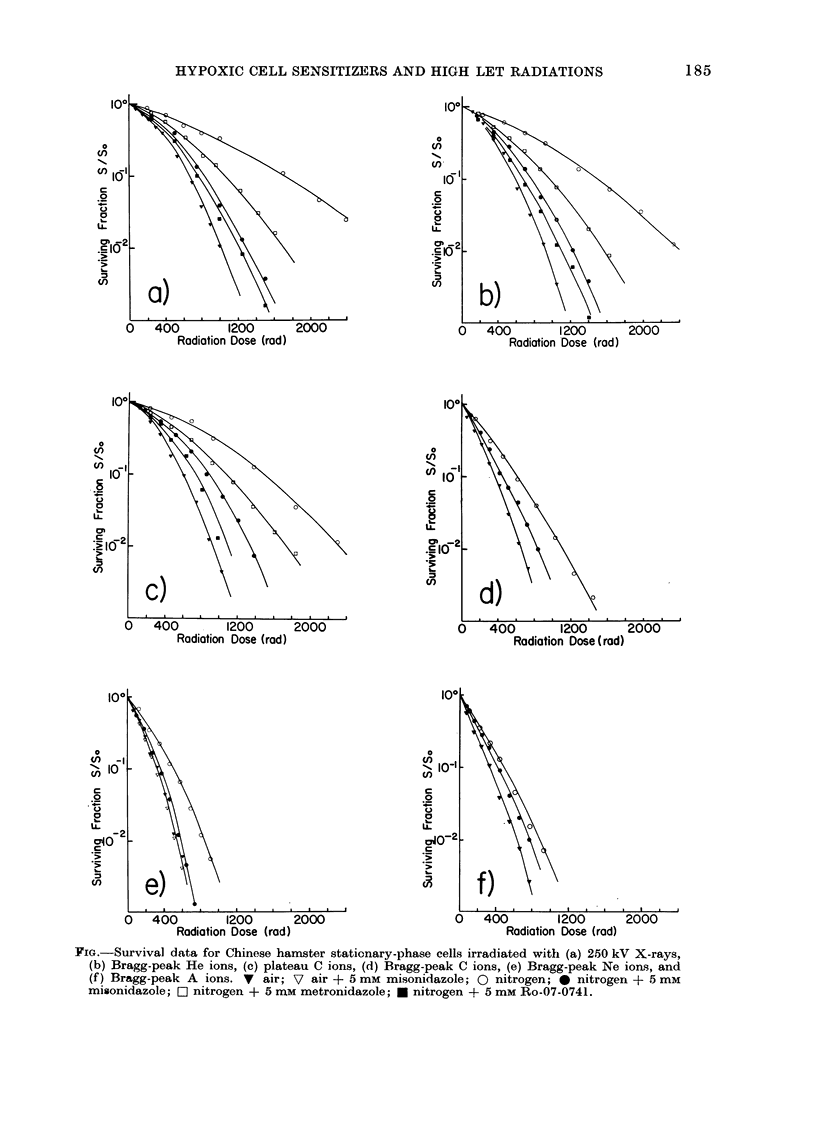
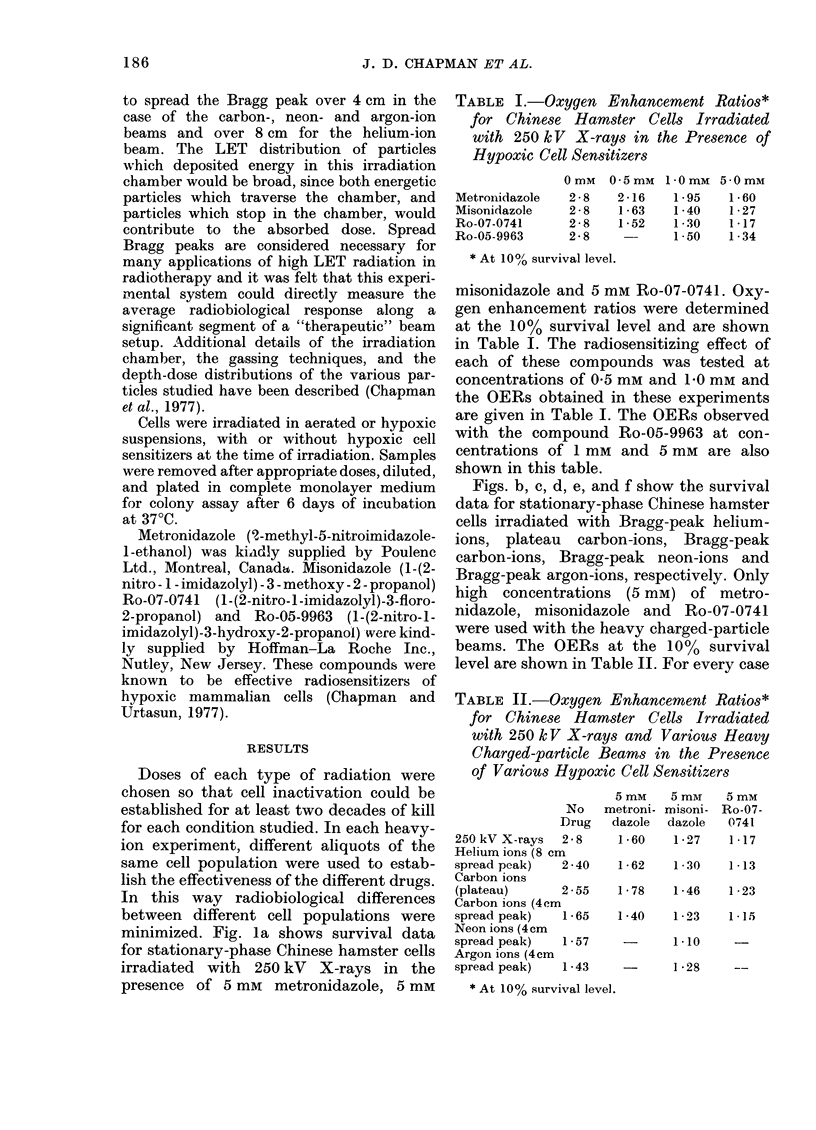
Stationary-phase populations of Chinese hamster V-79 cells were irradiated with 250 kV X-rays and the Bragg peaks (spread to a width of 4 cm) of energetic He-, C-, Ne-, and A-ion beams produced at the 184-inch cyclotron and BEVALAC at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory. Survival curves were generated with each radiation for cells suspended in air-saturated and nitrogen-saturated medium with and without sensitizer present. The oxygen enhancement ratios (OERs) measured for X-rays with 1mM metronidazole and 0.5 mM misonidazole were 2.0 and 1.6 respectively. The OERs without sensitizer for He-, C-, Ne-, and A-ion Bragg peaks were 2.4, 1.7, 1.6 and 1.4 respectively. For each type of radiation tested the presence of hypoxic-cell sensitizers resulted in an additional reduction in the measured OERs, indicating that these drugs should be of benefit in the radiotherapy planned with these and other high LET radiations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. E. Chemical radiosensitization of hypoxic cells. Br Med Bull. 1973 Jan;29(1):48–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Urtasun R. C. The application in radiation therapy of substances which modify cellular radiation response. Cancer. 1977 Jul;40(1 Suppl):484–488. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197707)40:1+<484::aid-cncr2820400713>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J., Roizin-Towie L., Theus R. B., August L. S. Radiobiological properties of high-energy cyclotron-produced neutrons used for radiotherapy. Radiology. 1975 Oct;117(1):173–178. doi: 10.1148/117.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally N. J. Letter: The effect of a change in radiation quality on the ability of electron affinic sensitizers to sensitize hypoxic cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1976 Feb;29(2):191–196. doi: 10.1080/09553007614550211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias C. A. Pretherapeutic investigations with accelerated heavy ions. Radiology. 1973 Jul;108(1):145–158. doi: 10.1148/108.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Band P., Chapman J. D., Rabin H. R., Wilson A. F., Fryer C. G. Clinical phase I study of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer RO-07-0582, a 2-nitroimidazole derivative. Radiology. 1977 Mar;122(3):801–804. doi: 10.1148/122.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Band P., Rabin H. R., Fryer C. G., Sturmwind J. Phase 1 study of high-dose metronidazole: a specific in vivo and in vitro radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Radiology. 1975 Oct;117(1):129–133. doi: 10.1148/117.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


