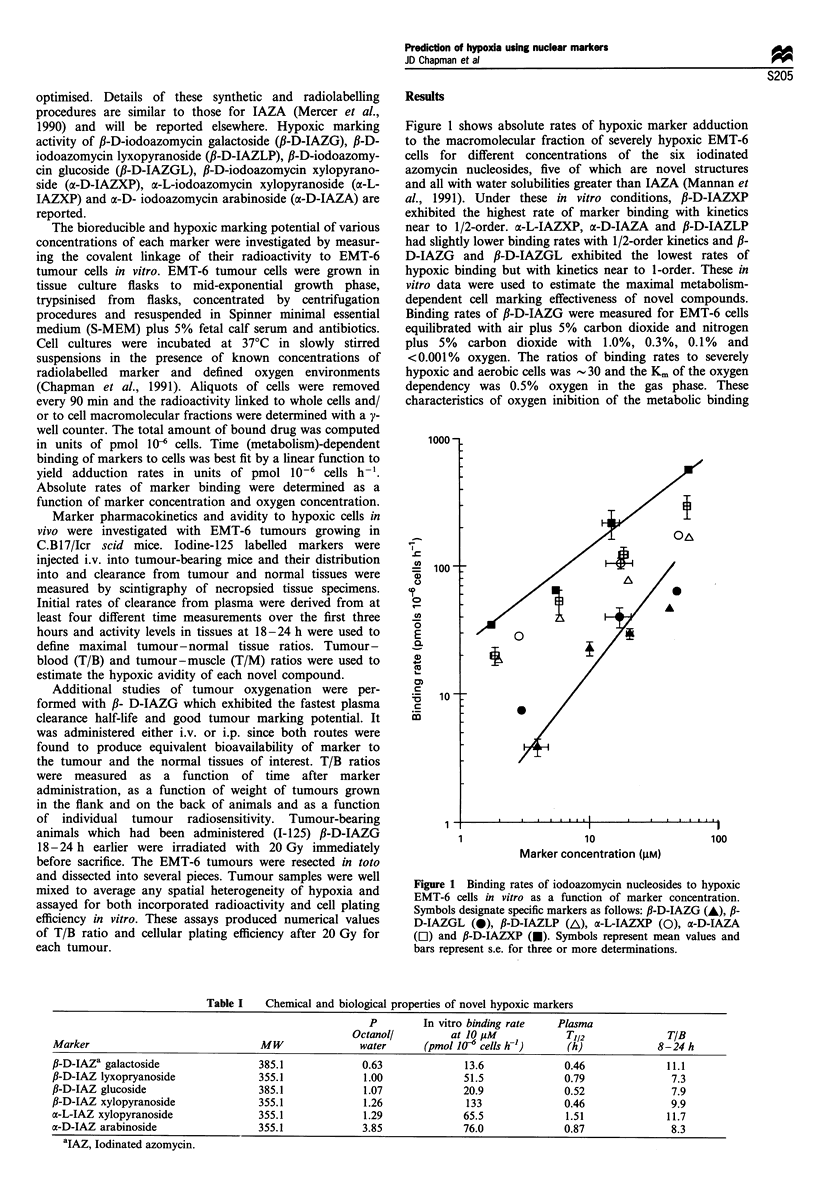
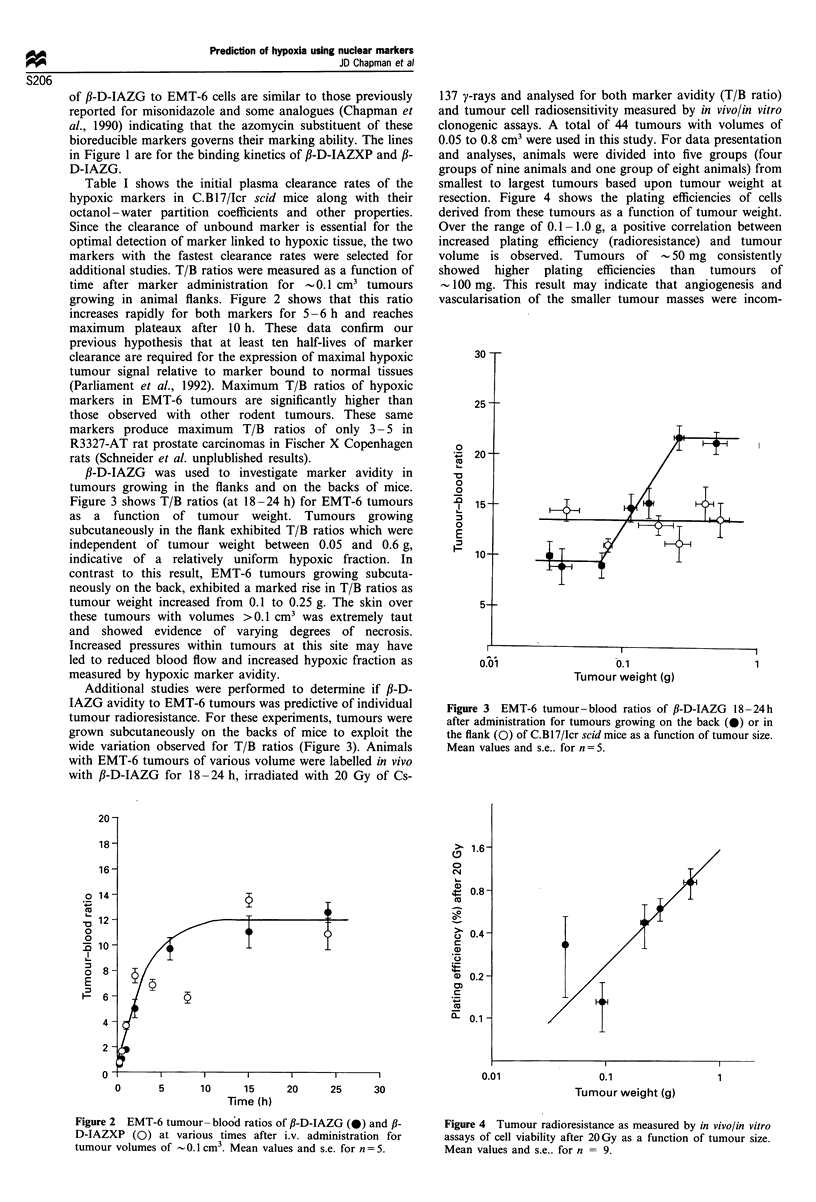
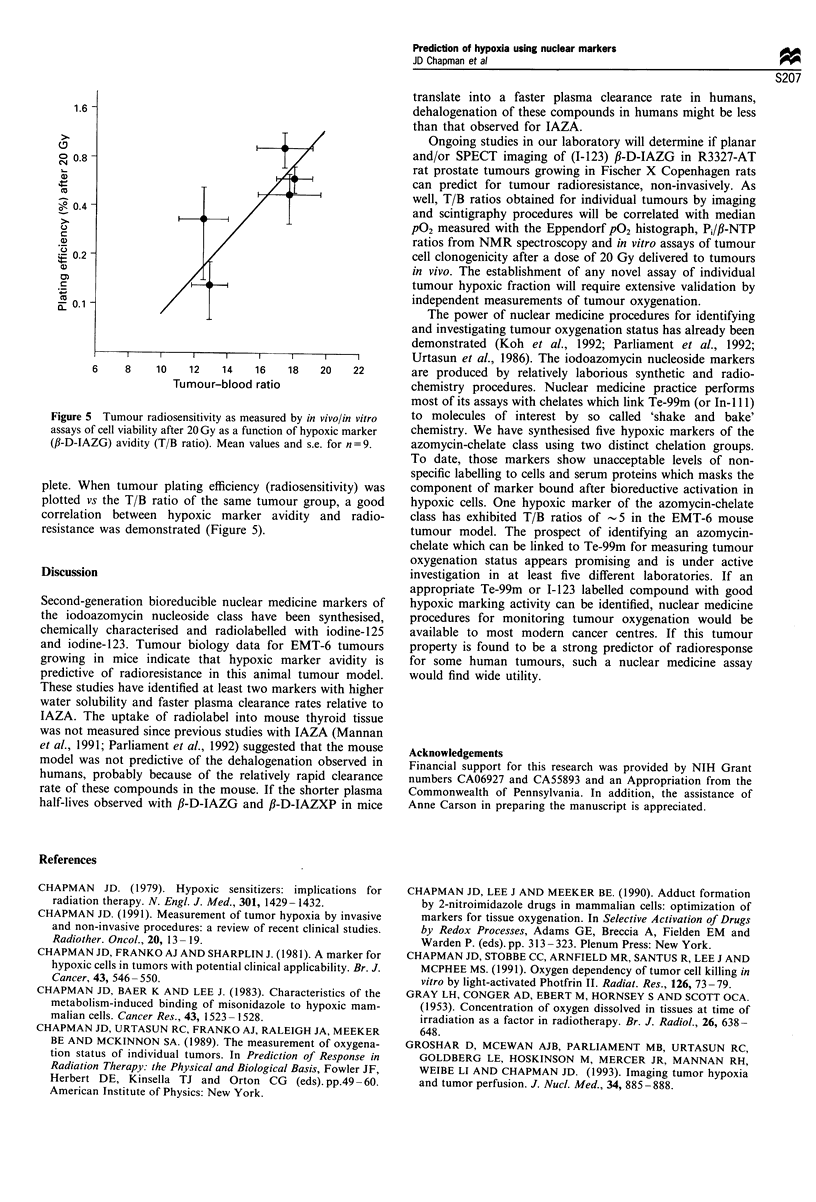
Abstract
Second-generation nuclear medicine markers of tumour hypoxia have been synthesised and screened for hypoxic marking activity in cell cultures and in mouse tumours (EMT-6). Markers of the iodinated azomycin nucleoside class with greater water solubility and faster plasma clearance rates relative to iodoazomycin arabinoside (IAZA) were of particular interest. The test systems used to characterise hypoxic marking activity of compounds included (1) covalent linkage of radiolabelled markers to cells in suspension culture equilibrated with specific O2 concentrations; (2) biodistribution of radiolabelled markers in EMT-6 tumour-bearing mice; and (3) biodistribution in R3327-AT tumour-bearing rats by nuclear medicine procedures. Of the iodinated azomycin nucleosides produced to date, beta-D-iodoazomycin galactoside (beta-D-IAZG) and beta-D-iodoazomycin xylopyranoside (beta-D-IAZXP) exhibited high metabolism-dependent hypoxic cell uptake, rapid clearance kinetics from the blood and excellent tumour marking activity in vivo. Tumour-blood (T/B) ratio (a measure of tumour hypoxic fraction) was dependent upon EMT-6 tumour size and implantation site. The radioresistance of individual tumours was measured by in vivo/in vitro assay and correlated well with the T/B ratio of hypoxic marker. These studies have identified beta-D-IAZG and beta-D-IAZXP as effective hypoxic markers for planar and single photon emission computerised tomography (SPECT) imaging studies of tumour oxygenation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapman J. D., Baer K., Lee J. Characteristics of the metabolism-induced binding of misonidazole to hypoxic mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1523–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Franko A. J., Sharplin J. A marker for hypoxic cells in tumours with potential clinical applicability. Br J Cancer. 1981 Apr;43(4):546–550. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D. Hypoxic sensitizers--implications for radiation therapy. N Engl J Med. 1979 Dec 27;301(26):1429–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197912273012606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D. Measurement of tumor hypoxia by invasive and non-invasive procedures: a review of recent clinical studies. Radiother Oncol. 1991;20 (Suppl 1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(91)90181-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. D., Stobbe C. C., Arnfield M. R., Santus R., Lee J., McPhee M. S. Oxygen dependency of tumor cell killing in vitro by light-activated Photofrin II. Radiat Res. 1991 Apr;126(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY L. H., CONGER A. D., EBERT M., HORNSEY S., SCOTT O. C. The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1953 Dec;26(312):638–648. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-26-312-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groshar D., McEwan A. J., Parliament M. B., Urtasun R. C., Golberg L. E., Hoskinson M., Mercer J. R., Mannan R. H., Wiebe L. I., Chapman J. D. Imaging tumor hypoxia and tumor perfusion. J Nucl Med. 1993 Jun;34(6):885–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höckel M., Knoop C., Schlenger K., Vorndran B., Baussmann E., Mitze M., Knapstein P. G., Vaupel P. Intratumoral pO2 predicts survival in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Radiother Oncol. 1993 Jan;26(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(93)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh W. J., Rasey J. S., Evans M. L., Grierson J. R., Lewellen T. K., Graham M. M., Krohn K. A., Griffin T. W. Imaging of hypoxia in human tumors with [F-18]fluoromisonidazole. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;22(1):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(92)91001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannan R. H., Somayaji V. V., Lee J., Mercer J. R., Chapman J. D., Wiebe L. I. Radioiodinated 1-(5-iodo-5-deoxy-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-2-nitroimidazole (iodoazomycin arabinoside: IAZA): a novel marker of tissue hypoxia. J Nucl Med. 1991 Sep;32(9):1764–1770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parliament M. B., Chapman J. D., Urtasun R. C., McEwan A. J., Golberg L., Mercer J. R., Mannan R. H., Wiebe L. I. Non-invasive assessment of human tumour hypoxia with 123I-iodoazomycin arabinoside: preliminary report of a clinical study. Br J Cancer. 1992 Jan;65(1):90–95. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. B., Brown J. M., Phillips T. L., Sutherland R. M. Oxygen in human tumors: correlations between methods of measurement and response to therapy. Summary of a workshop held November 19-20, 1992, at the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland. Radiat Res. 1993 Dec;136(3):422–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Koch C. J., Franko A. J., Raleigh J. A., Chapman J. D. A novel technique for measuring human tissue pO2 at the cellular level. Br J Cancer. 1986 Sep;54(3):453–457. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P., Schlenger K., Hoeckel M. Blood flow and tissue oxygenation of human tumors: an update. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;317:139–151. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P., Schlenger K., Knoop C., Höckel M. Oxygenation of human tumors: evaluation of tissue oxygen distribution in breast cancers by computerized O2 tension measurements. Cancer Res. 1991 Jun 15;51(12):3316–3322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Whitmore G. F., Gulyas S. Studies on the toxicity and radiosensitizing ability of misonidazole under conditions of prolonged incubation. Radiat Res. 1978 Sep;75(3):541–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh K. A., Biade S., Lanciano R. M., Brown D. Q., Fenning M. C., Babb J. S., Hanks G. E., Chapman D. C. Polarographic needle electrode measurements of oxygen in rat prostate carcinomas: accuracy and reproducibility. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995 Aug 30;33(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(95)00036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


