Abstract
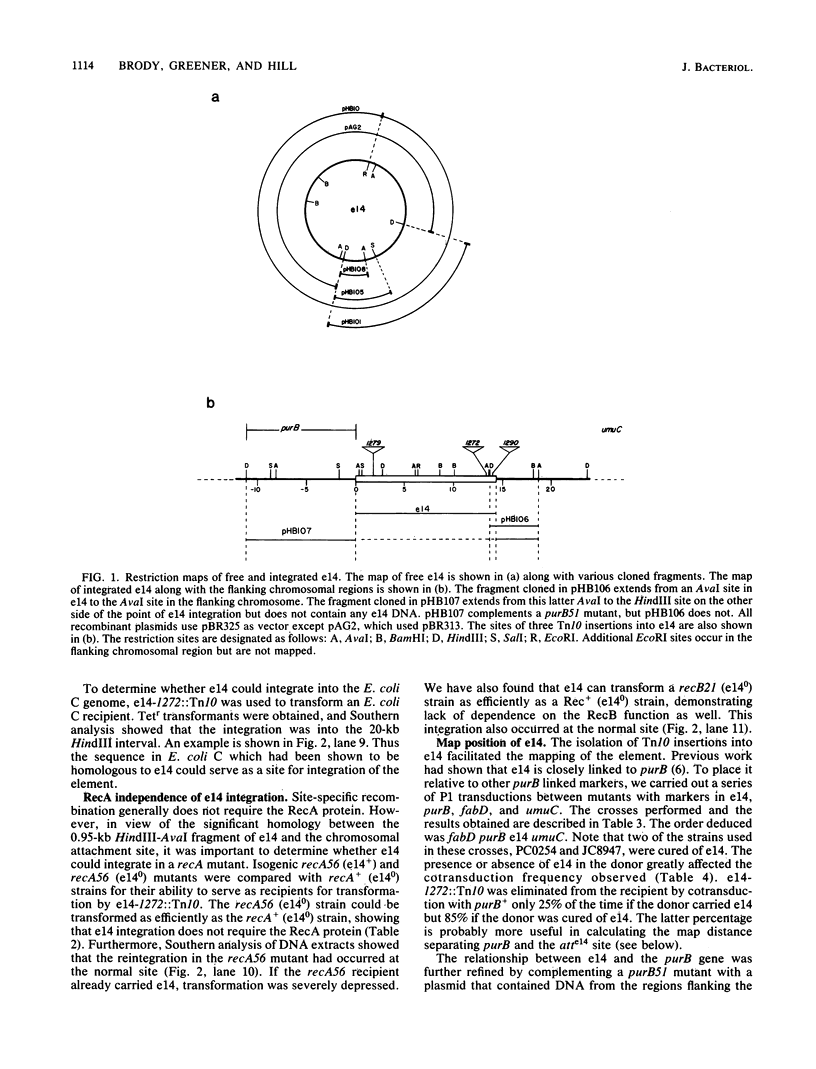
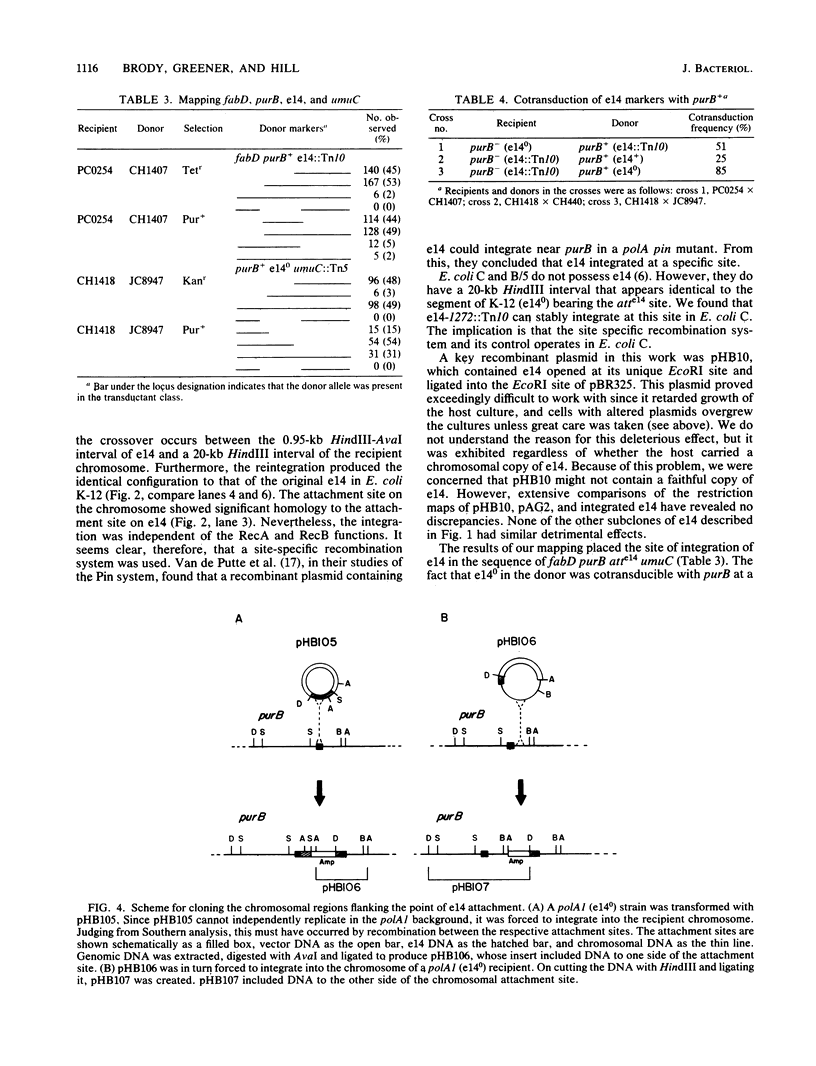
The genetic element e14 is a natural component of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. On induction of the SOS pathways, e14 excises as a 14.4-kilobase circle. We report here on the reintegration of e14 into the chromosome of cured (e14 degrees) E. coli K-12 derivatives. Using a Tn10 insertion mutant of e14, we found that reintegration occurred specifically at the locus originally occupied by e14 and with the same orientation. The reintegration event required neither the RecA nor the RecB functions. The attachment site of the free form was located within a 950-base-pair HindIII-AvaI fragment and shared sufficient homology with the host attachment site to form detectable DNA-DNA hybrids. Even though E. coli C and B/5 did not contain e14, they did possess a HindIII restriction fragment that hybridized to the free e14 attachment fragment. E. coli C could be transformed with e14-1272::Tn10, resulting in integration at this site of homology. The Tn10 mutants were also used in mapping the point of e14 attachment. We found the following sequence: fabD purB atte14 umuC. Furthermore, analysis of a recombinant plasmid that contained both the e14 attachment site and the purB locus showed that these two loci occur within 11 kilobases of each other.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capage M. A., Scott J. R. SOS induction by P1 Km miniplasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):473–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.473-480.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capage M., Hill C. W. Preferential unequal recombination in the glyS region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 5;127(1):73–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90460-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto M., Oosawa K., Momota H. Mapping of the pin locus coding for a site-specific recombinase that causes flagellar-phase variation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):663–668. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.663-668.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greener A., Hill C. W. Identification of a novel genetic element in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):312–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.312-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E., Miller R. D., Green L., de Framond J. Transposable element IS50 improves growth rate of E. coli cells without transposition. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Foulds J., Soll L., Berg P. Instability of a missense suppressor resulting from a duplication of genetic material. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):563–581. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Inversions between ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7069–7072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Barker D. F., Ross D. G., Botstein D. Properties of the translocatable tetracycline-resistance element Tn10 in Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1978 Nov;90(3):427–461. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semple K. S., Silbert D. F. Mapping of the fabD locus for fatty acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1036–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1036-1046.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C., Carbon J., Hill C. W. Glycine transfer RNA of Escherichia coli. I. Structural genes for two glycine tRNA species. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):557–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Plasterk R., Kuijpers A. A Mu gin complementing function and an invertible DNA region in Escherichia coli K-12 are situated on the genetic element e14. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.517-522.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]