Abstract
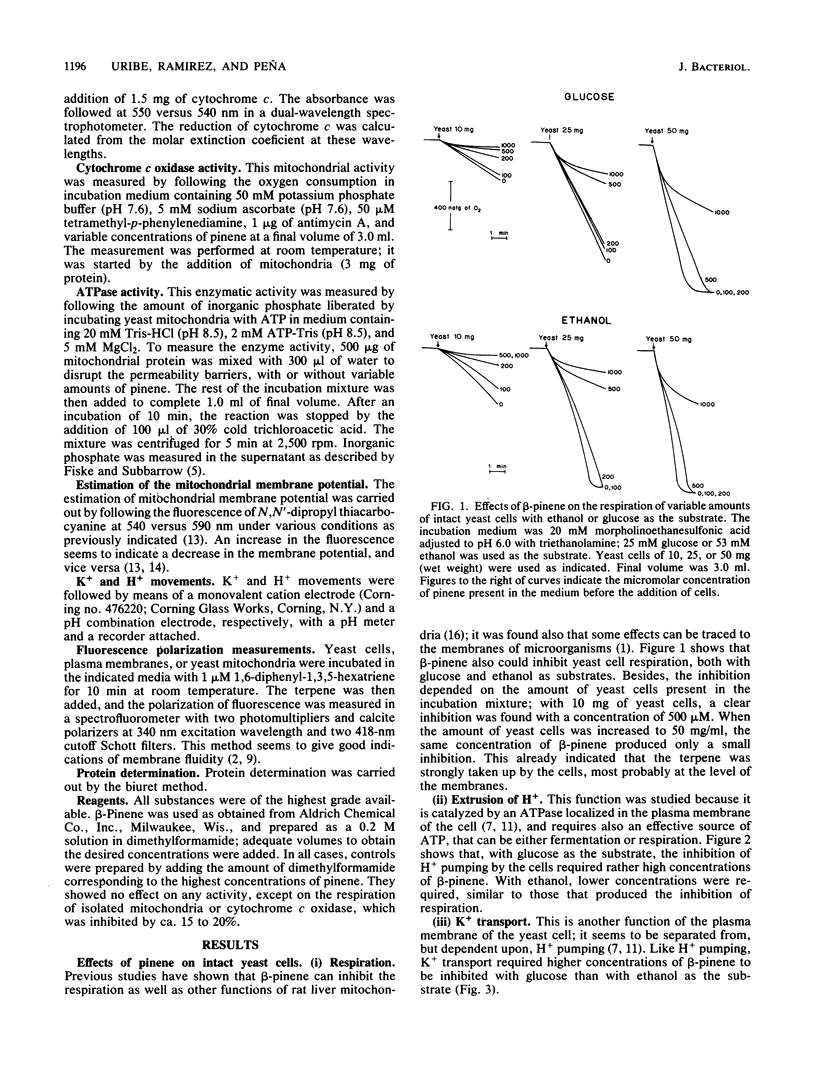
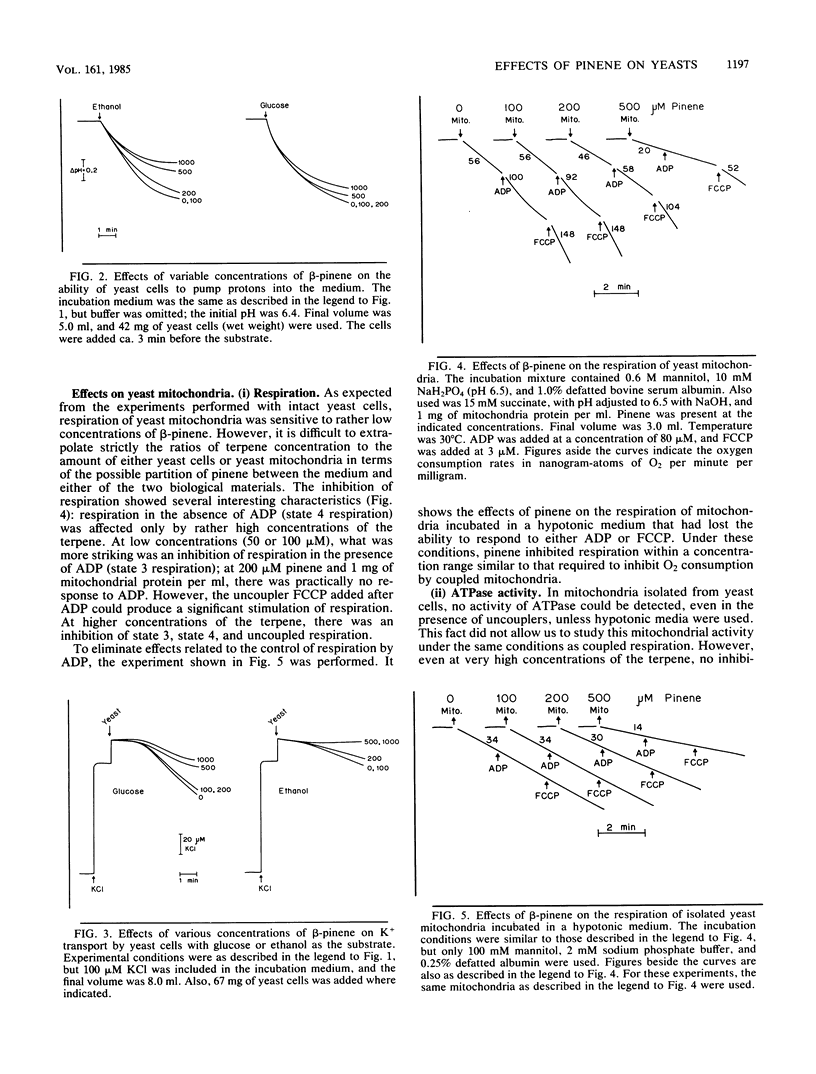
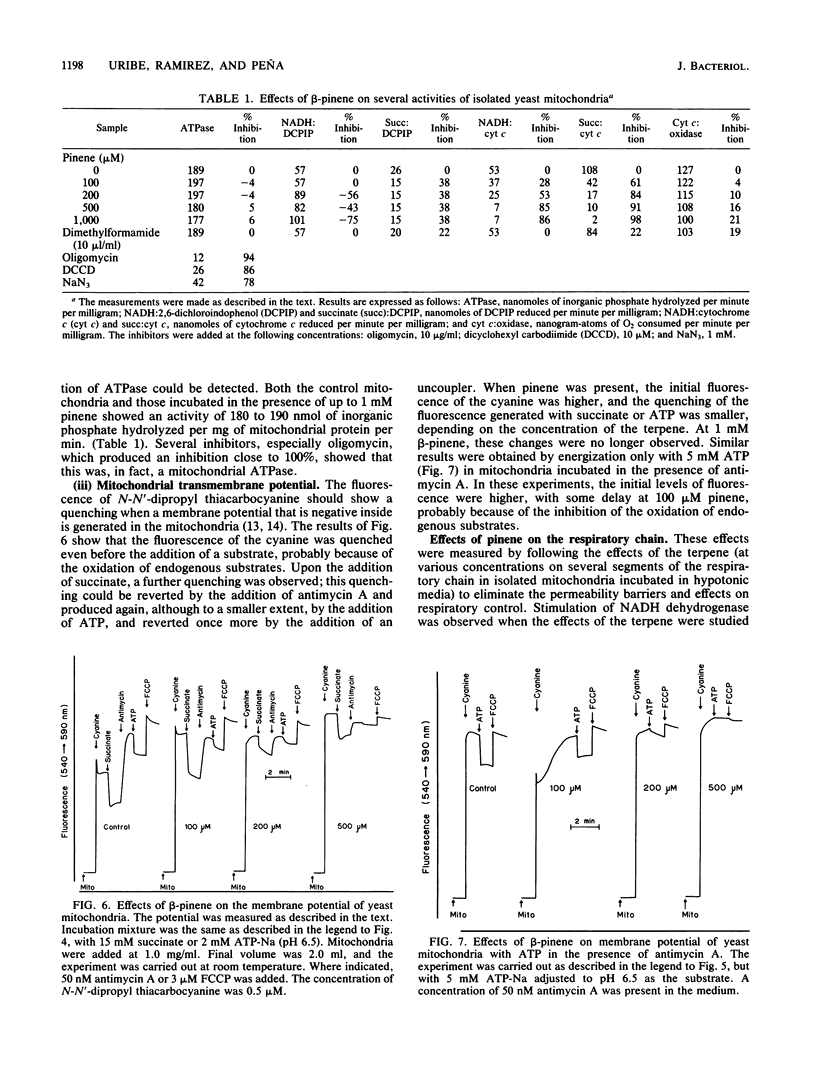
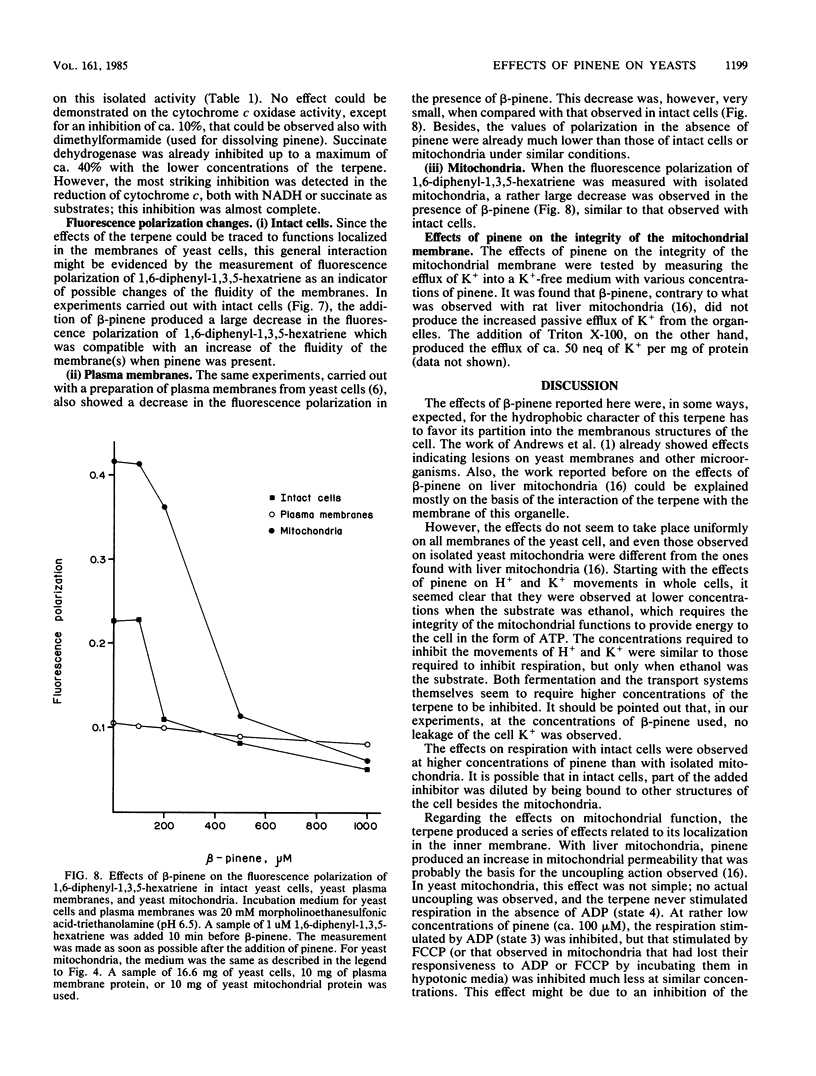
The effects of beta-pinene on yeast cells were studied. This terpene inhibited respiration with glucose or ethanol as the substrate. The inhibition depended on the ratio of the terpene to the amount of yeast cells; for a fixed concentration of pinene, inhibition decreased as the amount of yeast cells increased. Pinene also inhibited the pumping of protons and K+ transport, but this inhibition was more marked with with ethanol than with glucose as the substrate, indicating the mitochondrial localization of the inhibition. The studies on isolated mitochondria showed a series of effects, starting with the disappearance of the respiratory control and deenergization of the organelles and followed by an inhibition of respiration at higher concentrations of the terpene. The effect on respiration could be localized to the cytochrome b region of the electron transport chain. No effect could be detected on the activity of ATPase. The effects can be ascribed to a localization of pinene on membranes which was also accompanied by a decrease in the fluorescence polarization of diphenyl hexatriene, probably meaning an increase in the fluidity of the membrane, localized preferentially to the mitochondria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. E., Parks L. W., Spence K. D. Some effects of douglas fir terpenes on certain microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):301–304. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.301-304.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann G. F., Boehm C., Theuvenet A. P. Sugar transport and potassium permeability in yeast plasma membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):583–596. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A., Piña M. Z., Escamilla E., Piña E. A novel method for the rapid preparation of coupled yeast mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. Studies on the mechanism of K+ transport in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A., Uribe S., Pardo J. P., Borbolla M. The use of a cyanine dye in measuring membrane potential in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 15;231(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90381-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Hoffman J. F. Studies on the mechanism by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3315–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnoff W. A., Hutchison P. M. Bacteriostatic and bacteriocidal effects of extracts of foliage from various plant species on Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis Berliner. J Invertebr Pathol. 1965 Sep;7(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(65)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de KLOET S., van WERMESKERKEN R., KONINGSBERGER V. V. Studies on protein synthesis by protoplasts of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. I. The effect of ribonuclease on protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Feb 12;47:138–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Barros F., Gascón S., Ramos S., Lazo P. S. The electrochemical proton gradient of Saccharomyces. The role of potassium. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


