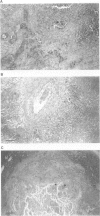
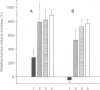
Abstract
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) is a new therapeutic approach combining the effects of a low-permeant cytotoxic drug, bleomycin (BLM), administered i.v. and cell-permeabilizing electric pulses (EPs) locally delivered to tumours. The transient permeabilization of the cell membrane by the EPs allows free access of BLM to its intracellular targets, largely enhancing BLM's cytotoxic effects. ECT efficacy has been proved so far on transplanted subcutaneous murine tumours and on subcutaneous metastases in humans. Here, we present the first study of the effects of ECT on tumours transplanted to livers in rabbits. We used a recently developed EP applicator consisting of an array of parallel and equidistant needles to be inserted in tissues. Effects of EPs alone or of ECT were assessed by histological analysis, tumour growth rates and survival of the treated animals. A transient blood hypoperfusion was seen in the electropulsed areas, with or without BLM, related to EP-dependent vasoconstriction but this had no major effects on cell survival. Long-term effects depended on the presence of BLM at the time of EP delivery. Almost complete tumour necrosis was observed after ECT, resulting from both BLM direct cytotoxic effects on electropermeabilized tumour cells and indirect effects on the tumour vessels. A large reduction in tumour growth rate and significantly longer survival times were scored in comparison with control rabbits. Moreover, ECT of liver tumours was well tolerated and devoid of systemic side-effects. When ECT was associated with a local interleukin 2-based immunotherapy, increased local anti-tumour effectiveness as well as a large decrease in the number of metastases were observed. Thus, ECT could become a novel treatment modality for liver tumours and other solid internal malignancies.
Full text
PDF

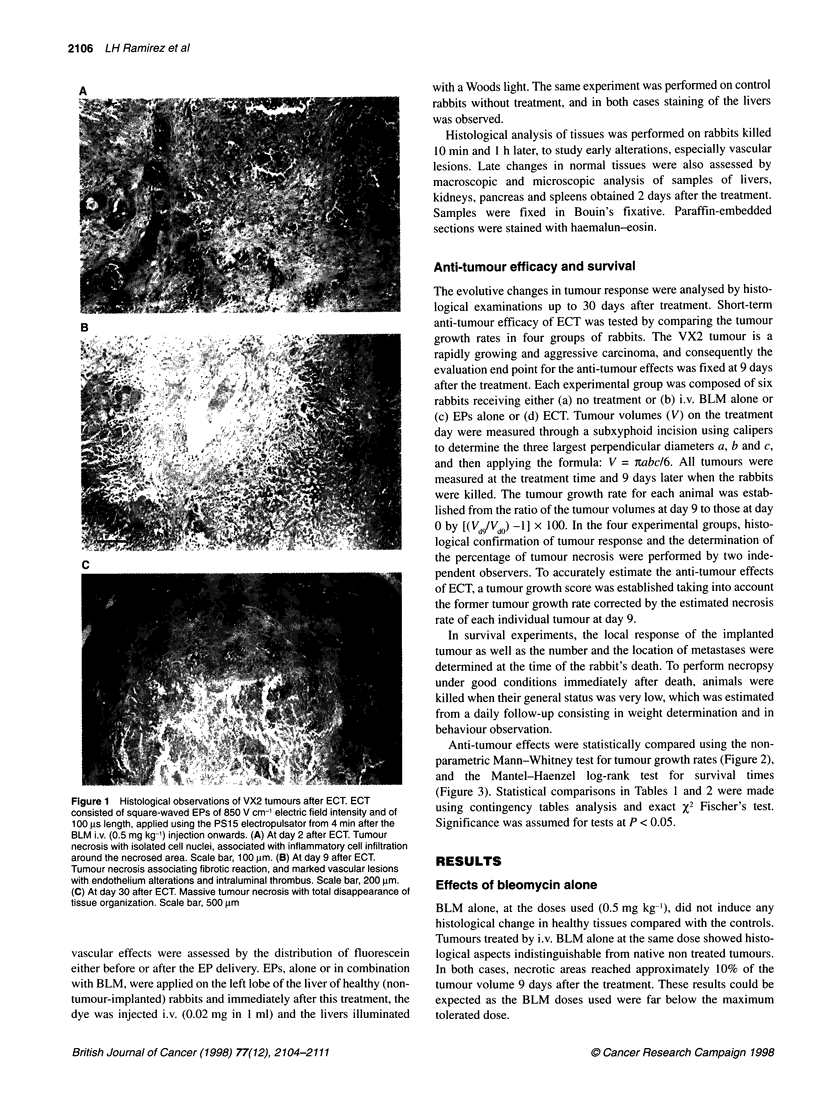
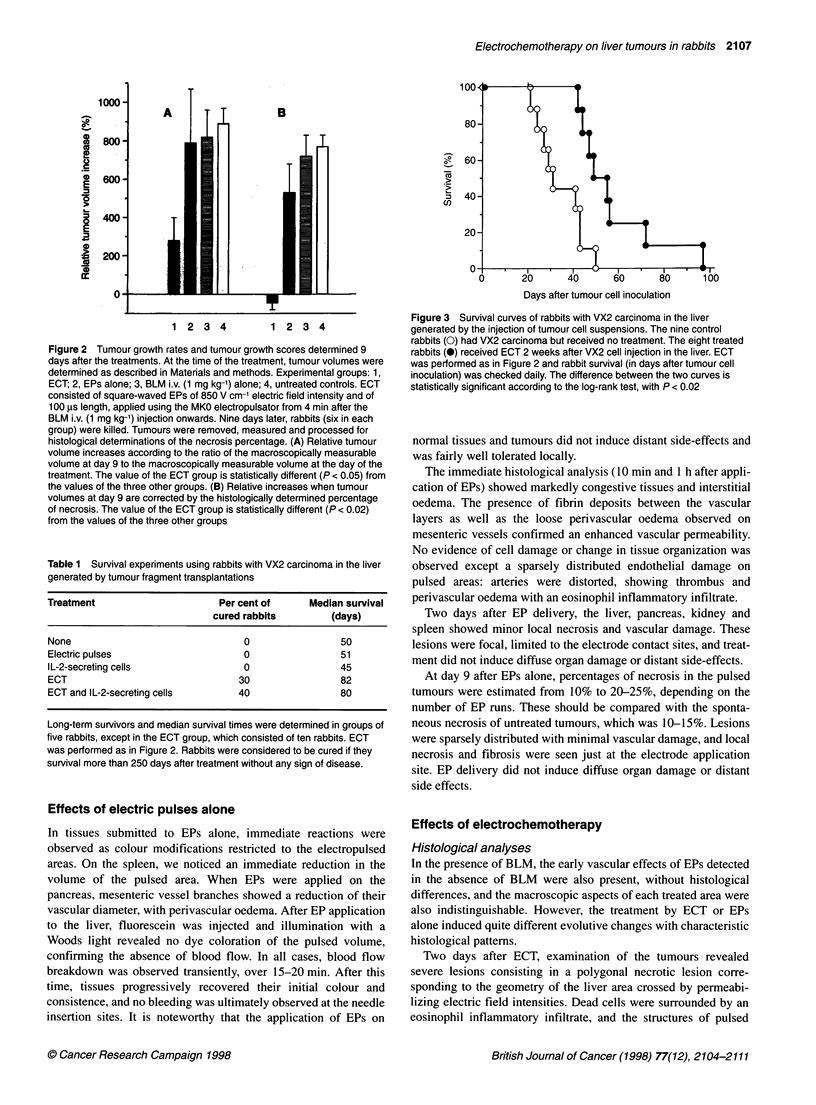



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belehradek J., Jr, Orlowski S., Poddevin B., Paoletti C., Mir L. M. Electrochemotherapy of spontaneous mammary tumours in mice. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90065-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belehradek J., Jr, Orlowski S., Ramirez L. H., Pron G., Poddevin B., Mir L. M. Electropermeabilization of cells in tissues assessed by the qualitative and quantitative electroloading of bleomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Feb 23;1190(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belehradek M., Domenge C., Luboinski B., Orlowski S., Belehradek J., Jr, Mir L. M. Electrochemotherapy, a new antitumor treatment. First clinical phase I-II trial. Cancer. 1993 Dec 15;72(12):3694–3700. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931215)72:12<3694::aid-cncr2820721222>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Pecceu F., Marchese E., Vita N., Roskam W., Lupker J. Characterization of recombinant glycosylated human interleukin 2 produced by a recombinant plasmid transformed CHO cell line. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 21;226(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80548-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R., Jaroszeski M. J., Glass L. F., Messina J. L., Rapaport D. P., DeConti R. C., Fenske N. A., Gilbert R. A., Mir L. M., Reintgen D. S. Phase I/II trial for the treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors using electrochemotherapy. Cancer. 1996 Mar 1;77(5):964–971. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19960301)77:5<964::aid-cncr24>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., O'Leary T. J., Girton M. Distribution of iodized oil within the liver after hepatic arterial injection. Radiology. 1987 Mar;162(3):849–852. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.3.3027747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir L. M., Devauchelle P., Quintin-Colonna F., Delisle F., Doliger S., Fradelizi D., Belehradek J., Jr, Orlowski S. First clinical trial of cat soft-tissue sarcomas treatment by electrochemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1997;76(12):1617–1622. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir L. M., Orlowski S., Belehradek J., Jr, Paoletti C. Electrochemotherapy potentiation of antitumour effect of bleomycin by local electric pulses. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90064-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir L. M., Orlowski S., Poddevin B., Belehradek J., Jr Electrochemotherapy tumor treatment is improved by interleukin-2 stimulation of the host's defenses. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1992 May-Jun;3(3):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mir L. M., Tounekti O., Orlowski S. Bleomycin: revival of an old drug. Gen Pharmacol. 1996 Jul;27(5):745–748. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(95)02101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck J. N., Riggi M., Rougier P., Chabot G. G., Ramirez L. H., Zhao Z., Bognel C., Ardouin P., Herait P., Gouyette A. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic advantages of pirarubicin over adriamycin after intraarterial hepatic administration in the rabbit VX2 tumor model. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1550–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski S., Belehradek J., Jr, Paoletti C., Mir L. M. Transient electropermeabilization of cells in culture. Increase of the cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 15;37(24):4727–4733. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski S., Mir L. M. Cell electropermeabilization: a new tool for biochemical and pharmacological studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 8;1154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90016-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pron G., Belehradek J., Jr, Orlowski S., Mir L. M. Involvement of membrane bleomycin-binding sites in bleomycin cytotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 19;48(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salford L. G., Persson B. R., Brun A., Ceberg C. P., Kongstad P. C., Mir L. M. A new brain tumour therapy combining bleomycin with in vivo electropermeabilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 30;194(2):938–943. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tounekti O., Pron G., Belehradek J., Jr, Mir L. M. Bleomycin, an apoptosis-mimetic drug that induces two types of cell death depending on the number of molecules internalized. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5462–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]