Abstract
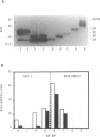
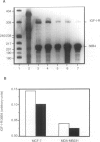
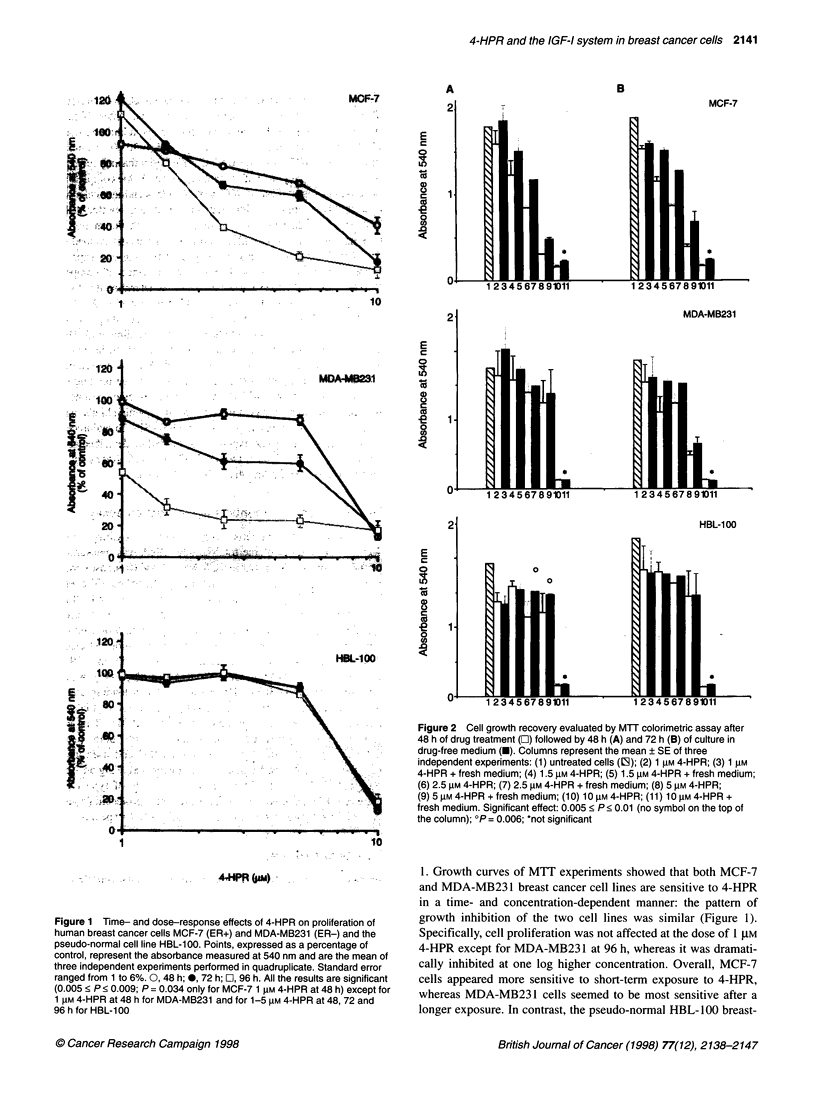
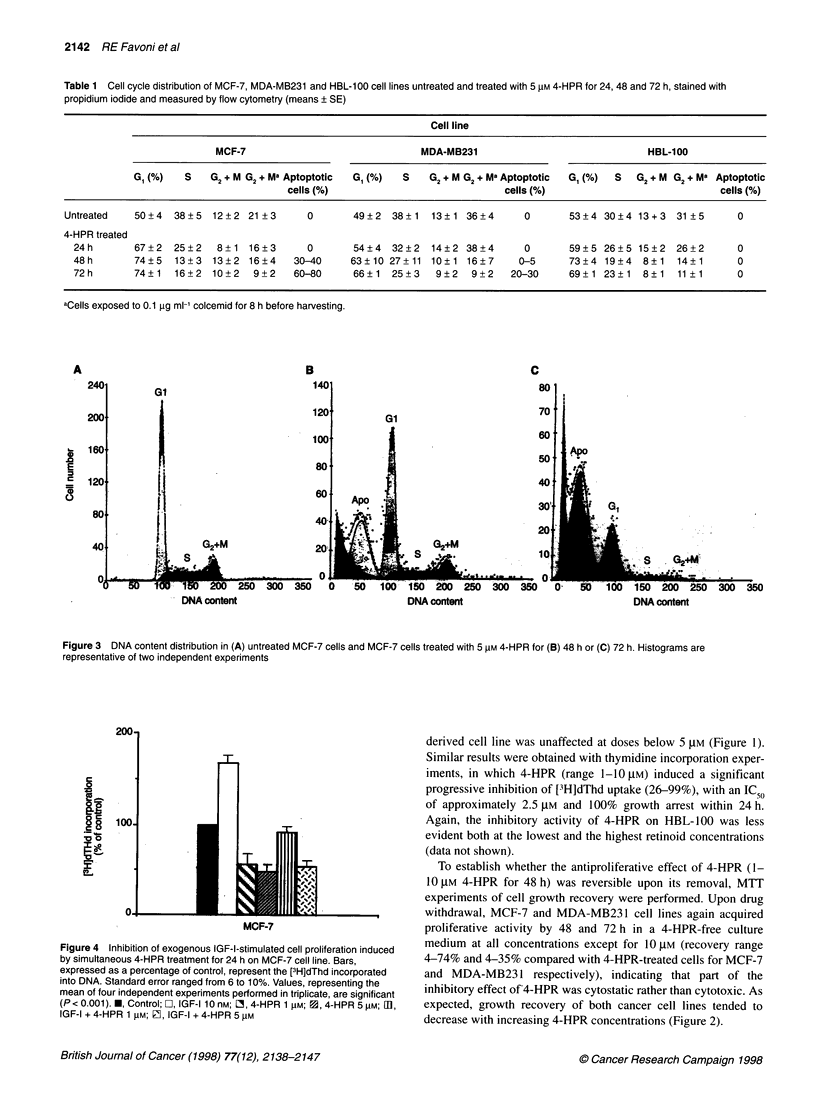
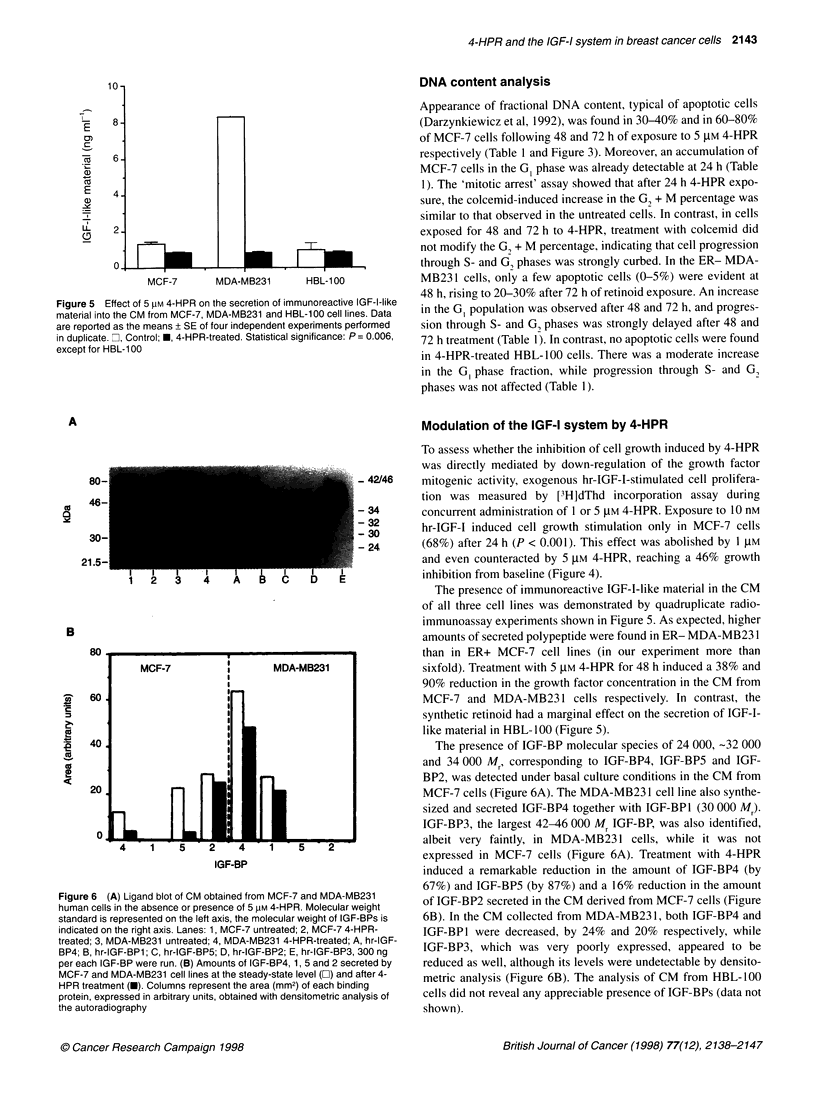
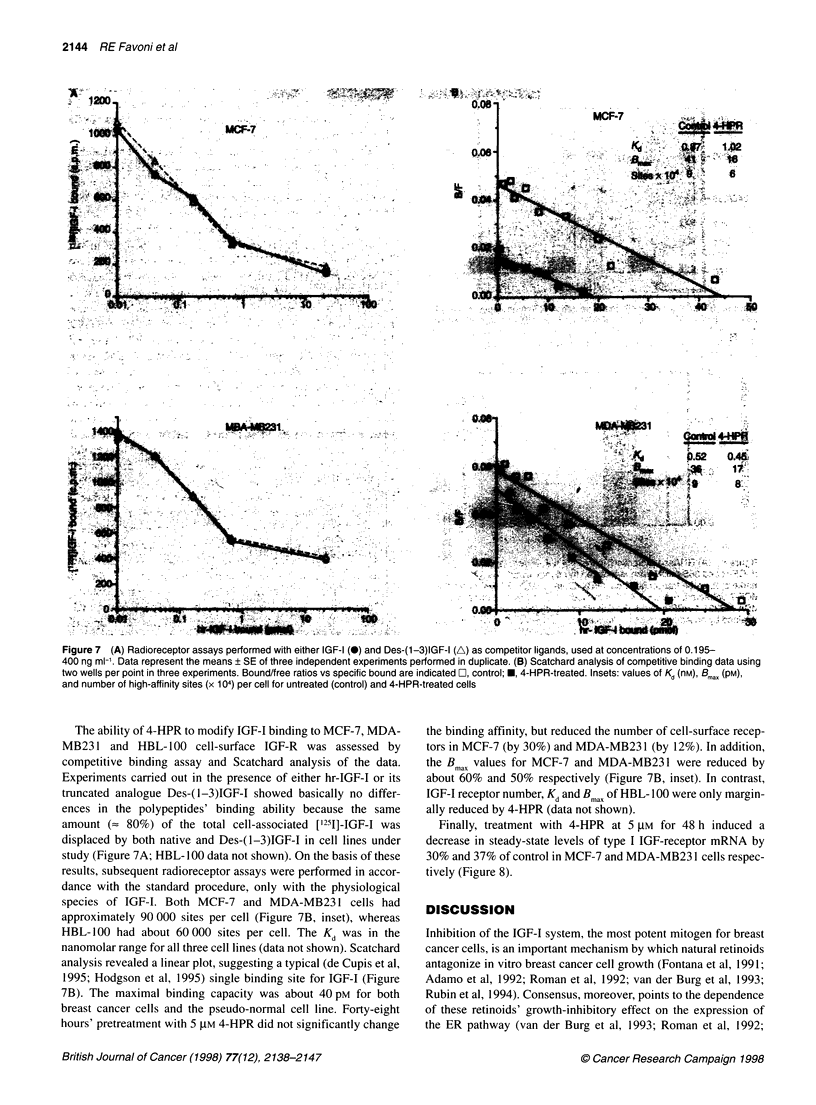
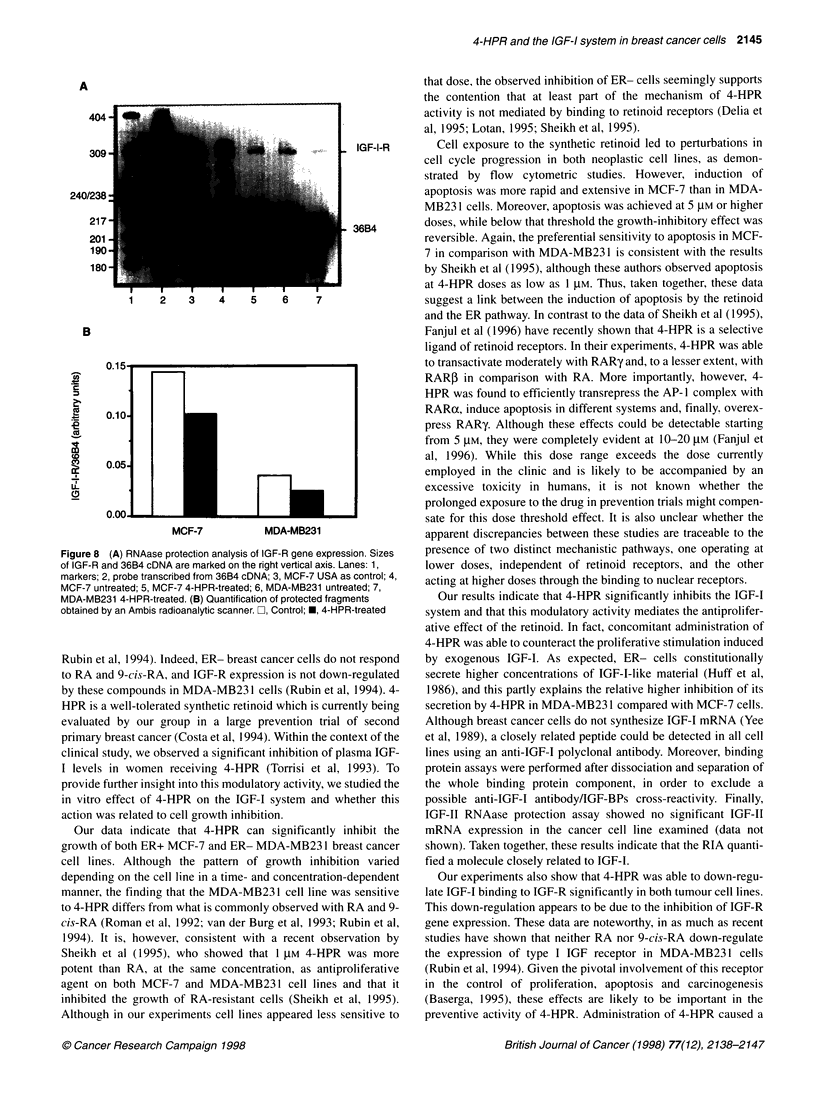
The potent mitogenic activity of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) on breast epithelium is inhibited by retinoic acid in oestrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer cell lines. We studied and compared the effects of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide (4-HPR) in terms of growth inhibition and modulation of the IGF-I system in ER+ (MCF-7) and oestrogen receptor-negative (ER-) (MDA-MB231) breast cancer cell lines. Treatment with 1-10 microM 4-HPR for up to 96 h induced a dose- and time-dependent inhibition of proliferation in both breast cancer cell lines. Induction of apoptosis was much more evident in MCF-7 than in MDA-MB231 cells (30-40% compared with 0-5% respectively at 5 microM for 48 h). Exogenous human recombinant IGF-I (hr-IGF-I)-stimulated cell proliferation was abolished by 1 microM 4-HPR in MCF-7 cells. Immunoreactive IGF-I-like protein concentration in conditioned medium was reduced by 38% in MCF-7 and by 90% in MDA-MB231 cell lines following treatment for 48 h with 5 microM 4-HPR. Western ligand blot analysis showed a reduction of IGF-binding protein 4 (BP4) and BP5 by 67% and 87%, respectively, in MCF-7, whereas IGF-BP4 and -BP1 were reduced by approximately 20% in MDA-MB231 cells. Exposure to 5 microM 4-HPR for 48 h inhibited [125I]IGF-I binding and Scatchard analysis revealed a decrease of more than 50% in maximum binding capacity (Bmax) and a reduced receptor number/cell in both cancer cell lines. Steady-state type I IGF-receptor mRNA levels were reduced by approximately 30% in both tumour cell lines. We conclude that 4-HPR induces a significant down-regulation of the IGF-I system in both ER+ (MCF-7) and ER- (MDA-MB231) breast cancer cell lines. These findings suggest that, in our model, interference with the ER signalling pathway is not the only mechanism of breast cancer growth inhibition by 4-HPR.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M. L., Shao Z. M., Lanau F., Chen J. C., Clemmons D. R., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Fontana J. A. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and retinoic acid modulation of IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs): IGFBP-2, -3, and -4 gene expression and protein secretion in a breast cancer cell line. Endocrinology. 1992 Oct;131(4):1858–1866. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.4.1382963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R. The insulin-like growth factor I receptor: a key to tumor growth? Cancer Res. 1995 Jan 15;55(2):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruning P. F., Bonfrèr J. M., van Noord P. A., Hart A. A., de Jong-Bakker M., Nooijen W. J. Insulin resistance and breast-cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 1992 Oct 21;52(4):511–516. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Camacho-Hubner C., Coronado E., Osborne C. K. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein secretion by breast carcinoma cell lines: correlation with estrogen receptor status. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):2679–2686. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-2679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Bruno S., Del Bino G., Gorczyca W., Hotz M. A., Lassota P., Traganos F. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):795–808. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delia D., Aiello A., Formelli F., Fontanella E., Costa A., Miyashita T., Reed J. C., Pierotti M. A. Regulation of apoptosis induced by the retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and effect of deregulated bcl-2. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):359–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanjul A. N., Delia D., Pierotti M. A., Rideout D., Yu J. Q., Pfahl M., Qiu J. 4-Hydroxyphenyl retinamide is a highly selective activator of retinoid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1996 Sep 13;271(37):22441–22446. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.37.22441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favoni R. E., de Cupis A., Perrotta A., Sforzini S., Amoroso D., Pensa F., Miglietta L. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding proteins blood serum levels in women with early- and late-stage breast cancer: mutual relationship and possible correlations with patients' hormonal status. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1995;121(11):674–682. doi: 10.1007/BF01218526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favoni R. E., de Cupis A., Ravera F., Cantoni C., Pirani P., Ardizzoni A., Noonan D., Biassoni R. Expression and function of the insulin-like growth factor I system in human non-small-cell lung cancer and normal lung cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1994 Mar 15;56(6):858–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. A., Jackson J. G., McGuire W. L., Krywicki R. F., Yee D. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer correlates with estrogen receptor status. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jun;52(2):196–205. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240520211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa J. A., Yee D. The insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992;22(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01833336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gucev Z. S., Oh Y., Kelley K. M., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 mediates retinoic acid- and transforming growth factor beta2-induced growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 1;56(7):1545–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson D. R., May F. E., Westley B. R. Mutations at positions 11 and 60 of insulin-like growth factor 1 reveal differences between its interactions with the type I insulin-like-growth-factor receptor and the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Oct 1;233(1):299–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.299_1.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D., Olefsky J. M. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins and their role in modulating IGF-I action in BHK cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25576–25582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K. K., Kaufman D., Gabbay K. H., Spencer E. M., Lippman M. E., Dickson R. B. Secretion of an insulin-like growth factor-I-related protein by human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4613–4619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh H., Yang X., Pollak M. Estradiol and antiestrogens regulate a growth inhibitory insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 autocrine loop in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):1016–1021. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazer R. R. Insulin resistance, insulin-like growth factor I and breast cancer: a hypothesis. Int J Cancer. 1995 Aug 9;62(4):403–406. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laborda J. 36B4 cDNA used as an estradiol-independent mRNA control is the cDNA for human acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein PO. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3998–3998. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix A., Lippman M. E. Binding of retinoids to human breast cancer cell lines and their effects on cell growth. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):586–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI109703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Baserga R., Helman L., Roberts C. T., Jr Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Jan 1;122(1):54–59. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-1-199501010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Clemmons D., Nissley P., Rechler M. M. NIH conference. Insulin-like growth factors in health and disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 15;116(10):854–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. S., Chen J. C., Sheikh M. S., Shao Z. M., Fontana J. A. Retinoic acid inhibition of insulin-like growth factor I stimulation of c-fos mRNA levels in a breast carcinoma cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Mar;211(1):68–73. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Different susceptibilities of human melanoma and breast carcinoma cell lines to retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition. Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):1014–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Retinoids and apoptosis: implications for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Nov 15;87(22):1655–1657. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.22.1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth C., Böck G., Daxenbichler G. Effect of 4-hydroxyphenylretinamide and retinoic acid on proliferation and cell cycle of cultured human breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Nov;75(5):871–875. doi: 10.1093/jnci/75.5.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Jr, Jackson J. G., Figueroa J. A., Shimasaki S., Powell D. R., Yee D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) expression by breast cancer cells: use of IGFBP-1 as an inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor action. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Sep 2;84(17):1336–1341. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.17.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. C., Thompson H. J., Becci P. J., Grubbs C. J., Gander R. J., Newton D. L., Smith J. M., Phillips S. L., Henderson W. R., Mullen L. T. N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)retinamide, a new retinoid for prevention of breast cancer in the rat. Cancer Res. 1979 Apr;39(4):1339–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzoni M., Bocca P., Chiesa V., Decensi A., Pistoia V., Raffaghello L., Rozzo C., Montaldo P. G. Differential effects of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and retinoic acid on neuroblastoma cells: apoptosis versus differentiation. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 15;55(4):853–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rishi A. K., Shao Z. M., Baumann R. G., Li X. S., Sheikh M. S., Kimura S., Bashirelahi N., Fontana J. A. Estradiol regulation of the human retinoic acid receptor alpha gene in human breast carcinoma cells is mediated via an imperfect half-palindromic estrogen response element and Sp1 motifs. Cancer Res. 1995 Nov 1;55(21):4999–5006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman S. D., Clarke C. L., Hall R. E., Alexander I. E., Sutherland R. L. Expression and regulation of retinoic acid receptors in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2236–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M., Fenig E., Rosenauer A., Menendez-Botet C., Achkar C., Bentel J. M., Yahalom J., Mendelsohn J., Miller W. H., Jr 9-Cis retinoic acid inhibits growth of breast cancer cells and down-regulates estrogen receptor RNA and protein. Cancer Res. 1994 Dec 15;54(24):6549–6556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Shao Z. M., Hussain A., Clemmons D. R., Chen J. C., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Fontana J. A. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding-protein-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6: synthesis, secretion, and gene expression in estrogen receptor-negative human breast carcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Jun;155(3):556–567. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041550314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Shao Z. M., Li X. S., Ordonez J. V., Conley B. A., Wu S., Dawson M. I., Han Q. X., Chao W. R., Quick T. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4-HPR)-mediated biological actions involve retinoid receptor-independent pathways in human breast carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Oct;16(10):2477–2486. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.10.2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Parkinson D. R., Cheson B. D., Friedman M. A. Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1992 May;10(5):839–864. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.5.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi R., Pensa F., Orengo M. A., Catsafados E., Ponzani P., Boccardo F., Costa A., Decensi A. The synthetic retinoid fenretinide lowers plasma insulin-like growth factor I levels in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4769–4771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traganos F., Kimmel M. The stathmokinetic experiment: a single-parameter and multiparameter flow cytometric analysis. Methods Cell Biol. 1990;33:249–270. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Cullen K. J., Paik S., Perdue J. F., Hampton B., Schwartz A., Lippman M. E., Rosen N. Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6691–6696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Favoni R. E., Lippman M. E., Powell D. R. Identification of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1991 Mar;18(1):3–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01975437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Lebovic G. S., Marcus R. R., Rosen N. Identification of an alternate type I insulin-like growth factor receptor beta subunit mRNA transcript. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21439–21441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Paik S., Lebovic G. S., Marcus R. R., Favoni R. E., Cullen K. J., Lippman M. E., Rosen N. Analysis of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in malignancy: evidence for a paracrine role in human breast cancer. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):509–517. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Sharma J., Hilsenbeck S. G. Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein expression in axillary lymph node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Dec 7;86(23):1785–1789. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.23.1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Burg B., Isbrücker L., van Selm-Miltenburg A. J., de Laat S. W., van Zoelen E. J. Role of estrogen-induced insulin-like growth factors in the proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7770–7774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Burg B., van der Leede B. M., Kwakkenbos-Isbrücker L., Salverda S., de Laat S. W., van der Saag P. T. Retinoic acid resistance of estradiol-independent breast cancer cells coincides with diminished retinoic acid receptor function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Feb;91(1-2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90267-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]