Abstract
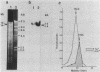
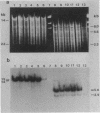
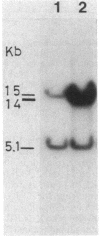
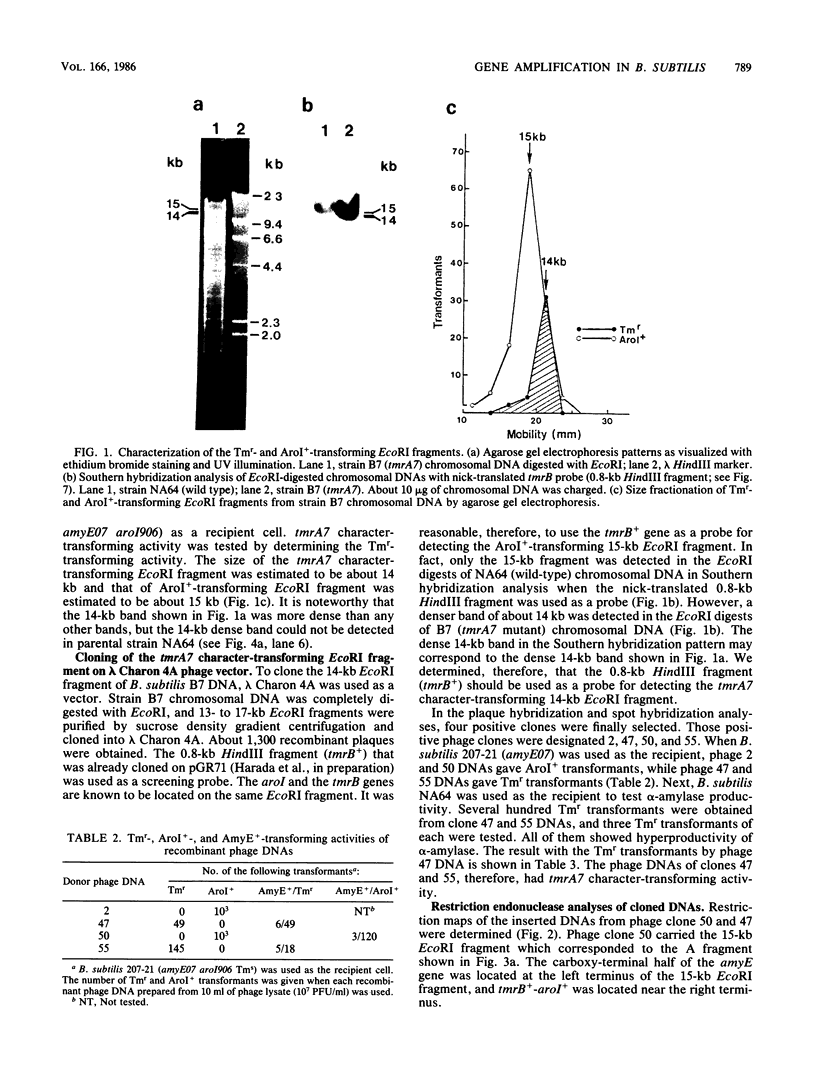
Bacillus subtilis B7, a mutant which acquired gene amplification of the amyE-tmrB region, showed, as a result, hyperproductivity (about a 5- to 10-fold increase) of alpha-amylase and tunicamycin resistance. The mutational character was transferred to recipient cells by competence transformation. A 14-kilobase (kb) EcoRI chromosomal DNA fragment of strain B7 was found to have the transforming activity. We cloned a 6.4-kb EcoRI fragment on a phage vector lambda Charon 4A through a spontaneous deletion of 7.6 kb from the 14-kb fragment and subcloned a 1.6-kb HindIII fragment on pGR71. The cloned 6.4-kb EcoRI and 1.6-kb HindIII fragments retained the transforming activity of inducing gene amplification of the amyE-tmrB region. At the junction point (J) of the repeating units (16 kb), the tmrB gene was linked to a DNA region (M) located 4 kb upstream of amyE. The essential structure of the cloned, transforming (gene amplification-inducing) DNA was deduced to be that around J. The subcloned 1.6-kb HindIII fragment that retained the transforming activity was shown to be almost solely composed of the tmrB-J-M region. In addition, the DNA sequence around J was determined.
Full text
PDF

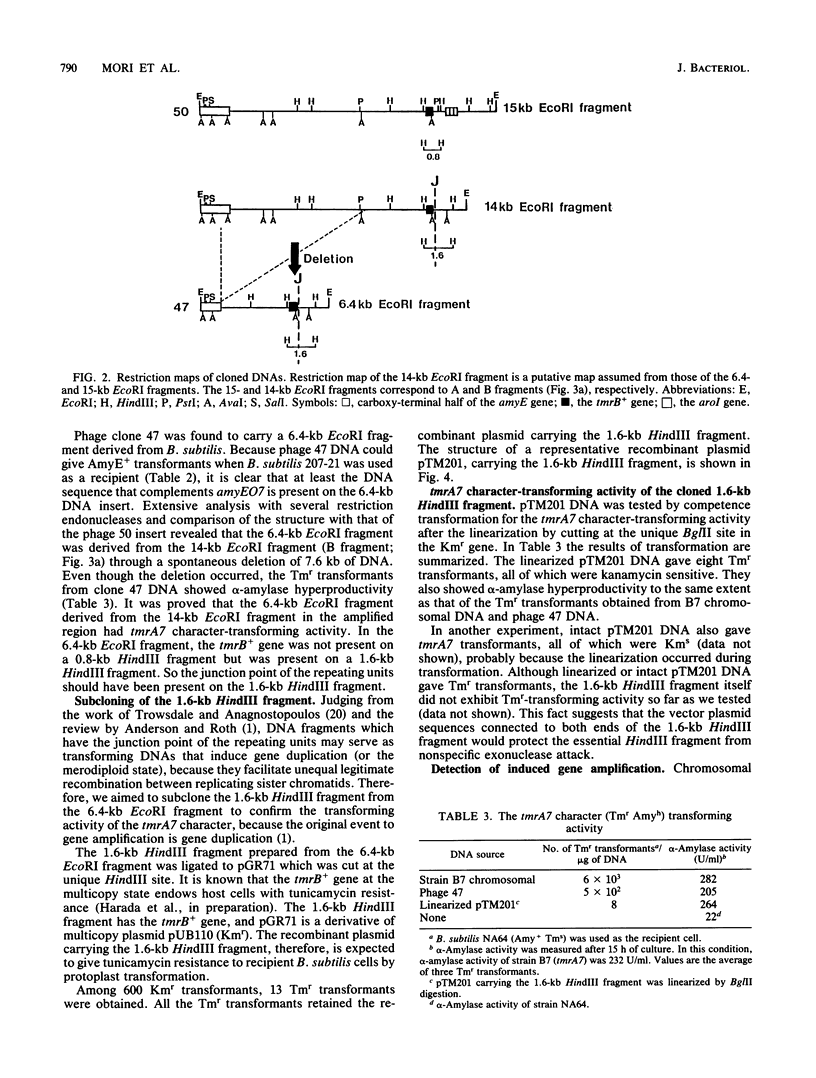
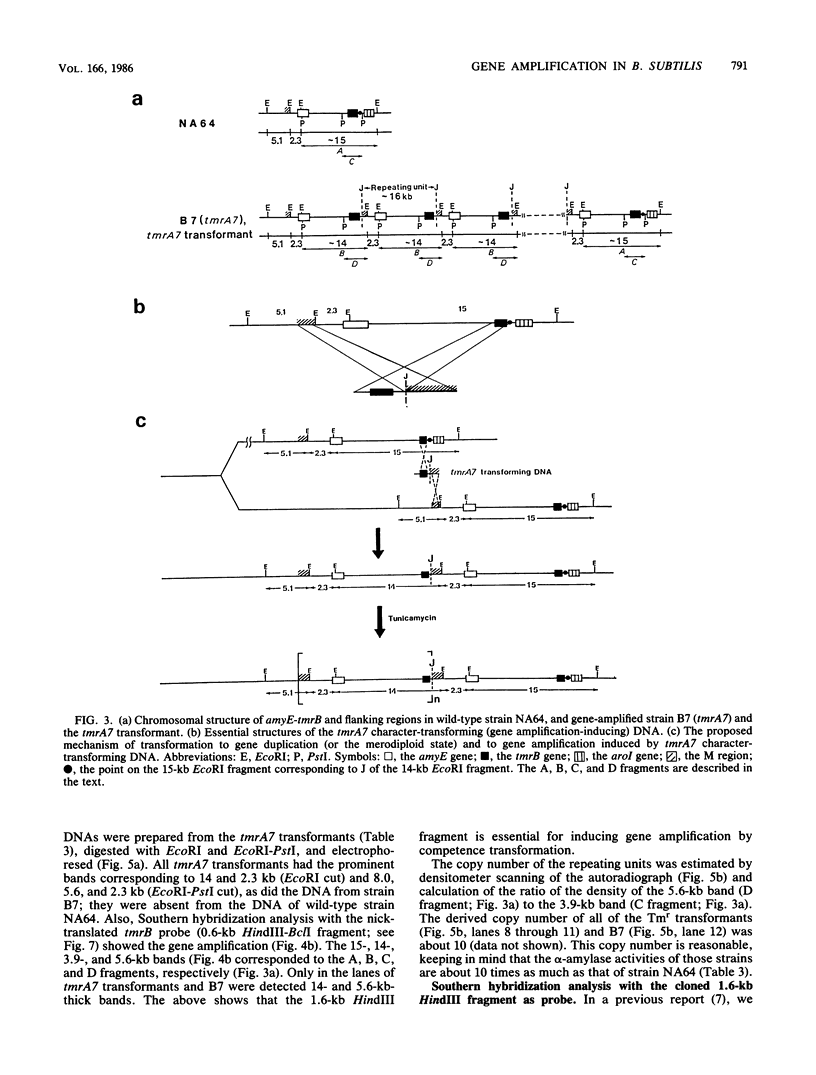
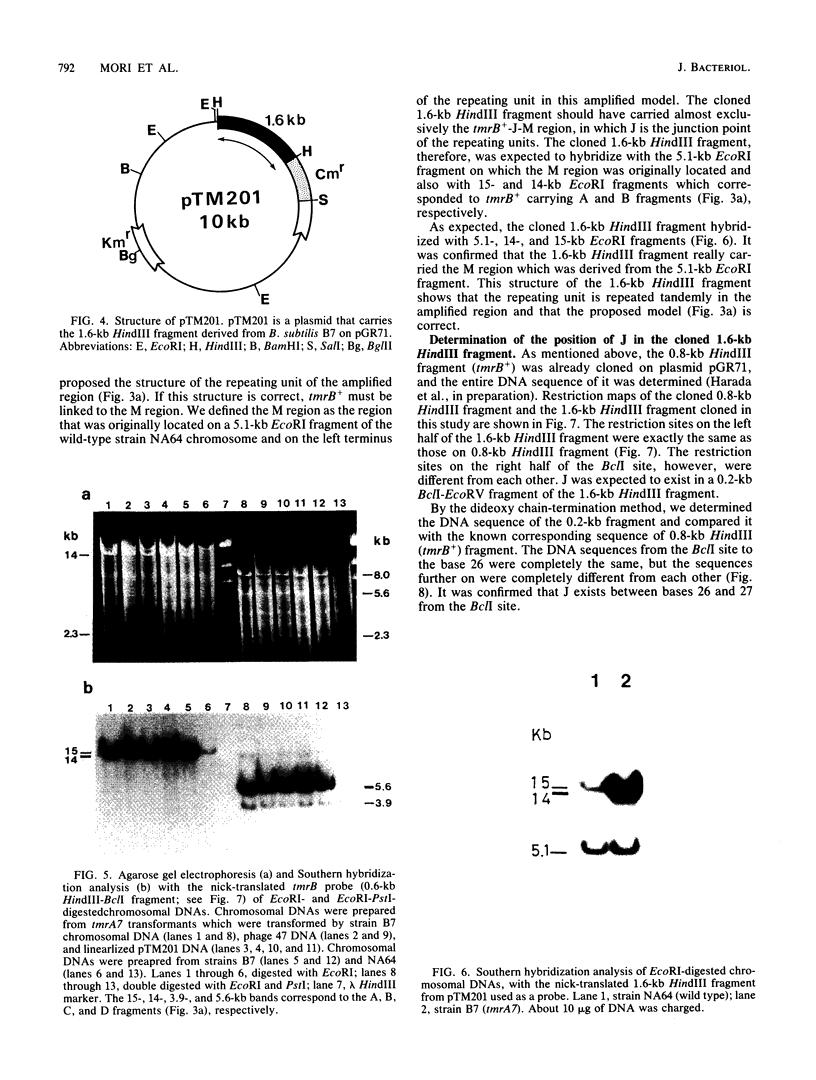
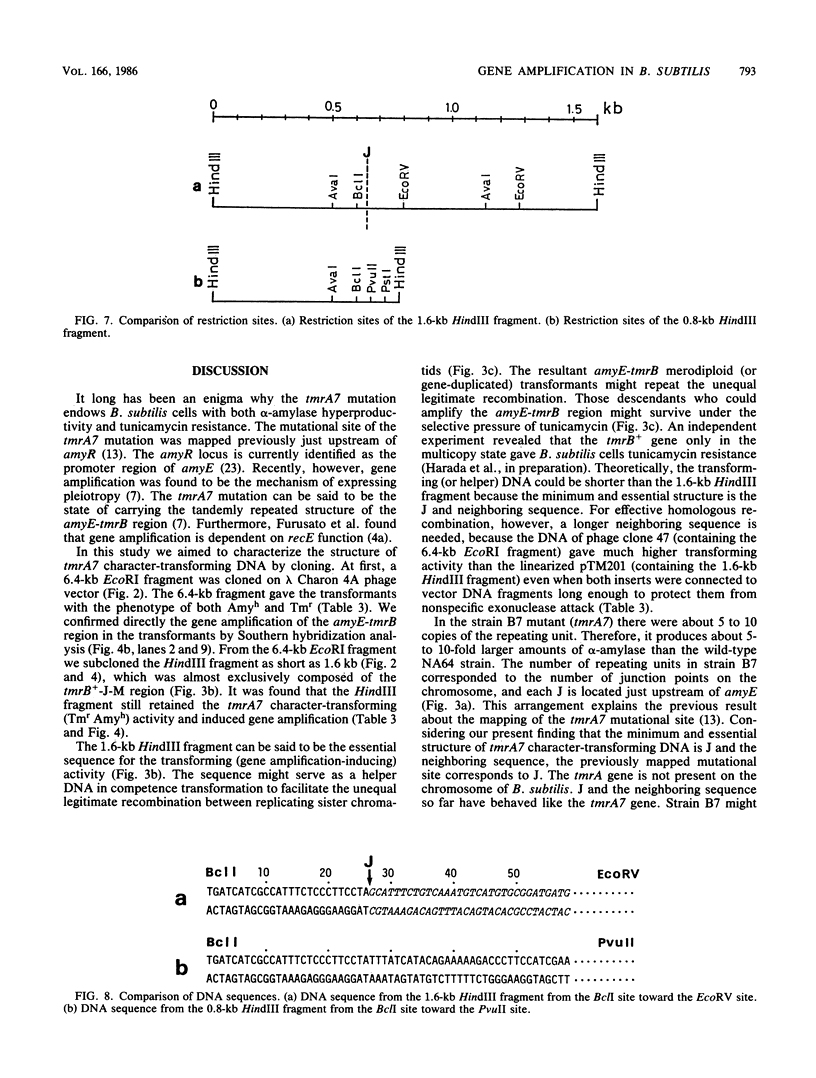

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. P., Roth J. R. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:473–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furusato T., Takano J., Yamane K., Hashiguchi K., Tanimoto A., Mori M., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Amplification and deletion of the amyE+-tmrB+ gene region in a Bacillus subtilis recombinant-phage genome by the tmrA7 mutation. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):549–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.549-556.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Doi R. H., Rodriguez R. L. Expression of Tn9-derived chloramphenicol resistance in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):309–311. doi: 10.1038/293309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis. II. Intracellular development of the induced prophage. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):248–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.248-260.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Saito H., Ikeda Y. A method for construction of specialized transducing phage rho 11 of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Integration of linear, heterologous DNA molecules into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome: mechanism and use in induction of predictable rearrangements. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.111-120.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Yamane K., Sasaki T., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Maruo B. Tunicamycin-resistant mutants and chromosomal locations of mutational sites in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):818–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.818-821.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Yamasaki M., Maruo B., Yoneda Y., Yamane K. Hyperproductivity of extracellular alpha-amylase by a tunicamycin resistant mutant of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Saito H. Repair of ultraviolet-induced DNA damage in the subcellular systems of Bacillus subtilis. Mutat Res. 1973 Nov;20(2):159–173. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Arima K., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Anagnostopoulos C. Evidence for the Translocation of a Chromosome Sement in Bacillus subtilis Strains Carrying the trpE26 Mutation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):886–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.886-898.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Oskarsson M., Enquist L. W., Nomura S., Sullivan M., Fischinger P. J. Cloning of integrated Moloney sarcoma proviral DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki H., Ohmura K., Nakayama A., Takeichi Y., Otozai K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Yamane K. Alpha-amylase genes (amyR2 and amyE+) from an alpha-amylase-hyperproducing Bacillus subtilis strain: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):327–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.327-337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]